|
162nd Meridian West
The meridian 162° west of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, North America, the Pacific Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole. The 162nd meridian west forms a great circle with the 18th meridian east. From Pole to Pole Starting at the North Pole and heading south to the South Pole The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipod ..., the 162nd meridian west passes through: : See also * 161st meridian west * 163rd meridian west {{geographical coordinates, state=collapsed w162 meridian west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Meridian
A prime meridian is an arbitrary meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°. Together, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian in a 360°-system) form a great circle. This great circle divides a spheroid, like the Earth, into two hemispheres: the Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere (for an east-west notational system). For Earth's prime meridian, various conventions have been used or advocated in different regions throughout history. The Earth's current international standard prime meridian is the IERS Reference Meridian. It is derived, but differs slightly, from the Greenwich Meridian, the previous standard. A prime meridian for a planetary body not tidally locked (or at least not in synchronous rotation) is entirely arbitrary, unlike an equator, which is determined by the axis of rotation. However, for celestial objects that are tidally locked (more specifically, synchronous), th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seward Peninsula
The Seward Peninsula is a large peninsula on the western coast of the U.S. state of Alaska whose westernmost point is Cape Prince of Wales. The peninsula projects about into the Bering Sea between Norton Sound, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi Sea, and Kotzebue Sound, just below the Arctic Circle. The entire peninsula is about long and wide. Like Seward, Alaska, it was named after William H. Seward, the United States Secretary of State who fought for the U.S. purchase of Alaska. The Seward Peninsula is a remnant of the Bering land bridge, a roughly thousand mile wide swath of land connecting Siberia with mainland Alaska during the Pleistocene Ice Age. This land bridge aided in the migration of humans, as well as plant and animal species, from Asia to North America. Excavations at sites such as the Trail Creek Caves and Cape Espenberg in the Bering Land Bridge National Preserve as well as Cape Denbigh to the south have provided insight into the timeline of prehistorical migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
161st Meridian West
The meridian 161° west of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, North America, the Pacific Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole. The 161st meridian west forms a great circle with the 19th meridian east. From Pole to Pole Starting at the North Pole and heading south to the South Pole, the 161st meridian west passes through: : See also *160th meridian west The meridian 160° west of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, North America, the Pacific Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole. The 160th meridian west forms a great ... * 162nd meridian west {{geographical coordinates, state=collapsed w161 meridian west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Antarctic Territorial Claims
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be altered without permission * Lists (jousting), the barriers used to designate the tournament area where medieval knights jousted * ''The Book of Lists'', an American series of books with unusual lists See also * The List (other) * Listing (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Dependency
The Ross Dependency is a region of Antarctica defined by a sector originating at the South Pole, passing along longitudes 160° east to 150° west, and terminating at latitude 60° south. It is claimed by New Zealand, a claim accepted only by the other six countries with territorial claims in Antarctica. Under the 1961 Antarctic Treaty, of which all territorial claimants are signatories, including New Zealand, all claims are held in abeyance. Article IV states: "No acts or activities taking place while the present Treaty is in force shall constitute a basis for asserting, supporting or denying a claim to territorial sovereignty in Antarctica or create any rights of sovereignty in Antarctica". The Dependency takes its name from Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered the Ross Sea, and includes part of Victoria Land, and most of the Ross Ice Shelf. Ross, Balleny, Scott and Roosevelt Islands also form part of the Dependency. History of claim Following his discovery of Victo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
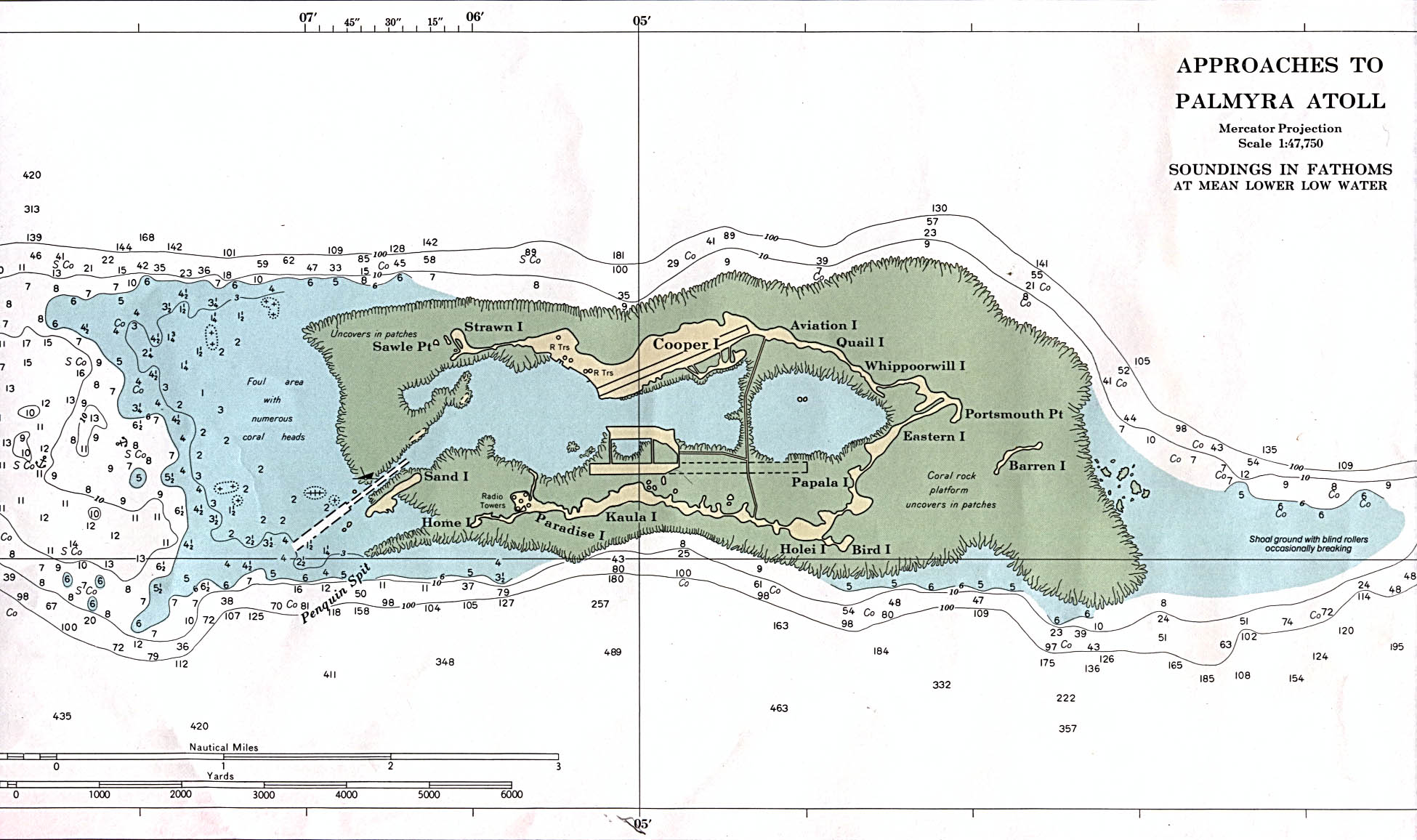
Palmyra Atoll
Palmyra Atoll (), also referred to as Palmyra Island, is one of the Line Islands, Northern Line Islands (southeast of Kingman Reef and north of Kiribati). It is located almost due south of the Hawaiian Islands, roughly one-third of the way between Hawaii and American Samoa. North America is about northeast and New Zealand the same distance southwest, placing the atoll at the approximate center of the Pacific Ocean. The land area is , with about 9 miles (14 km) of sea-facing coastline and reef. There is one boat Anchorage (maritime), anchorage known as West Lagoon, accessible from the sea by a narrow artificial channel. It is the second-to-northernmost of the Line Islands, and one of three American islands in the archipelago, along with Jarvis Island and Kingman Reef. Palmyra Atoll is part of the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument, the world's largest marine protected area. The atoll is composed of submerged sand flats along with dry land and reefs. It consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state geographically located within the tropics. Hawaii comprises nearly the entire Hawaiian archipelago, 137 volcanic islands spanning that are physiographically and ethnologically part of the Polynesian subregion of Oceania. The state's ocean coastline is consequently the fourth-longest in the U.S., at about . The eight main islands, from northwest to southeast, are Niihau, Kauai, Oahu, Molokai, Lānai, Kahoolawe, Maui, and Hawaii—the last of these, after which the state is named, is often called the "Big Island" or "Hawaii Island" to avoid confusion with the state or archipelago. The uninhabited Northwestern Hawaiian Islands make up most of the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, the United States' largest protected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nihoa
Nihoa (; haw, Nīhoa ), also known as Bird Island or Moku Manu, is the tallest of ten islands and atolls in the uninhabited Northwestern Hawaiian Islands (NWHI). The island is located at the southern end of the NWHI chain, southeast of Necker Island. Nihoa is the closest NWHI in proximity to the eight main windward Hawaiian Islands at approximately northwest of the island of Kauai. The island has two peaks, Miller's Peak in the west, and Tanager Peak in the east. Nihoa's area is about and is surrounded by a coral reef. Its jagged outline gives the island its name, , which is Hawaiian for "tooth".. Captain William Douglas, the second Western explorer to find Nihoa, describes the island as "earingthe form of a saddle, high at each end, and low in the middle. To the south, it is covered with verdure; but on the north, west, and east sides it is a barren rock, perpendicularly steep..." The island is home to 25 species of plants and several animals, making it the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavlof Islands
The Pavlof Islands (Qudugin in Aleut) are a group of seven islands that lie south of Pavlof Bay on the Alaska Peninsula. They are part of the Aleutians East Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. The islands include Dolgoi Island (Anganax̂six̂), Goloi (Atx̂uunux̂), Inner Iliasik (Iluuĝix̂ Ixsaĝdaaĝux̂), Outer Iliasik (Qagaaĝix̂ Ixsaĝdaaĝux̂), Poperechnoi (Kuyagdax̂), Ukolnoi (Kitaĝutax̂̂), and Wosnesenski (Unatxux̂). Dolgoi Island is the largest of these in area. They have a total land area of and are uninhabited. An increase in earthquake activity was noted at Pavlof on June 1, 1997. Two days later the National Weather Service in Cold Bay reported a steam plume rising above Pavlof's summit. The Alaska Volcano Observatory monitors the volcano and expects renewed activity. Pavlof last erupted from September to December 1996. This update is based on information posted by the U.S. Geological Survey's Alaska Volcano Observatory on Volcan ListServ on June 3, 1997. 183 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Peninsula
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ale, Alasxix̂; Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a peninsula extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. The peninsula separates the Pacific Ocean from Bristol Bay, an arm of the Bering Sea. In literature (especially Russian) the term "Alaska Peninsula" was used to denote the entire northwestern protrusion of the North American continent, or all of what is now the state of Alaska, exclusive of its panhandle and islands. The Lake and Peninsula borough, the Alaskan equivalent of a county, is named after the peninsula. The Alaska/Aleutian Peninsula is also grouped into Southwest Alaska. The other largest peninsulas in Alaska include the Kenai Peninsula and Seward Peninsula. Geography The base of the Alaska Peninsula extends out from the end of the Alaska Range. The Aleutian Range is a highly active volcanic mountain range which runs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Bay
Bristol Bay ( esu, Iilgayaq, russian: Залив Бристольский) is the easternmost arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km (250 mi) long and 290 km, (180 mi) wide at its mouth. A number of rivers flow into the bay, including the Cinder, Egegik, Igushik, Kvichak, Meshik, Nushagak, Naknek, Togiak, and Ugashik. Upper reaches of Bristol Bay experience some of the highest tides in the world. One such reach, the Nushagak Bay near Dillingham and another near Naknek in Kvichak Bay have tidal extremes in excess of 10 m (30 ft), ranking them — and the area — as eighth highest in the world. Coupled with the extreme number of shoals, sandbars, and shallows, it makes navigation troublesome, especially during the area's frequently strong winds. As the shallowest part of the Bering Sea, Bristol Bay is one of the most dangerous regions for large vessels. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Newenham Long Range Radar Site
Cape Newenham Air Force Station (AAC ID: F-05, LRR ID: A-09) is a closed United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station. It is located west-southwest of Togiak, Alaska. The radar surveillance station was closed on 1 November 1983, and was re-designated as a Long Range Radar (LRR) site as part of the Alaska Radar System. Today, it remains active as part of the Alaska NORAD Region under the jurisdiction of the 611th Air Support Group, Elmendorf AFB, Alaska. History Cape Newenham AFS was a continental defence radar station constructed to provide the United States Air Force early warning of an attack by the Soviet Union on Alaska. A construction contract was awarded to Haddock Engineers, Ltd., on 13 June 1950. Work was started on 12 September, and considerable construction difficulties ensued. The only means of getting construction materials and supplies to the site was by barge or Navy LSTs, however this was restricted to when the sea was not frozen and had to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_033.jpg)