|
1539 In Science
The year 1539 in science and technology included many events, some of which are listed here. Botany * Hieronymus Bock publishes the first edition of his flora of Germany, the ''Kreutterbuch'', adopting a new system of classification based on his observations. Cartography * Olaus Magnus publishes his ''Carta marina'' in Italy, the first detailed map of Scandinavia. Exploration * May 30 – Hernando de Soto lands at Tampa Bay, Florida. * August–September – Francisco de Ulloa explores the Gulf of California. Medicine * Johannes Baptista Montanus is appointed professor of medicine at the University of Padua where he introduces clinical medicine, including bedside examination, into the curriculum, integrating theory and practice. Births * September/October – José de Acosta, naturalist (died 1600) * ''exact date unknown'' – Olivier de Serres, soil scientist (died 1619 Events January–June * January 12 – James I of England's Banqueting House, Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
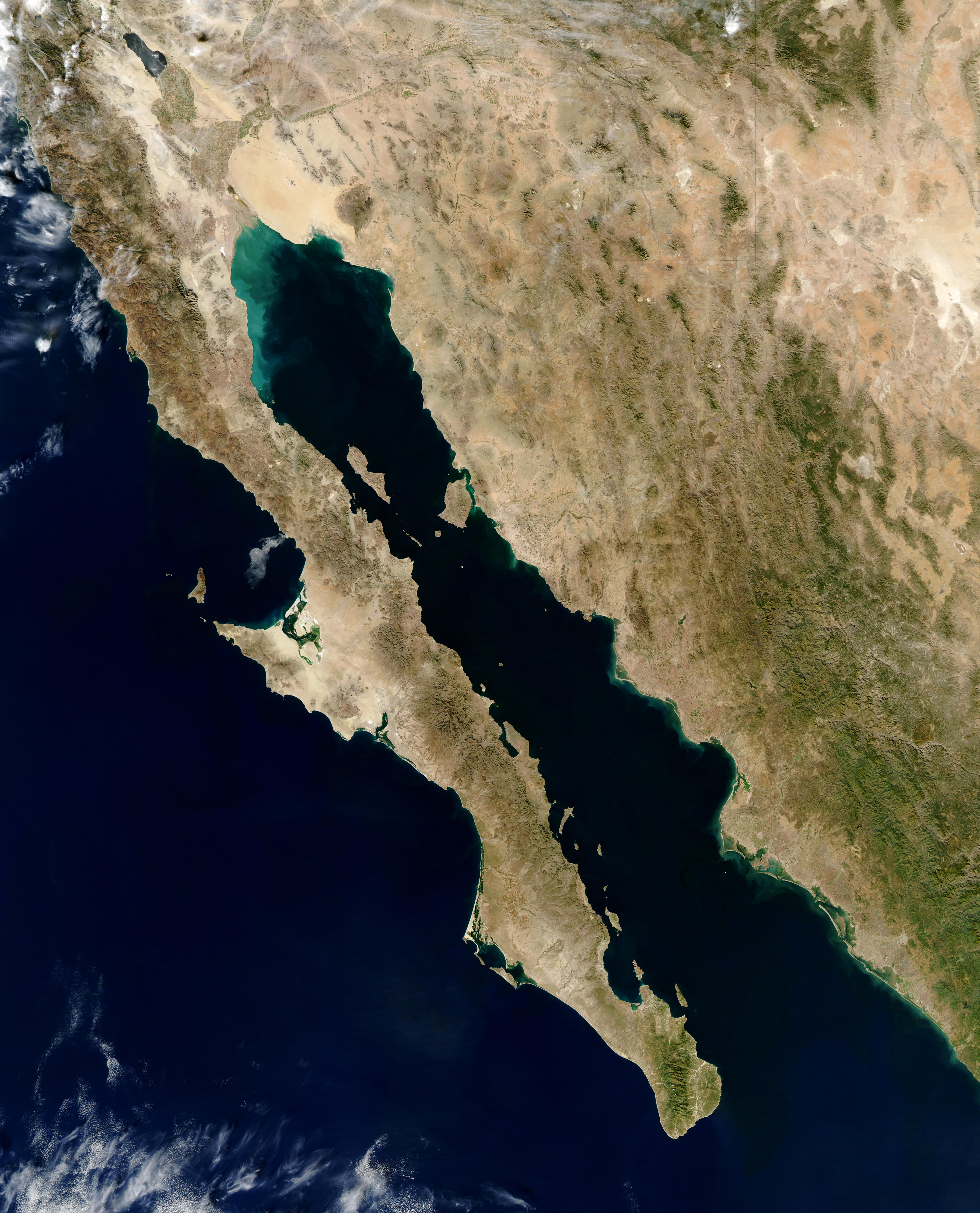
Gulf Of California
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexico, Mexican mainland. It is bordered by the states of Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, and Sinaloa with a coastline of approximately . Rivers that flow into the Gulf of California include the Colorado River, Colorado, Fuerte River, Fuerte, Mayo River (Mexico), Mayo, Sinaloa River, Sinaloa, Sonora River, Sonora, and the Yaqui River, Yaqui. The surface of the gulf is about . Maximum depths exceed because of the complex geology, linked to plate tectonics. The gulf is thought to be one of the most diverse seas on Earth and is home to more than 5,000 species of micro-invertebrates. Parts of the Gulf of California are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography History The marine expeditions of Fortún ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1539 In Science
The year 1539 in science and technology included many events, some of which are listed here. Botany * Hieronymus Bock publishes the first edition of his flora of Germany, the ''Kreutterbuch'', adopting a new system of classification based on his observations. Cartography * Olaus Magnus publishes his ''Carta marina'' in Italy, the first detailed map of Scandinavia. Exploration * May 30 – Hernando de Soto lands at Tampa Bay, Florida. * August–September – Francisco de Ulloa explores the Gulf of California. Medicine * Johannes Baptista Montanus is appointed professor of medicine at the University of Padua where he introduces clinical medicine, including bedside examination, into the curriculum, integrating theory and practice. Births * September/October – José de Acosta, naturalist (died 1600) * ''exact date unknown'' – Olivier de Serres, soil scientist (died 1619 Events January–June * January 12 – James I of England's Banqueting House, Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vannoccio Biringuccio
Vannoccio Biringuccio, sometimes spelled Vannocio Biringuccio (c. 1480 – c. 1539), was an Italian metallurgist. He is best known for his manual on metalworking, ''De la pirotechnia'', published posthumously in 1540. 20th Century translation by Cyril Stanley Smith and Martha Teach Gnudi Biography Biringuccio was born in Siena as the son of Paolo Biringuccio, presumably an architect, and Lucrezia di Bartolommeo Biringuccio. He was baptised on October 20, 1480. He was a follower of Pandolfo Petrucci, the head of the powerful Petrucci family. Pandolfo employed him as a metallurgist. When Pandolfo died, Biringuccio remained tied to the Petrucci family, being employed by Pandolfo's son Borghese Petrucci. However, the uprising of 1515 forced Borghese to flee from Siena, taking Biringuccio with him. Biringuccio traveled about Italy, and visited Sicily in 1517. In 1523 Pope Clement VII caused the reinstatement of the Petrucci family, and along with them Biringuccio was able to ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1619 In Science
The year 1619 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * Publication of Johannes Kepler's third law of planetary motion in his ''Harmonices Mundi''. He also recognises the duality of convex polyhedra. * Publication of the Jesuit Giuseppe Biancani's ''Sphaera mundi, seu cosmographia demonstrativa, ac facili methodo tradita'' in Bologna. Biochemistry * Lactose is discovered by Fabriccio Bartoletti; the word ''lactose'' comes from the Latin word ''lac'' which means "milk". Exploration * In North America, the Churchill River is discovered by Danish explorer Jens Munk, and it will be used for over 100 years as a trading route of the Hudson's Bay Company from their fort at its mouth to the interior. * Frederick de Houtman and Jans van Edel discover the Houtman Abrolhos islands. Medicine *Dermod O'Meara's text on genetic disorders, ''De Moribus: Pathologia Haereditaria Generalis'' is published in Dublin, the first medical text published in Ireland. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivier De Serres
Olivier de Serres (; 1539–1619) was a French author and soil scientist whose '' Théâtre d'Agriculture'' (1600) was the accepted textbook of French agriculture in the 17th century. Biography Serres was born in 1539 at Villeneuve-de-Berg, Ardèche. His brother, Jean de Serres, was a well-known French humanist and translated the complete works of Plato. His book was notable for recommending winegrowers to plant 5 to 6 varieties in their vineyards to balance the risk of a crop failing, an early advocacy of crop rotation. It also recommended ''métayage'' (sharecropping) so that cash tenants would take all the risks and thus demand lower rent, as hired labour is expensive to manage. Sharecroppers administer themselves and risks are divided with the landlord. According to him, only large landowners should take the risk of hiring labourers and running the estate themselves.The Economic Theory of Sharecropping in Early Modern France, Philip Hoffman, The Journal of Economic Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1600 In Science
The year 1600 CE in science and technology included some significant events. Astronomy * January 1 – Scotland adopts today as being New Year's Day. * February 4 – Johannes Kepler joins Tycho Brahe as his assistant at the castle of Benátky, near Prague. * February 17 – Giordano Bruno is burned at the stake for heresy in Rome. * July – Danish astronomer Longomontanus arrives in Prague, where he works with the Moon orbital theory; he brings the rest of Tycho's astronomical instruments with him. Biology * University of Copenhagen Botanical Garden established. * Olivier de Serres publishes ''Le Théâtre d'Agriculture'' in France. * First recorded use of the word '' Naturalist'' in its modern English sense, in Christopher Sutton's ''Disce Mori''. Earth sciences * February 19 – The Peruvian volcano Huaynaputina erupts catastrophically. This is the largest known volcanic explosion in South America and triggers severe global climatic events including the Russian famine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José De Acosta
José de Acosta (1539 or 1540 in Medina del Campo, Spain – February 15, 1600 in Salamanca, Spain) was a sixteenth-century Spanish Jesuit missionary and naturalist in Latin America. His deductions regarding the ill effects of crossing over the Andes in 1570 related to the atmosphere being too thin for human needs; a variety of altitude sickness is now referred to as ''Acosta's disease''. Life José de Acosta was born at Medina del Campo in Spain, where his parents lived in this city of the plain, about twenty-four miles from Valladolid, in Old Castile, on the left bank of the swampy river Zapardiel, and overlooked by the old castle of La Mota. He was of converso background, His parents had five sons, Gerónimo, Christóval, José, Diego, and Bernardo. The Acosta brothers were fellow townsmen of the old soldier Bernal Diaz, who told the story of the conquest of Mexico, but they were many years younger than him. In 1553, at the age of thirteen, Acosta became a novice in the Socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Padua
The University of Padua ( it, Università degli Studi di Padova, UNIPD) is an Italian university located in the city of Padua, region of Veneto, northern Italy. The University of Padua was founded in 1222 by a group of students and teachers from Bologna. Padua is the second-oldest university in Italy and the world's fifth-oldest surviving university. In 2010, the university had approximately 65,000 students. In 2021, it was ranked second "best university" among Italian institutions of higher education with more than 40,000 students according to Censis institute, and among the best 200 universities in the world according to ARWU. History The university is conventionally said to have been founded in 1222 when a large group of students and professors left the University of Bologna in search of more academic freedom ('Libertas scholastica'). The first subjects to be taught were law and theology. The curriculum expanded rapidly, and by 1399 the institution had divided in two: a ''Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Baptista Montanus
Johannes Baptista Montanus (; 1498 – May 6, 1551) is the Latinized name of Giovanni Battista Monte, or Gian Battista da Monte, one of the leading Renaissance humanist physicians of Italy. Montanus promoted the revival of Greek medical texts and practice, producing revisions of Galen as well as of Islamic medical texts by Rhazes and Avicenna. He was himself a medical writer and was regarded as a second Galen. Biography Montanus was born in Verona, and became a friend of the pioneering anatomist Andreas Vesalius. He introduced autopsies as a means of acquiring anatomical data, and established the first permanent anatomical theatre, where Vesalius, Gabriele Falloppio, Hieronymus Fabricius and others carried out studies. Montanus became a professor of practical medicine at the University of Ferrara and at the University of Padua in 1539. His greatest innovation was to introduce clinical medicine into the curriculum as a way to integrate medical theory and practice. His student ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco De Ulloa
Francisco de Ulloa () (died 1540) was a Spanish explorer who explored the west coast of present-day Mexico and the Baja California Peninsula under the commission of Hernán Cortés. Ulloa's voyage was among the first to disprove the cartographic misconception of the existence of the Island of California. Exploring career It is not known whether Ulloa accompanied Cortés on his first expedition to the New Spain. By the account of historian Bernal Díaz del Castillo, he came to Mexico later while transporting letters to Cortés from his wife. According to some early historians, Ulloa was influential in helping subdue the Aztec capital Tenochtitlan by naval power. In 1539, at the private expense of Cortés, he embarked on an expedition in three small vessels, sailing north from Acapulco to explore the Pacific Coast, and to seek a sea route through the North American continent that supposedly led to the Gulf of St. Lawrence, proving the existence of a northern passage. The exped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

