|
14th Infantry Division (Poland)
14 Greater Poland Infantry Division (Polish: ''14 Wielkopolska Dywizja Piechoty'') was a unit of the Polish Army in the interbellum period, which took part in the Polish September Campaign. It was created in January 1919 in Poznań, as part of Polish forces fighting in the Greater Poland Uprising (1918–1919). Its organizer and first commandant was General Filip Dubiski. In the following months, several regiments created in the Greater Poland towns joined the unit, and in the summer of 1919, the Division was sent to the east, to fight the Red Army south of Polotsk. On December 19, 1919, its name was changed from 1st Division of Greater Poland rifles into 14 Greater Poland Infantry Division. The unit fought in the Polish-Soviet war, and in December 1920, after the truce, it returned to its homeland, to Poznań. According to the Plan Wschod, the Division was supposed to serve as a rear unit, but as in late 1930s German threat became real, on March 23, 1939, the Division became pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Armed Forces (Second Polish Republic)
Polish Armed Forces ( pl, Wojsko Polskie) were the armed forces of the Second Polish Republic from 1919 until the demise of independent Poland at the onset of Second World War in September 1939. History The outbreak of First World War meant that a huge number of Poles from the lands of the Polish partitions were forced to stand as soldiers in the ranks of German, Russian and Austro-Hungarian armies. In addition to these troops, Polish volunteer units were formed, fighting either on the side of the coalition or central states. A branch of 'Bajonians' was established in France, and in Gorczynski's Legion of Puławy. However, these were small units. The first ceased to exist due to losses, and the second could not grow due to political considerations. The Polish Legions were the greater union of the Polish Army of the independent Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. They were created in 1914 by brigadier Józef Piłsudski. The members of these formations were members of underground ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plan Zachod
Plan West ( pl, Plan Zachód) was a military plan of the Polish Army of the Second Polish Republic, for defence against invasion from Nazi Germany. It was designed in the late 1930s. Background While Józef Piłsudski was the dictator of Poland, planning concentrated on a possible attack on Poland from the east. It was only after Piłsudski's death in 1935 that the new Polish government and military re-evaluated the situation and decided that the current Polish plan for a Polish–German war, dating from the mid-1920s (Plan "S"), was inadequate and needed to be revised. However up to 1938, the priority remained in the east, not the west, and most Polish fortifications were being erected on the Polish–Soviet border.POLSKI PLAN OBRONNY ZACHÓD Details The first version predicted t ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Polish Divisions In World War II
This is a list of Polish divisions in World War II. Polish divisions in September 1939 Campaign * 1st Legions Infantry Division of Józef Piłsudski (stationed in Wilno) - Brig. Gen. Wincenty Kowalski * 2nd Legions Infantry Division (stationed in Kielce) - Col. Edward Dojan-Surówka, after September 8, 1939 col. Antoni Staich * 3rd Legions Infantry Division (stationed in Zamość) - Col. Marian Turowski * 4th Toruń Infantry Division (stationed in Toruń) - Col. Tadeusz Lubicz-Niezabitowski, after September 4, 1939 Col. Mieczysław Rawicz-Mysłowski, after September 12 Col. Józef Werobej * 5th Lwów Infantry Division (stationed in Lwów) - Gen. Juliusz Zulauf * 6th Kraków Infantry Division (stationed in Kraków) - Gen. Bernard Mond * 7th Częstochowa Infantry Division (stationed in Częstochowa) - Brig. Gen. Janusz Gąsiorowski * 8th Infantry Division (stationed in Modlin) - Col. Tadeusz Wyrwa-Furgalski * 9th Siedlce Infantry Division (stationed in Siedlce) - Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1939 Infantry Regiment (Poland)
The Polish Infantry Regiment; (Polish: Pulk Piechoty) during World War 2 comprised on average some 2,900 men and 60 officers organised around 3 rifle battalions armed with either the Karabinek wz.29 or the Wz. 98, 7.92mm bolt-action rifles. Each 19-man squad was also issued the RKM wz.28 light machine gun. Other regimental weapons included the Polish version of the French Model 1897 75-mm field gun, the Wz. 35 anti-tank rifle, the Ckm wz.30 heavy machine gun A heavy machine gun (HMG) is significantly larger than light, medium or general-purpose machine guns. HMGs are typically too heavy to be man-portable (carried by one person) and require mounting onto a weapons platform to be operably stable or ..., the wz.31 81 mm mortar, and the wz.36 46mm light mortar/grenade launcher. Table of Organization and Equipment * 1 Recon Company **4 light machine guns **2 antitank rifles * 1 Antitank Company **9 37 mm antitank guns * 1 Pioneer Platoon * 1 Artillery Platoon **2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Contribution To World War II
In World War Two, the Polish armed forces were the fourth largest Allied forces in Europe, after those of the Soviet Union, United States, and Britain. Poles made substantial contributions to the Allied effort throughout the war, fighting on land, sea, and in the air. Polish forces in the east, fighting alongside the Red army and under Soviet high command, took part in the Soviet offensives across Belarus and Ukraine into Poland and across the Vistula and Oder Rivers to the Battle of Berlin. In the west, Polish ground troops were present in the North Africa Campaign ( siege of Tobruk); the Italian campaign (including the capture of the monastery hill at the Battle of Monte Cassino); and in battles following the invasion of France (the battle of the Falaise pocket; an airborne-brigade parachute drop during Operation Market Garden; and an armored division in the Western Allied invasion of Germany). Particularly well-documented was the service of 145 Polish pilots flying Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
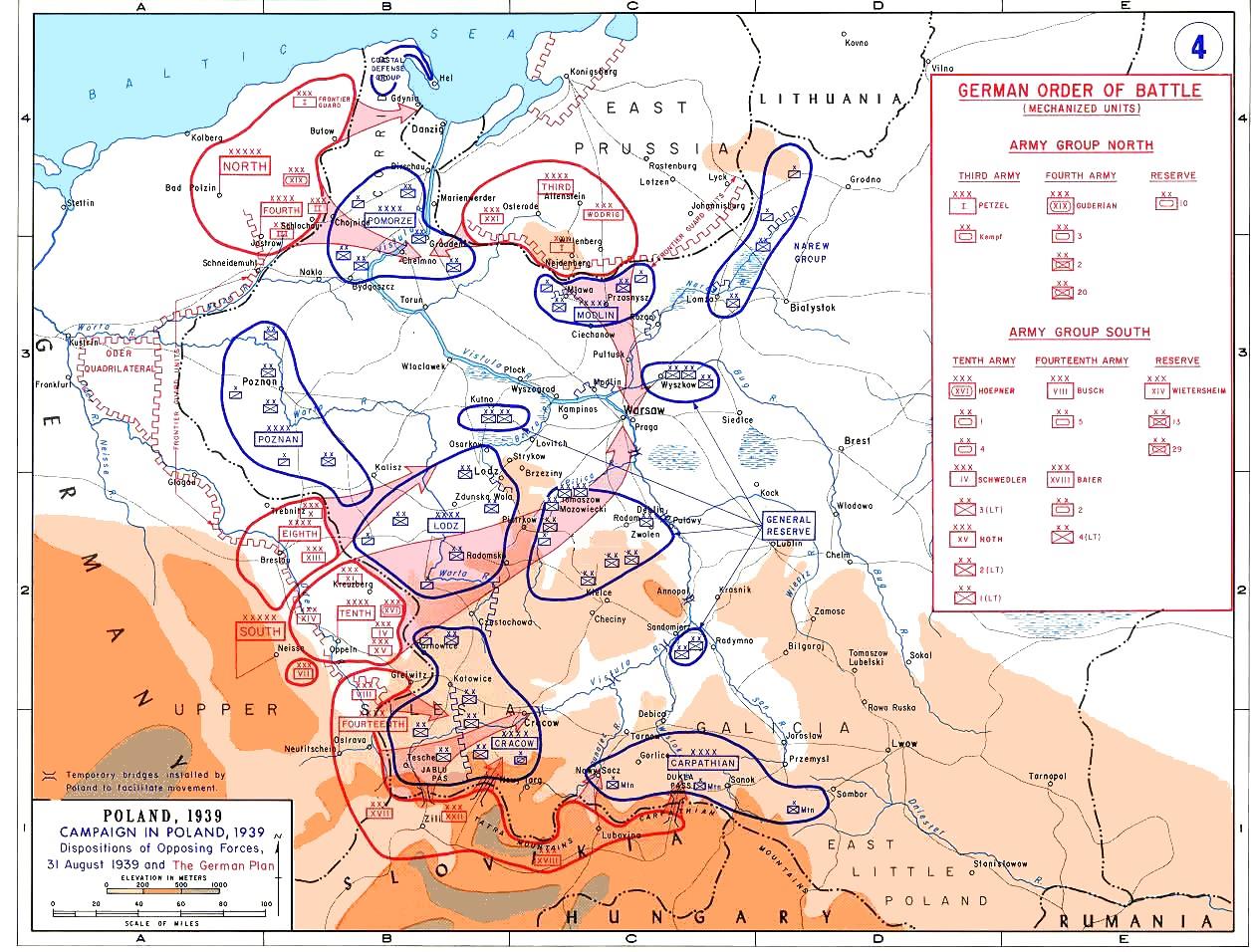
Polish Army Order Of Battle In 1939
This article discusses the Polish order of battle during the invasion of Poland. In the late 1930s Polish headquarters prepared "Plan Zachód" (''Plan "West''), a plan of mobilization of Polish Land Forces, Polish Army in case of war with Germany. Earlier, the Poles did not regard the Germans as their main threat, priority was given to threat from the Soviet Union, Soviets (see: Plan Wschod, Plan East). The overall operational plan assumed the creation of thirty infantry division (military), divisions, nine reserve divisions, eleven cavalry brigade, brigades, two motorized brigades, three mountain brigades and a number of smaller units. Most Polish forces were grouped into six armies and a number of corps-sized "Operational Groups". Later in the course of the war other operational units were created. Armies Karpaty Army Created on July 11, 1939, under Major General Kazimierz Fabrycy. ''Armia Karpaty'' was created after Germany annexed Second Czechoslovak Republic, Czechosl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kampinos Forest
Kampinos Forest () is a large forest complex located in Masovian Voivodeship, west of Warsaw in Poland. It covers a part of the ancient valley of the Vistula basin, between the Vistula and the Bzura rivers. Once a forest covering 670 km2 of central Poland, it currently covers roughly 240 km2. Kampinos National Park Most of the Kampinos forest is currently protected within Kampinos National Park (''Kampinoski Park Narodowy''). Among the distinctive features of the area is a combination of sandy dunes and marshes, with dense pine and spruce forest. The forest is a Natura 2000 EU Special Protection Area. See also * *Special Protection Areas in Poland Special Protection Areas for birds in Poland are called OSOPs ( pl, Obszar Specjalnej Ochrony Ptaków). As of 2005, 72 OSOPs were designated. See also * * Protected areas of Poland References {{Polish protected areas * Protected areas ... * External links Forests of Poland Geography of Masovian Voivo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bzura
The Bzura is a river in central Poland, a tributary of the Vistula river (in Wyszogród), with a length of 173 kilometres and a basin area of 7,764 km2. , p. 85-86 It was noteworthy during the as Polish forces made a major stand against the |
Kurt Von Briesen
__NOTOC__ Kurt von Briesen (3 May 1886 – 20 November 1941) was a general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany. He was a recipient of the Knight’s Cross of the Iron Cross. Briesen led the 30th Infantry Division in the invasion of Poland in 1939. On 1 August 1940, Briesen was promoted to the rank of general. On 25 November 1940 he was appointed commanding general of the LII Army Corps. Briesen was killed by Soviet aircraft near Isjum on the Seversky Donets River, southeast of Kharkov, on 20 November 1941. Awards and decorations * Iron Cross (1914) 2nd Class (September 1914) & 1st Class (December 1914)Thomas & Wegmann 1993, p. 114. * Knight's Cross of the House Order of Hohenzollern with Swords (April 1918) * Clasp to the Iron Cross (1939) 2nd Class (20 September 1939) & 1st Class (4 October 1939) * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 27 October 1939 as Generalleutnant is the Germanic variant of lieutenant general, used in some German speaking countries. Austria Generalleut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bzura
The Battle of the Bzura (or the Battle of Kutno) was the largest Polish counter-attack of the German invasion of Poland and was fought from 9 to 19 September.''The Second World War: An Illustrated History '', Putnam, 1975, Google Print snippet (p.38)/ref>Sources vary regarding the end date, with some giving 18 September and others 19 September. Brockhaus Multimedial Lexikon gives 19 September 1939 as to the battle's end date. The battle took place west of Warsaw, near the Bzura River. It began as a Polish counter-offensive, which gained initial success, but the Germans outflanked the Polish forces with a concentrated counter-attack. That weakened Polish forces and the Poznań and Pomorze Armies were destroyed. Western Poland was now under German occupation.Zaloga, S.J., ''Poland 1939'', Oxford, Osprey Publishing Ltd., 2002, The battle has been described as "the bloodiest and most bitter battle of the entire Polish campaign". Winston Churchill called the battle an "ever-gloriou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and audacious moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi régime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and defense spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military power. In the early part of the Second World War, the ''Wehrmacht'' employed combined arms tactics (close-cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |