|
13th Army (Soviet Union)
The 13th Army (, ) was a name given to several field armies of the Soviet Union's Red Army. Later armies existed until the 1990s, and the army survived as part of the Ukrainian Ground Forces for some years. Russo-Finnish War The 13th Army was created again at the end of December 1939 as a ''separate 13th Army'' in the course of the Soviet advance into the Karelian Isthmus when the 7th Army was split into two, and also renamed separate, after being substantially reinforced. As part of the 1940 February Vyborg offensive they were coordinated by the North Western Front in Leningrad, both armies were able to breach either first or second defensive positions in the Mannerheim Line, but were unable to breach the main position. The separate 13th Army was allocated three of the eight rifle corps assigned to the operation. Commanders * Vladimir Grendal (25 December 1939 – March 1940) * Filipp Parusinov (March 1940 – April 1940). World War II The 13th Army (1st formation) headquar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sovnarkom
The Councils of People's Commissars (SNK; russian: Совет народных комиссаров (СНК), ''Sovet narodnykh kommissarov''), commonly known as the ''Sovnarkom'' (Совнарком), were the highest executive authorities of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR), the Soviet Union (USSR), and the Soviet republics from 1917 to 1946. The Sovnarkom of the RSFSR was founded in the Russian Republic soon after the October Revolution in 1917 and its role was formalized in the 1918 Constitution of the RSFSR to be responsible to the Congress of Soviets of the RSFSR for the "general administration of the affairs of the state". Unlike its predecessor the Russian Provisional Government which had representatives of various political parties, the Sovnarkom was a government of a single party, the Bolsheviks. The Sovnarkom of the USSR and Congress of Soviets of the USSR founded in 1922 were modelled on the RSFSR system, and identical Sovnarkom bodies we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
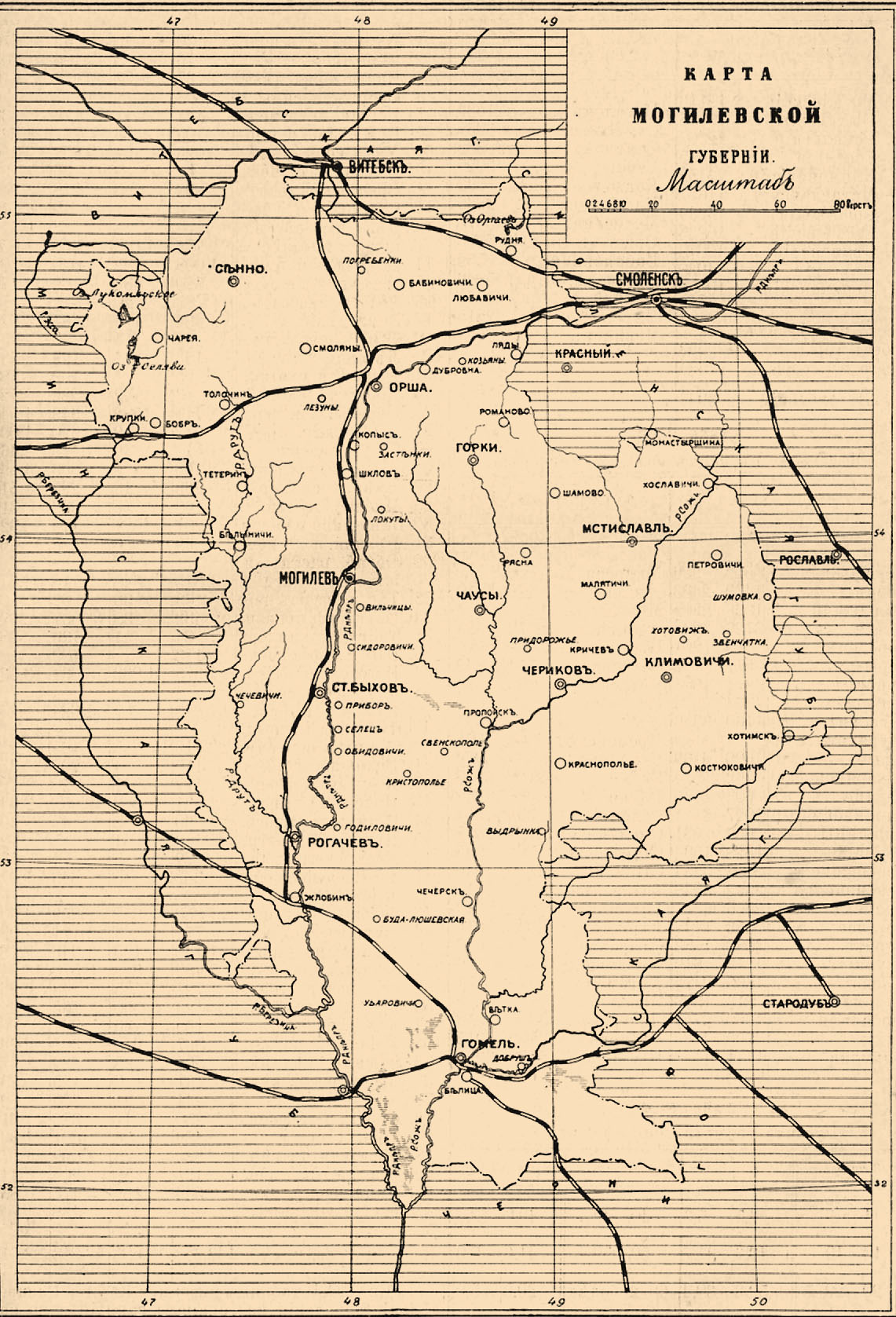
Mogilyev
Mogilev (russian: Могилёв, Mogilyov, ; yi, מאָלעוו, Molev, ) or Mahilyow ( be, Магілёў, Mahilioŭ, ) is a city in eastern Belarus, on the Dnieper River, about from the border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from the border with Russia's Bryansk Oblast. , its population was 360,918, up from an estimated 106,000 in 1956. It is the administrative centre of Mogilev Region and the third-largest city in Belarus. History The city was first mentioned in historical records in 1267. From the 14th century, it was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and since the Union of Lublin (1569), part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, where it became known as ''Mohylew''. In the 16th-17th centuries, the city flourished as one of the main nodes of the east–west and north–south trading routes. In 1577, Polish King Stefan Batory granted it city rights under Magdeburg law. In 1654, the townsmen negotiated a treaty of surrender to the Russians peacefully, if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and audacious moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi régime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and defense spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military power. In the early part of the Second World War, the ''Wehrmacht'' employed combined arms tactics (close-cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Central Front
The Central Front was a major formation of the Red Army during the Second World War formed on July 24, 1941. The Central Front describes either of two distinct organizations during the war. The first entity existed for just a month during the German invasion of 1941, before it was annihilated. A year and a half later, the name was revived for the second creation, which existed for about eight months in 1943, until it was incorporated into the Belorussian group of Fronts and renamed accordingly. First formation The first version was created on July 24, 1941 from the right wing of the forces in the Western Front, including a new designation of the 3rd Army and the headquarters of the (disbanded) 4th Army, whose former HQ formed the Front headquarters. Colonel General Fyodor I. Kuznetsov took command. The Front was a combination of the 13th and 21st Armies. * The 13th Army (Konstantin Golubev) had under command ** in the area of Mogilev, the *** 61st Rifle Corps, ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Western Front
The Western Front was a front of the Red Army, one of the Red Army Fronts during World War II. The Western Front was created on 22 June 1941 from the Western Special Military District (which before July 1940 was known as Belorussian Special Military District). The first Front Commander was Dmitry Pavlov (continuing from his position as District Commander since June 1940). The western boundary of the Front in June 1941 was long, from the southern border of Lithuania to the Pripyat River and the town of Włodawa. It connected with the adjacent North-Western Front, which extended from the Lithuanian border to the Baltic Sea, and the Southwestern Front in Ukraine. Operational history Front dispositions 22 June 1941 The 1939 partition of Poland according to the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact established a new western border with no permanent defense installations, and the army deployment within the Front created weak flanks. At the outbreak of war with Germany, the Western Special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnieper River
} The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth-longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers. It is approximately long, with a drainage basin of . In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road trade routes. During the Ruin in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia, dividing Ukraine into areas described by its right and left banks. During the Soviet period, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat, immediately above that tributary's confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine and is connected by the Dnieper–Bug Canal to other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minsk Fortified Region
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administrative centre of Minsk Region (oblast, voblast) and Minsk District (Raion, raion). As of January 2021, its population was 2 million, making Minsk the Largest cities in Europe, 11th most populous city in Europe. Minsk is one of the administrative capitals of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU). First documented in 1067, Minsk became the capital of the Principality of Minsk before being annexed by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1242. It received town privileges in 1499. From 1569, it was the capital of the Minsk Voivodeship, an administrative division of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was part of a region annexed by the Russian Empire in 1793, as a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th Anti-Tank Artillery Brigade
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. In mathematics 8 is: * a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2. * a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of the form , being an integer greater than 1. * the first number which is neither prime nor semiprime. * the base of the octal number system, which is mostly used with computers. In octal, one digit represents three bits. In modern computers, a byte is a grouping of eight bits, also called an octet. * a Fibonacci number, being plus . The next Fibonacci number is . 8 is the only positive Fibonacci number, aside from 1, that is a perfect cube. * the only nonzero perfect power that is one less than another perfect power, by Mihăilescu's Theorem. * the order of the smallest non-abelian group all of whose subgroups are normal. * the dimension of the octonions and is the highest possible dimension of a normed division algebra. * the first number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
50th Rifle Division (Soviet Union)
The 50th Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Red Army from 1936 to 1946. The division took part in the Soviet invasion of Poland and the Winter War. After Germany launched Operation Barbarossa, the 50th fought in the Battle of Moscow, the Battles of Rzhev, the Donbass Strategic Offensive, the Dnieper–Carpathian Offensive, the First and Second Jassy–Kishinev Offensive, the Vistula–Oder Offensive and the Berlin Offensive. History In May 1936, the division was formed from Construction Headquarters No. 27 as the Urovskaya Division of the Polotsk Fortified Region. It took part in the Soviet invasion of Poland in September 1939. On 17 September, it was part of the 3rd Army's 4th Rifle Corps. On 2 October, it was transferred to the 10th Rifle Corps of the same army. The 50th Rifle Division then fought in the Winter War. On 28 December, it was stationed in the region near Lake Sukhodolskoye. On 18 January 1940, it was subordinated to the 13th Army. The division ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st Rifle Corps (Soviet Union)
The 21st Rifle Corps was a corps of the Soviet Red Army. It was part of the Western Front. It took part in the Great Patriotic War. The headquarters formed in the Moscow Military District in September 1939. Assigned to the WSMD with the 17th, 24th, and 37th Rifle Divisions. The commander was Major General Vladimir Borisovich Borisov Vladimir Borisovich Borisov (; 15 July 1902 – 30 June 1941) was a Red Army major general. A veteran of the Russian Civil War, Borisov served in command positions at military schools during the 1920s and in the late 1930s rose to division comman .... The corps was disbanded in summer 1945. References Citations Bibliography * * * Rifle corps of the Soviet Union {{Russia-mil-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after Frederick Barbarossa ("red beard"), a 12th-century Holy Roman emperor and German king, put into action Nazi Germany's ideological goal of conquering the western Soviet Union to repopulate it with Germans. The German aimed to use some of the conquered people as forced labour for the Axis war effort while acquiring the oil reserves of the Caucasus as well as the agricultural resources of various Soviet territories. Their ultimate goal was to create more (living space) for Germany, and the eventual extermination of the indigenous Slavic peoples by mass deportation to Siberia, Germanisation, enslavement, and genocide. In the two years leading up to the invasion, Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union signed political and economic pacts for st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)