|
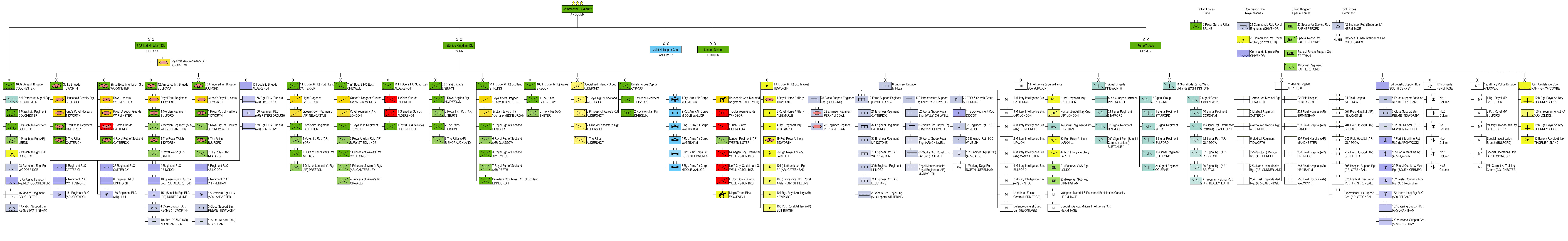
13 Signal Regiment (United Kingdom)
The 13th Signal Regiment is a specialist signals unit of the Royal Corps of Signals of the British Army. Originally formed in 1934, the regiment had a long history of service before being disbanded in 1994 following the initial Options for Change reforms. The regiment was be reformed in June 2020 as part of 1st Signal Brigade. History Formation During the World War I, the Wireless Observation Groups of the Corps of Royal Engineers proven to be successful. As a result, a Royal Corps of Signals was planned to be formed in 1917 however, its formation was delayed until 1920.Lord and Watson, Page 49 The 4th Wireless Signal Company (War Office Signals) was formed in 1934 at Aldershot Garrison to provide signal intelligence activities under the command of the War Office. In 1938, the company was re-titled as No. 2 Company, General Headquarters Signals. The company later expanded its responsibility to provide secure communications for the army. In September 1939, the unit was deplo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap Badge
A cap badge, also known as head badge or hat badge, is a badge worn on uniform headgear and distinguishes the wearer's nationality and/or organisation. The wearing of cap badges is a convention commonly found among military and police forces, as well as uniformed civilian groups such as the Boy Scouts, civil defence organisations, ambulance services (e.g. the St. John Ambulance Brigade), customs services, fire services etc. Cap badges are a modern form of heraldry and their design generally incorporates highly symbolic devices. Some badges that contain images of Lions or other cats are sometimes informally referred to as Cat Badges. Instances in military forces British armed forces The British Armed Forces utilise a variety of metal and cloth cap badges on their headdress, generally on caps and berets. They are also worn on Sikh turbans. British Army In the British Army (as well as other Commonwealth armies) each regiment and corps has its own cap badge. The cap badge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (European part of Turkey), Egypt, Iran, the Levant (including Syria (region), Ash-Shām and Cyprus), Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), and the Socotra Governorate, Socotra Archipelago (a part of Yemen). The term came into widespread usage as a replacement of the term Near East (as opposed to the Far East) beginning in the early 20th century. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions, and has been viewed by some to be discriminatory or too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of Western Asia (including Iran), but without the South Caucasus, and additionally includes all of Egypt (not just the Sina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regiments Of The British Army In World War II
A regiment is a military unit. Its role and size varies markedly, depending on the country, service and/or a specialisation. In Medieval Europe, the term "regiment" denoted any large body of front-line soldiers, recruited or conscripted in one geographical area, by a leader who was often also the feudal lord ''in capite'' of the soldiers. Lesser barons of knightly rank could be expected to muster or hire a company or battalion from their manorial estate. By the end of the 17th century, infantry regiments in most European armies were permanent units, with approximately 800 men and commanded by a colonel. Definitions During the modern era, the word "regiment" – much like "corps" – may have two somewhat divergent meanings, which refer to two distinct roles: # a front-line military formation; or # an administrative or ceremonial unit. In many armies, the first role has been assumed by independent battalions, battlegroups, task forces, brigades and other, similarly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Units Of The Royal Corps Of Signals
This is a list of units of the British Army's Royal Corps of Signals. Brigades * 1st Signal Brigade (1982—1987) ** 1st Signal Group (1968—1982) *1st (United Kingdom) Signal Brigade (1995—Present) * 2nd (National Communications) Signal Brigade (1982—2012) ** 2nd (Static Communications) Signal Group (1968—1982) ** 2nd Signal Brigade (1982—1992) * 11th Signal Brigade and Headquarters West Midlands (2014—Present) ** 11th Signal Brigade (V) (1967—1992) ** 11th (Allied Rapid Reaction Corps) Signal Brigade (1992—1997) ** 11th Signal Brigade (1997—2014) * 12th Signal Brigade (1982—1992) Groups * 1st Signal Group (1968—1982), later 1st (United Kingdom) Signal Brigade * 2nd (Static Communications) Signal Group (1968—1982), later 2nd (National Communications) Signal Brigade * 3rd Signal Group (V) (1967—1975) * 4th Signal Group (1969—1992) * 12th Signal Group (1967—1982), later 12th Signal Brigade * 13th Signal Group (V) (1967—1972) * Headquarters, Radio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specialist Group Information Services
Specialist Group Information Services (SGIS) (known as the 254 (Specialist Group Information Services) Signal Squadron until 1 March 2019) is a British Army Reserve (United Kingdom), Army Reserve unit which recruits from across the United Kingdom. Currently the headquarters and other elements of its parent unit 13th Signal Regiment are located in Blandford Camp. SGIS became part of 71 (Yeomanry) Signal Regiment in 2019, before moving to the recently re-reformed 13 Signal Regiment in July 2020. Role As an outcome of the UK Strategic Defence and Security Review 2010, Strategic Defence and Security Review (SDSR) of 2010, the Future Reserves 2020 (FR20) consultation paper ''Delivering the Nation’s Security Together'', published in late 2012 explained how the Army Reserve needed to almost double in size to a trained strength of 30,000. Particular emphasis was placed upon the requirement for many more specialists, i.e. reservists who are recruited primarily for their professional e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MoD Corsham
MOD Corsham (formerly Basil Hill Barracks) is a Ministry of Defence establishment located between the towns of Corsham and Box in Wiltshire, England. History The War Office bought a section of the Pockeridge estate to provide space for Basil Hill Barracks in 1936. The barracks were used by 15 Company Royal Army Ordnance Corps as the administrative headquarters for a Central Ammunitions Depot serving the south of England, known as CAD Corsham or CAD Monkton Farleigh. The depot closed in 1964, although the site was retained by the Royal Army Ordnance Corps and was still used as the headquarters of their Territorial Army section in the 1980s. The site had two significant older buildings. Pockeridge House, to the east of the site, has origins in the 18th century, with additions including coach houses, stables and a walled garden; it was used as the Officer’s Mess. Sandhurst Block is a substantial two-storey office building which was built in 1938, reputedly in the style of a mona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
224 Signal Squadron (United Kingdom)
224 Signal Squadron (Cyber) is a company sized military communications unit of the British Army's Royal Corps of Signals and forms part of the corps' new 13th (Cyber) Signal Regiment. The squadron was originally formed in 1959 as part of the army's wider expansion of the Royal Signals, but disbanded in 1980 afters its tasks were taken over by a joint communications training group. In 2020, the squadron was reformed as part of the June 2020 reorganisation of the corps. First Formation (1959) In 1959, the Royal Corps of Signals went through a massive reorganisation, the first of its type since 1944. As part of the 1959 reorganisations, led by the 1957 Defence White Paper, the Royal Signals former squadrons were all brought into a 'standard numbering and organisation' system. This system was brought in and was to be modelled on the Royal Artillery and Royal Engineers recent reorganisations. As part of these reorganisations, 224 Signal Squadron (Wireless Training) was formed in Lou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blandford Camp
Blandford Forum ( ), commonly Blandford, is a market town in Dorset, England, sited by the River Stour about northwest of Poole. It was the administrative headquarters of North Dorset District until April 2019, when this was abolished and its area incorporated into the new Dorset unitary authority. Blandford is notable for its Georgian architecture, the result of rebuilding after the majority of the town was destroyed by a fire in 1731. The rebuilding work was assisted by an Act of Parliament and a donation by George II, and the rebuilt town centre—to designs by local architects John and William Bastard—has survived to the present day largely intact. Blandford Camp, a military base, is sited on the hills north-east of the town. It is the base of the Royal Corps of Signals, the communications wing of the British Army, and the site of the Royal Signals Museum. Dorset County Council estimates that in 2013 the town's civil parish had a population of 10,610. The town's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army 2020 Refine
Army 2020 Refine was the name given to the restructuring of the British Army, in light of the Strategic Defence and Security Review 2015. Army 2020 Refine The Strategic Defence and Security Review 2015 announced that the structure of the Reaction and Adaptable Forces would further change, in an evolution of the previous Army 2020 plan. The main changes of Army 2020 Refine were: *Creation of two new "Strike brigades", to be formed by converting an Armoured Infantry brigade and an Infantry brigade. These will be formed by 2025, comprising 5,000 personnel each, equipped with Ajax vehicles. *The UK's 3rd division will, by 2025, comprise two armoured infantry brigades, a strike brigade, and a strike experimentation group (which would later convert to a second Strike brigade). *Creation of a Specialised Infantry Group, to be formed by converting four infantry battalions and creation of a new battalion and training cell. *Two innovative brigades were to be established, comprising a mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1957 Defence White Paper
The 1957 White Paper on Defence (Cmnd. 124) was a British white paper issued in March 1957 setting forth the perceived future of the British military. It had profound effects on all aspects of the defence industry but probably the most affected was the British aircraft industry. Duncan Sandys, the recently appointed Minister of Defence, produced the paper. The decisions were influenced by two major factors: the finances of the country and the coming of the missile age. In the past, combat in the air would have been between aircraft, with high flying bombers carrying nuclear weapons and fast interceptor fighter aircraft trying to stop them. Now the ballistic missile could deliver these weapons with no possible defensive response. In this new environment, the interceptors and surface-to-air missiles (SAMs), along with their associated radar networks, seemed superfluous. Likewise, it appeared new manned aircraft of any sort would have little utility in airspace dominated by SAMs. Num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany–Netherlands Border
The Germany–Netherlands border (; ) consists of a land and maritime border across the Dollart through the Frisian Islands into the North Sea. Land border The border is located in the northwestern part of Germany and the east of the Netherlands. The border runs as a fairly irregular line from the shore of the Dollart bay which is part of the Ems river estuary in the north to the Belgium–Germany–Netherlands tripoint at Vaalserberg. The length of the border is around in length, although the straight distance between the two border end points is . The border runs along portions of rivers, including for along the large Rhine river. It also runs for about along the Meuse valley, although most of the time a few kilometres to the east of the Meuse river rather than along it, before leaving the valley at the last portion of border to the border tripoint located at Vaalserberg about west of Aachen. The German states which share the international border are (from north to sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Münster
Münster (; nds, Mönster) is an independent city (''Kreisfreie Stadt'') in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also a state district capital. Münster was the location of the Anabaptist rebellion during the Protestant Reformation and the site of the signing of the Treaty of Westphalia ending the Thirty Years' War in 1648. Today it is known as the bicycle capital of Germany. Münster gained the status of a ''Großstadt'' (major city) with more than 100,000 inhabitants in 1915. , there are 300,000 people living in the city, with about 61,500 students, only some of whom are recorded in the official population statistics as having their primary residence in Münster. Münster is a part of the international Euregio region with more than 1,000,000 inhabitants (Enschede, Hengelo, Gronau, Osnabrück). History Early history In 793, Charlemagne sent out Ludger as a miss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)