|
13-pounder
The Ordnance QF 13-pounder ( quick-firing) field gun was the standard equipment of the British and Canadian Royal Horse Artillery at the outbreak of World War I. History The QF 13-pounder was developed as a response to combat experience gained in the Boer War and entered service in 1904, replacing the Ehrhard QF 15-pounder and BL 12-pounder 6 cwt. It was intended as a rapid-firing and highly-mobile, yet reasonably powerful, field gun for Royal Horse Artillery (RHA) batteries supporting Cavalry brigades, and were expected to be engaged in mobile open warfare. It was developed in parallel with the QF 18-pounder used by Royal Field Artillery. The original Mk I barrel was wire wound. Later Mk II barrels had a tapered inner A tube which was pressed into the outer tube. A hydro-spring recoil system was mounted above the barrel. The carriage was a pole trail type with two seats for the gunners and a protective shield. The first British artillery round on the Western Front in Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QF 18-pounder Gun
The Ordnance QF 18-pounder,British military traditionally denoted smaller ordnance by the weight of its standard projectile, in this case approximately or simply 18-pounder gun, was the standard British Empire field gun of the World War I, First World War-era. It formed the backbone of the Royal Field Artillery during the war, and was produced in large numbers. It was used by British Forces in all the main theatres, and by British troops in Russia in 1919. Its calibre (84 mm) and shell weight were greater than those of the equivalent field guns in French (75 mm) and German (77 mm) service. It was generally horse drawn until mechanisation in the 1930s. The first versions were introduced in 1904. Later versions remained in service with British forces until early 1942. During the interwar period, the 18-pounder was developed into the early versions of the equally famous Ordnance QF 25-pounder, which would form the basis of the British artillery forces during and af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnance QF 15-pounder
} The Ordnance QF 15-pounder gun, commonly referred to as the ''Ehrhardt'', was a modern German field gun purchased by Britain in 1900 as a stopgap measure to upgrade its field artillery to modern QF standards, while it developed its own alternative. This was precipitated by the experience of the British Army in South Africa during the Second Boer War, where its standard field gun, the BL 15-pounder, was out-performed by modern French and German field guns deployed by the Boers. It bore no relation to the BL 15-pounder or BLC 15-pounder, two other guns in British service at the time, other than a common shell. History The gun as originally designed and supplied to Britain had a sprung telescoping trail to assist with recoil control, all-steel wheels, axle-tree seats and no shield. The British found the trail unsatisfactory in service, so they permanently pinned it in the closed position. The British also immediately replaced the original all-steel wheels with standard British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Carriage
A gun carriage is a frame and mount that supports the gun barrel of an artillery piece, allowing it to be maneuvered and fired. These platforms often had wheels so that the artillery pieces could be moved more easily. Gun carriages are also used on ships to facilitate the movement and aiming of large cannons. Early guns The earliest guns were laid directly onto the ground, with earth being piled up under the muzzle end of the barrel to increase the elevation. As the size of guns increased, they began to be attached to heavy wooden frames or beds that were held down by stakes. These began to be replaced by wheeled carriages in the early 16th century. Smoothbore gun carriages From the 16th to the mid-19th century, the main form of artillery remained the smoothbore cannon. By this time, the trunnion (a short axle protruding from either side of the gun barrel) had been developed, with the result that the barrel could be held in two recesses in the carriage and secured with an iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnance BL 12-pounder 6 Cwt
The Ordnance BL 12-pounder 6 cwtBritish military traditionally denoted smaller ordnance by the weight of its standard projectile, in this case approximately . "6 cwt" referred to the weight of the gun and barrel to differentiate it from other "12-pounder" guns. One hundredweight (cwt) is , so the total weight was was a lighter version of the British 12-pounder 7 cwt gun, used by the Royal Horse Artillery in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. History Problems arose when the standard BL 12-pounder 7 cwt gun was used in the great Indian cavalry manoeuvres of 1891. The carriage was found to be too complicated, and dust caused the metal surfaces of the axle traversing device to seize. It also proved too heavy for horse artillery, which was intended to support cavalry in battle, to manoeuvre. The 12-pounder 6 cwt gun was therefore developed in 1892, when the new more powerful cordite replaced gunpowder, as a lighter version of the BL 12-pounder 7 cwt gun. It had a barrel shor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
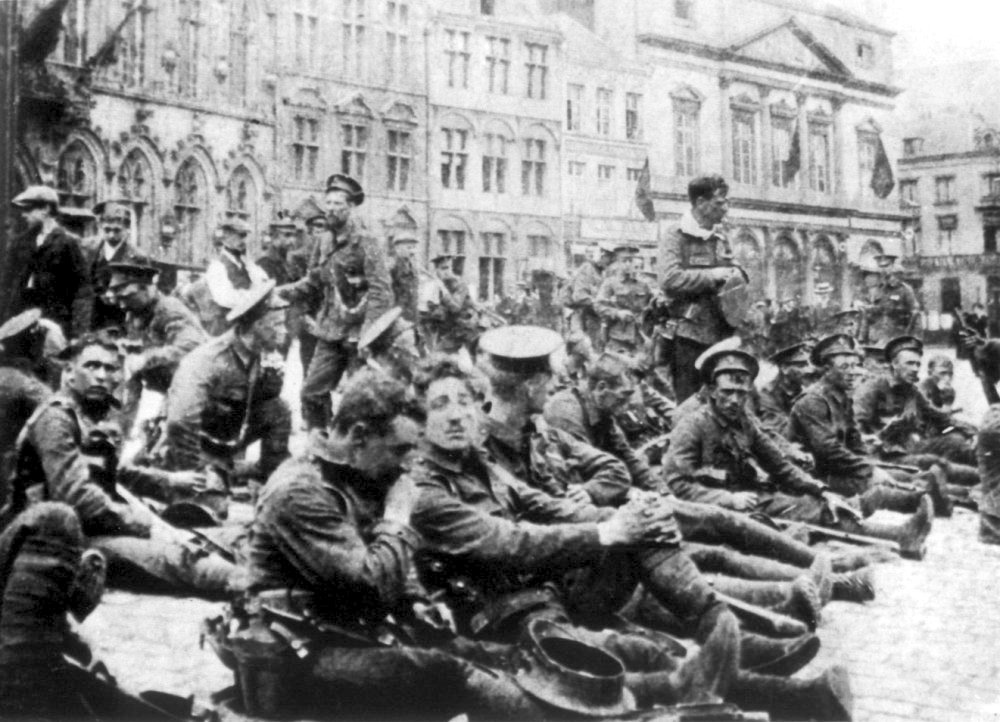
E Battery Royal Horse Artillery
E Battery Royal Horse Artillery is a Close Support Battery of 1st Regiment Royal Horse Artillery. It is currently based in Purvis Lines in Larkhill Camp. History E Battery Royal Horse Artillery was formed as E Troop on 1 November 1794. 19th century E Troop saw action in the Peninsular War in 1811 and also at the Battle of Waterloo. Between 1815 and 1856, the Troop saw service in England, Ireland and the Crimea. By this time E Troop had been renamed D Troop. In 1877, D Troop was re-designated as E Battery RHA. In 1878, E Battery was deployed to the Second Afghan War. World War I In 1914, E Battery was sent to France as part of the BEF, equipped with QF 13-pounder guns. At 0930 hours on 22 August 1914, northeast of Harmignies in Belgium, No. 4 gun of E Battery fired the first British artillery rounds on the Western Front in World War I, E Battery went on to fight in many of the battles on the Western Front and then joined the Army of Occupation. Between the World Wars E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial War Museum
Imperial War Museums (IWM) is a British national museum organisation with branches at five locations in England, three of which are in London. Founded as the Imperial War Museum in 1917, the museum was intended to record the civil and military war effort and sacrifice of Britain and British Empire, its Empire during the First World War. The museum's remit has since expanded to include all conflicts in which British or Commonwealth forces have been involved since 1914. As of 2012, the museum aims "to provide for, and to encourage, the study and understanding of the history of modern war and 'wartime experience'." Originally housed in the Crystal Palace at Sydenham Hill, the museum opened to the public in 1920. In 1924, the museum moved to space in the Imperial Institute in South Kensington, and finally in 1936, the museum acquired a permanent home that was previously the Bethlem Royal Hospital in Southwark. The outbreak of the Second World War saw the museum expand both its coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affair Of Néry
The Affair of Néry was a skirmish fought on 1 September 1914 between the British Army and the German Army, part of the Great Retreat from Mons during the early stages of the First World War. A British cavalry brigade preparing to leave their overnight bivouac were attacked by a German cavalry division of about twice their strength, shortly after dawn. Both sides fought dismounted; the British artillery was mostly put out of action in the first few minutes but a gun of L Battery, Royal Horse Artillery kept up a steady fire for two and a half hours, against a full battery of German artillery. British reinforcements arrived at around counter-attacked the Germans and forced them to retreat; the German division was routed and did not return to combat for several days. Three men of L Battery were awarded the Victoria Cross for their part in the battle, the battery was later awarded the honour title of "Néry", the only British Army unit to have this as a battle honour. Background ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrapnel Shell
Shrapnel shells were anti-personnel artillery munitions which carried many individual bullets close to a target area and then ejected them to allow them to continue along the shell's trajectory and strike targets individually. They relied almost entirely on the shell's velocity for their lethality. The munition has been obsolete since the end of World War I for anti-personnel use; high-explosive shells superseded it for that role. The functioning and principles behind Shrapnel shells are fundamentally different from high-explosive shell fragmentation. Shrapnel is named after Lieutenant-General Henry Shrapnel (1761–1842), a British artillery officer, whose experiments, initially conducted on his own time and at his own expense, culminated in the design and development of a new type of artillery shell. Usage of term "shrapnel" has changed over time to also refer to fragmentation of the casing of shells and bombs. This is its most common modern usage, which strays from the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L (Néry) Battery Royal Horse Artillery
L (Néry) Battery Royal Horse Artillery is the Tactical Group Battery of 1st Regiment Royal Horse Artillery. Previous role The Battery became a Tactical Group Battery in 2005, with its guns firing their last rounds in Otterburn in February 2005. *2006 – L/N (Nery) Battery (The Eagles Troop) RHA split to reform separately as L and N Batteries. N Battery returned to 3 RHA to become their Tactical Group Battery and L Battery became 1 RHA's Tactical Group Battery – supporting the HCR, 1st Mech Bde Formation Reconnaissance Regiment. Battery structure L (Nery) Battery are known as a Tactical Group Battery and they consist of approximately 30 personnel: * Battery Commanders FOO Party * FOO Party A - Commanded by the Battery Captain * FOO Party B - Commanded by a Captain. * Battery Commanders Tac Group Equipment L (Nery) Battery are currently equipped with CVRT, rather the Warrior OPV. They have Forward Air Controllers in each team. History Formation L (Nery) Battery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Expeditionary Force (World War I)
The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) was the six-divisions the British Army sent to the Western Front during the First World War. Planning for a British Expeditionary Force began with the 1906–1912 Haldane reforms of the British Army carried out by the Secretary of State for War Richard Haldane following the Second Boer War (1899–1902). The term ''British Expeditionary Force'' is often used to refer only to the forces present in France prior to the end of the First Battle of Ypres on 22 November 1914. By the end of 1914—after the battles of Mons, Le Cateau, the Aisne and Ypres—the existent BEF had been almost exhausted, although it helped stop the German advance.Chandler (2003), p. 211 An alternative endpoint of the BEF was 26 December 1914, when it was divided into the First and Second Armies (a Third, Fourth and Fifth being created later in the war). "British Expeditionary Force" remained the official name of the British armies in France and Flanders thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Le Cateau
The Battle of Le Cateau was fought on the Western Front during the First World War on 26 August 1914. The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and the French Fifth Army had retreated after their defeats at the Battle of Charleroi (21–23 August) and the Battle of Mons (23 August). The British II Corps fought a delaying action at Le Cateau to slow the German pursuit. Most of the BEF was able to continue its retreat to Saint-Quentin. Prelude Having retreated from Mons two days earlier, Le Cateau and Mons being apart, the British II Corps (General Sir Horace Smith-Dorrien) was exhausted. The corps had become separated from the rest of the BEF because of the unexpected retreat by Sir Douglas Haig, the commander of I Corps, who had fought his own rearguard action at Landrecies on 25 August. Following that engagement, where Haig had rallied his troops, revolver in hand, he succumbed to panic, writing to the French High Command about the imminent debacle. He had greatly ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honourable Artillery Company
The Honourable Artillery Company (HAC) is a reserve regiment in the British Army. Incorporated by royal charter in 1537 by King Henry VIII, it is the oldest regiment in the British Army and is considered the second-oldest military unit in the world. Today, it is also a charity whose purpose is to attend to the "better defence of the realm", primarily through supporting the HAC regiment and a detachment of City of London Special Constabulary. The word "artillery" in "Honourable Artillery Company" does not have the current meaning that is generally associated with it, but dates from a time when in the English language that word meant any projectile, including for example arrows shot from a bow. The equivalent form of words in modern English would be either "Honourable Infantry Company" or "Honourable Military Company". In the 17th century, its members played a significant part in the formation of both the Royal Marines and the Grenadier Guards. More recently, regiments, battalions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |