|
12th Motorised Brigade (South Africa)
The 12th Motorised Brigade (South Africa) was a South African brigade-level infantry unit that served with the Allies in the Italian Campaign of World War II under the 6th South African Armoured Division. It was the first South African unit to enter combat in Italy. The unit was activated in 1943 and had generally deactivated by 8 May 1945. Formation The 12th Motorized Brigade was officially formed under the 6th Armoured Division (South Africa) on 8 February 1943 as a mismatched collection of volunteers from various units previously serving in North Africa, as interest in fighting in Italy was low among South African soldiers. The unit was led by Brig. R.J. Palmer, and sailed, along with the rest of the 6th, to Port Tewfik on the Suez Canal on 30 April 1943. The brigade received training in the Kataba desert in the northwest of Cairo, Egypt, culminating in the three-day "Exercise Durban", which ran from 5–7 December 1943. Composition Units under the 12th Motorised Brigade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Smuts
Field Marshal Jan Christian Smuts, (24 May 1870 11 September 1950) was a South African statesman, military leader and philosopher. In addition to holding various military and cabinet posts, he served as prime minister of the Union of South Africa from 1919 to 1924 and 1939 to 1948. Smuts was born to Afrikaner parents in the British Cape Colony. He was educated at Victoria College, Stellenbosch before reading law at Christ's College, Cambridge on a scholarship. He was called to the bar at the Middle Temple in 1894 but returned home the following year. In the leadup to the Second Boer War, Smuts practised law in Pretoria, the capital of the South African Republic. He led the republic's delegation to the Bloemfontein Conference and served as an officer in a commando unit following the outbreak of war in 1899. In 1902, he played a key role in negotiating the Treaty of Vereeniging, which ended the war and resulted in the annexation of the South African Republic and Orange Free St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Machine Gun
A light machine gun (LMG) is a light-weight machine gun designed to be operated by a single infantryman, with or without an assistant, as an infantry support weapon. LMGs firing cartridges of the same caliber as the other riflemen of the same combat unit are often referred to as squad automatic weapons. Characteristics While early light machine guns fired full-powered rifle cartridges, modern light machine guns often fire smaller-caliber rifle cartridges than medium machine guns – generally the same intermediate cartridge fired by a service's standard assault rifle – and are usually lighter and more compact. Some LMGs, such as the Russian RPK, are modifications of existing designs and designed to share the same ammunition. Adaptations to the original rifle generally include a larger magazine, a heavier barrel to resist overheating, a more robust mechanism to support sustained fire and a bipod. A light machine gun is also defined by its usage as well as its specificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Artillery
The Royal Regiment of Artillery, commonly referred to as the Royal Artillery (RA) and colloquially known as "The Gunners", is one of two regiments that make up the artillery arm of the British Army. The Royal Regiment of Artillery comprises thirteen Regular Army regiments, the King's Troop Royal Horse Artillery and five Army Reserve regiments. History Formation to 1799 Artillery was used by the English army as early as the Battle of Crécy in 1346, while Henry VIII established it as a semi-permanent function in the 16th century. Until the early 18th century, the majority of British regiments were raised for specific campaigns and disbanded on completion. An exception were gunners based at the Tower of London, Portsmouth and other forts around Britain, who were controlled by the Ordnance Office and stored and maintained equipment and provided personnel for field artillery 'traynes' that were organised as needed. These personnel, responsible in peacetime for maintaining the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regiment De La Rey
The General de la Rey Regiment (formerly Regiment de la Rey) is an reserve infantry regiment of the South African Army. Formation The Regiment de la Rey was established in 1934 as one of the new Afrikaans language Citizen Force units of the Union Defence Force. The regimental badge depicts a lion's head, in memory of Boer General JH de la Rey, the ''Lion of the West'' after whom the regiment is named. Before the Second World War, battalion headquarters were at Rustenburg in the Transvaal. The unit had company headquarters at Potchefstroom, Klerksdorp and Ventersdorp, with a support company at Brits. Mrs J E Morkel, daughter of General De la Rey, became the first honorary colonel of the regiment. The regiment was affiliated to the Northamptonshire Regiment of the British Army. World War II RDLR was called up for full-time service on 18 July 1940. Because the commanding officer, Lt-Col (later Brig) H P van Noorden, was by then commanding a battalion of the Field Force Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witwatersrand Rifles
The Bambatha Rifles (formerly the Witwatersrand Rifles) is a reserve mechanised infantry regiment of the South African Army. History Origin The Witwatersrand Rifles (often familiarly known as the "Wits Rifles or the Wit Rifles") was formed by proclamation on 1 May 1903 and absorbed the members of the Railway Pioneer Regiment and the Rand Rifles, both of which had fought on the British side during the Second Anglo-Boer War of 1899 – 1902. As befitted a regiment based from the gold-rich Witwatersrand region, it had a very close relationship with the mining establishment of the time; and its cap badge further emphasised this link. Bambatha Rebellion The regiment first saw action during the Bambata Rebellion of 1906, when it deployed a contingent to (the then) Zululand. Absorption of the Transvaal Light Infantry In 1907 the regiment was further strengthened when it absorbed the Transvaal Light Infantry Regiment. World War 1 The regiment was mobilised again when World War I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Natal Carbineers
Royal may refer to: People * Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name * A member of a royal family Places United States * Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community * Royal, Illinois, a village * Royal, Iowa, a city * Royal, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Royal, Nebraska, a village * Royal, Franklin County, North Carolina, an unincorporated area * Royal, Utah, a ghost town * Royal, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Royal Gorge, on the Arkansas River in Colorado * Royal Township (other) Elsewhere * Mount Royal, a hill in Montreal, Canada * Royal Canal, Dublin, Ireland * Royal National Park, New South Wales, Australia Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Royal'' (Jesse Royal album), a 2021 reggae album * ''The Royal'', a British medical drama television series * ''The Royal Magazine'', a monthly British literary magazine published between 1898 and 1939 * ''Royal'' (Indian magazine), a men's lifestyle bimonthly * Royal Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morris CS8
The Morris Commercial CS8, also known as the "Morris 15 cwt" was a British light military truck of the Second World War. Introduced in 1934 it was the most numerous vehicle of that size in the British Army at the start of the war but was replaced by other vehicles. Development In 1933 the War Office issued a specification for a new type of purpose-built light trucks able to carry loads, the specification stipulated a short wheelbase, good ground clearance, a semi-forward driver's position and the use of commercial components as much as possible but with the usual cabin eliminated to simplify production. It was planned to issue one 15-cwt truck to every platoon in a re-equipped mechanised British Army to carry personnel and equipment. Morris, Ford, Commer, Guy and Bedford all tendered vehicles to meet the requirement and in 1934 Morris was the first to produce a design, the CS8, which used elements of Morris' civilian C range. The S denoted a 6-cylinder engine and 8 referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ML 3-inch Mortar
The Ordnance ML 3-inch mortar was the United Kingdom's standard mortar used by the British Army from the early 1930s to the late 1960s, superseding the Stokes mortar. Initially handicapped by its short range compared to similar Second World War mortars, improvements of the propellant charges enabled it to be used with great satisfaction by various armies of the British Empire and of the Commonwealth. Design The ML 3-inch mortar is a conventional Stokes-type mortar that is muzzle-loaded and drop-fired. It also reuses many of the Brandt mortar features. History Based on their experience in the First World War, the British infantry sought some sort of artillery for close support. The initial plan was for special batteries of artillery, but the cost was prohibitive and the mortar was accepted instead. The Mark II mortar (Mark I was the Stokes) was adopted by the British Army in the early 1930s; and this was the standard British mortar when the Second World War broke out i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Carrier
The Universal Carrier, also known as the Bren Gun Carrier and sometimes simply the Bren Carrier from the light machine gun armament, is a common name describing a family of light armoured tracked vehicles built by Vickers-Armstrongs and other companies. The first carriers – the Bren Carrier and the Scout Carrier with specific roles – entered service before the war, but a single improved design that could replace these, the Universal, was introduced in 1940. The vehicle was used widely by British Commonwealth forces during the Second World War. Universal Carriers were usually used for transporting personnel and equipment, mostly support weapons, or as machine gun platforms. Design and development The origins of the Universal Carrier family can be traced back generally to the Carden Loyd tankettes family, which was developed in the 1920s, and specifically the Mk VI tankette. In 1934, Vickers-Armstrongs produced, as a commercial venture, a light tracked vehicle that could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medium Machine Gun
A medium machine gun (MMG), in modern terms, usually refers to a belt-fed machine gun firing a full-powered rifle cartridge, and is considered "medium" in weight (). Medium machine guns are light enough to be infantry-portable (as opposed to a heavy machine gun, which completely relies on mounting onto a weapons platform for operational stability and mobility), but still cumbersome enough to require a crew for optimal operational efficiency (as opposed to a light machine gun, which can be operated to full capacity by only a single gunner). History Late 19th century In the late 19th century, Gatling guns and other externally powered types, such as the Nordenfelt, were often made in different ranges of calibers, such as half-inch and one-inch. Thanks to their many barrels, overheating was not a major issue, and they were also quite heavy, being, essentially, heavy machine guns. When Hiram Maxim developed his recoil-powered machine gun that used a single barrel, the first ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portée (military)
describes the practice of carrying an artillery piece on a truck which can be fired from the vehicle or quickly dismounted and fired from the ground. The term is most often used to describe anti-tank equipments used by the British, Commonwealth and imperial forces in the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. Modern terms for mounting weapons on vehicles are technical or gun truck. Interwar US Cavalry cavalry was horse cavalry – horses and riders – carried in trucks or other vehicles. The cavalry is thus mechanized for strategic and operational movement and horse-mounted for tactical deployment. cavalry units were briefly tested in the American army during the interwar period change from fully-horsed cavalry to fully-mechanized cavalry but were generally found to be overcomplicated and not worthwhile. British Army, 1939–1943 2-pounder anti-tank gun An Ordnance QF 2 pounder (40 mm) anti-tank gun mounted on a Morris CS8 15 cwt truck, Chevrolet WA or WB 30- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


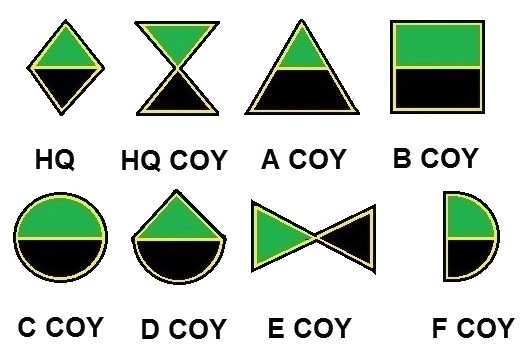



.png)
