|
119th Infantry (The Mooltan Regiment)
The 119th Infantry (The Mooltan Regiment) was an infantry regiment of the British Indian Army. The regiment originated in 1817, when it was raised as the 1st Battalion, 10th Regiment of Bombay Native Infantry. The regiment's first action was in the Battle of Ghazni in the First Afghan War. After Afghanistan it took part in the Siege of Multan in the Second Anglo-Sikh War. It returned to Afghanistan in the Second Afghan War and took part in the Siege of Multan. During World War I it was attached to the 6th (Poona) Division and served in the Mesopotamian campaign. It fought in the Battle of Basra, the Battle of Qurna, the Battle of Es Sinn before suffering a setback at the Battle of Ctesiphon, after which it withdrew to Kut. Trapped in the city in the Siege of Kut the regiment was forced to surrender after 147 days. A second battalion was raised from men on leave and reinforcements, and sent to Mesopotamia. After World War I the Indian government reformed the army moving from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombay Army
The Bombay Army was the army of the Bombay Presidency, one of the three presidencies of British India. It was established in 1662 and governed by the East India Company until the Government of India Act 1858 transferred all presidencies to the direct authority of the British Crown. On 1 April 1895 the army was incorporated into the newly created Indian Army, and became known as the Bombay Command until 1908. History 18th century In the early stages of HEIC rule Bombay was rated as an unhealthy and unprofitable region. Accordingly, only a small garrison was maintained while emphasis was placed on creating a local navy (the "Bombay Marine") to control piracy. In 1742 the Bombay Army consisted of eight companies of European and Eurasian garrison troops, numbering 1,593 of all ranks. These had evolved from independent companies dating back as far as 1668 when the Company took over control of the city of Bombay.Raugh, p. 55 The Mahars served in both Bombay Army and Marine battalio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Qurna
The Battle of Qurna, (3 to 9 December 1914) was between British forces and Ottoman forces that had retreated from Basra, which they lost at the Battle of Basra (1914) during the Mesopotamian campaign of World War I. Background By capturing Basra, the British had taken an important communications and industrial centre. The Ottomans retreated up the Tigris River. The British needed to secure their position in Basra and the oil fields at Abadan. After the defeat at Basra, the Ottomans decided to take up a defensive position at the small town of Qurna to the north. Since both the Tigris and Euphrates join at Qurna, it made for an ideal position to make a stand since the British would have to cross the two rivers. The Ottomans had about 1,000 men under the command of Colonel Subhi Bey, the Wali or Governor of Basra. The British had about 2,100 under Major General Charles Irwin Fry. The battle On 3 December, the Ottomans were dug in at Qurna. A British force of two Indian ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombay Presidency
The Bombay Presidency or Bombay Province, also called Bombay and Sind (1843–1936), was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India, with its capital in the city that came up over the seven islands of Bombay. The first mainland territory was acquired in the Konkan region with the Treaty of Bassein (1802). Mahabaleswar was the summer capital. The Bombay province has its beginnings in the city of Bombay that was leased in fee tail to the East India Company, via the Royal Charter of 27 March 1668 by King Charles II of England, who had in turn acquired Bombay on 11 May 1661, through the royal dowry of Catherine Braganza by way of his marriage treaty with the Portuguese princess, daughter of John IV of Portugal. The English East India Company transferred its Western India headquarters from Surat in the Gulf of Cambay after it was sacked, to the relatively safe Bombay Harbour in 1687. The province was brought under Direct rule along with other parts of British I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Indian Army Infantry Regiments
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial War Museum
Imperial War Museums (IWM) is a British national museum organisation with branches at five locations in England, three of which are in London. Founded as the Imperial War Museum in 1917, the museum was intended to record the civil and military war effort and sacrifice of Britain and British Empire, its Empire during the First World War. The museum's remit has since expanded to include all conflicts in which British or Commonwealth forces have been involved since 1914. As of 2012, the museum aims "to provide for, and to encourage, the study and understanding of the history of modern war and 'wartime experience'." Originally housed in the Crystal Palace at Sydenham Hill, the museum opened to the public in 1920. In 1924, the museum moved to space in the Imperial Institute in South Kensington, and finally in 1936, the museum acquired a permanent home that was previously the Bethlem Royal Hospital in Southwark. The outbreak of the Second World War saw the museum expand both its coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four-star general. Two officers have been conferred with the rank of field marshal, a five-star rank, which is a ceremonial position of great honour. The Indian Army was formed in 1895 alongside the long established presidency armies of the East India Company, which too were absorbed into it in 1903. The princely states had their own armies, which were merged into the national army after independence. The units and regiments of the Indian Army have diverse histories and have participated in several battles and campaigns around the world, earning many battle and theatre honours before and after Independence. The primary mission of the Indian Army is to ensure national security and national unity, to defend the nation from external aggression an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th Jat Regiment
The 9th Jat Regiment was an infantry regiment of the British Indian Army. It was formed in 1922, after the Indian government reformed the army, moving from single battalion regiments to multi battalion regiments. World War II The Regiment saw a great deal of fighting with the Jats showing their mettle in North Africa, Ethiopia, Burma, Malaya, Singapore, and Java-Sumatra. A large number of gallantry awards were won including a Victoria Cross (by Jemadar Abdul Hafiz) and two George Crosses (by Islam-ud-Din and Abdul Rahman). At the end of the war the Regiment, in company with other regiments of the Indian Infantry, dropped the numeral 9 from its title and became simply the Jat Regiment. After independence it was allocated to the new Indian Army. The Regiment at independence had about 1/4th or 25% Muslims recruited from Panwar Rajput Muslims from around Rohtak and Hisar, Haryana and from Muslim Jats in Montgomery and Okara in West Punjab, in all-Muslim companies of the 10th Jat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
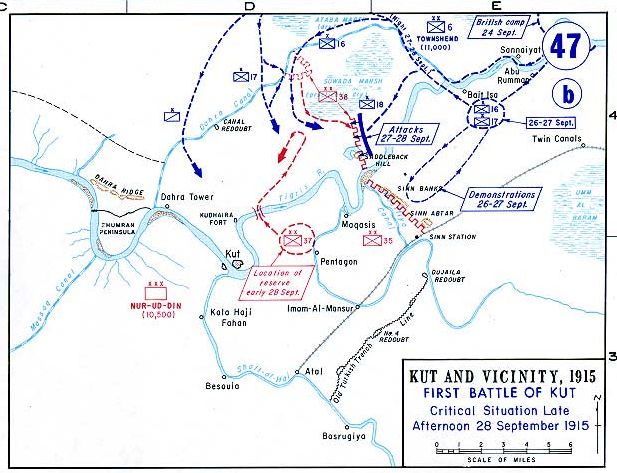
Siege Of Kut
The siege of Kut Al Amara (7 December 1915 – 29 April 1916), also known as the first battle of Kut, was the besieging of an 8,000 strong British Army garrison in the town of Kut, south of Baghdad, by the Ottoman Army. In 1915, its population was around 6,500. Following the surrender of the garrison on 29 April 1916, the survivors of the siege were marched to imprisonment at Aleppo, during which many died. Historian Christopher Catherwood has called the siege "the worst defeat of the Allies in World War I". Ten months later, the British Indian Army, consisting almost entirely of newly recruited troops from Western India, conquered Kut, Baghdad and other regions in between in the Fall of Baghdad. Prelude The 6th (Poona) Division of the Indian Army, under Major-General Charles Townshend, had fallen back to the town of Kut after retreating from Ctesiphon. The British Empire forces arrived at Kut around 3 December 1915. They had suffered significant losses, numbering only 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ctesiphon (1915)
The Battle of Ctesiphon ( Turkish: ''Selman-ı Pak Muharebesi'') was fought in November 1915 by the British Empire, against the Ottoman Empire, within the Mesopotamian Campaign of World War I. Indian Expeditionary Force D, mostly made up of Indian units and under the command of Gen. Sir John Nixon, had met with success in Mesopotamia since it had landed at Al-Faw Peninsula upon the Ottoman Empire's declaration of war on 5 November 1914. One of the primary reasons for initiating the campaign in Mesopotamia was to defend the oil refinery at Abadan at the mouth of the Shatt al-Arab. Adopting a forward defence policy, the British army under General Townshend fought off a series of small Ottoman forces. Then after a year of a string of defeats, the Ottoman forces were able to halt the British advance in two days of hard fighting at Ctesiphon. Battleground Ctesiphon lies on the Western bank of the Tigris River in the barren Iraqi desert, about upstream from Basra, north of K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Es Sinn
The Battle of Es Sinn was a World War I military engagement between Anglo-Indian and Ottoman forces. It took place on 28 September 1915, during the Mesopotamian Campaign. The sides fought to determine control of the lower Tigres and Euphrates rivers, in what is now Iraq. The British and Indian governments also viewed it as a test of the Ottoman forces, and whether a further advance to capture Baghdad was possible. The Anglo-Indian forces of Indian Expeditionary Force D were under the command of Major-General Charles Vere Ferres Townshend, and the Ottoman forces by Colonel Nureddin. The engagement took place just south of the town of Kut-al-Amarah, along the banks of the Tigris River. Following a night march, the British and Indian troops defeated the Ottoman forces, driving them from their defensive positions along the Tigris. The capture of the Es Sinn position allowed for the capture of Kut, and with it control over the lower Tigris and Euphrates rivers, by British forces the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Basra (1914)
The Battle of Basra was a battle of World War I which took place south of the city of Basra (modern-day Iraq) between British British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, ... and Ottoman troops from November 11 to November 22, 1914. The battle resulted in the British capture of Basra. Background After the capture of Fao by the British, the Ottoman army began to converge on Basra. The British had the mission of securing the Persian oil fields by capturing Basra, and they advanced up the river towards Basra. The battle On November 7, 1914, British troops began the march from Fao to Basra.Corp., American. "Battle of Basra 1914." Encyclopedia Americana. University of Michigan, MI: American corp., 1965. The Ottomans attacked the British camp at dawn on November 11, but were def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombay Command
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second-most populous city in India after Delhi and the eighth-most populous city in the world with a population of roughly 20 million (2 crore). As per the Indian government population census of 2011, Mumbai was the most populous city in India with an estimated city proper population of 12.5 million (1.25 crore) living under the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation. Mumbai is the centre of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, the sixth most populous metropolitan area in the world with a population of over 23 million (2.3 crore). Mumbai lies on the Konkan coast on the west coast of India and has a deep natural harbour. In 2008, Mumbai was named an Globalization and World Cities Research Network, alpha world city. It has the highest number of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |