|
1188 In Europe
Year 1188 ( MCLXXXVIII) was a leap year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events By place Europe * January 22 – King Ferdinand II dies after returning from a pilgrimage to Santiago de Compostela. He is succeeded by his 16-year-old son Alfonso IX, who becomes ruler of León and Galicia. He convenes representatives of the nobility, clergy and towns at the Basilica of San Isidoro the Cortes of León. These Corteses are considered to be the first parliament in Europe. * Spring – King Henry II and Philip II (Augustus) meet at Le Mans, with Archbishop Josias (or Joscius) in attendance. Both kings agree to peace terms, and to contribute to a joint Crusade. It is decided to raise a new tax to pay for the expedition. This tax, known as the Saladin Tithe, is imposed on the people of England and France to raise funds for the Third Crusade. * March 27 – Emperor Frederick I (Barbarossa) holds a Diet at Mainz an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
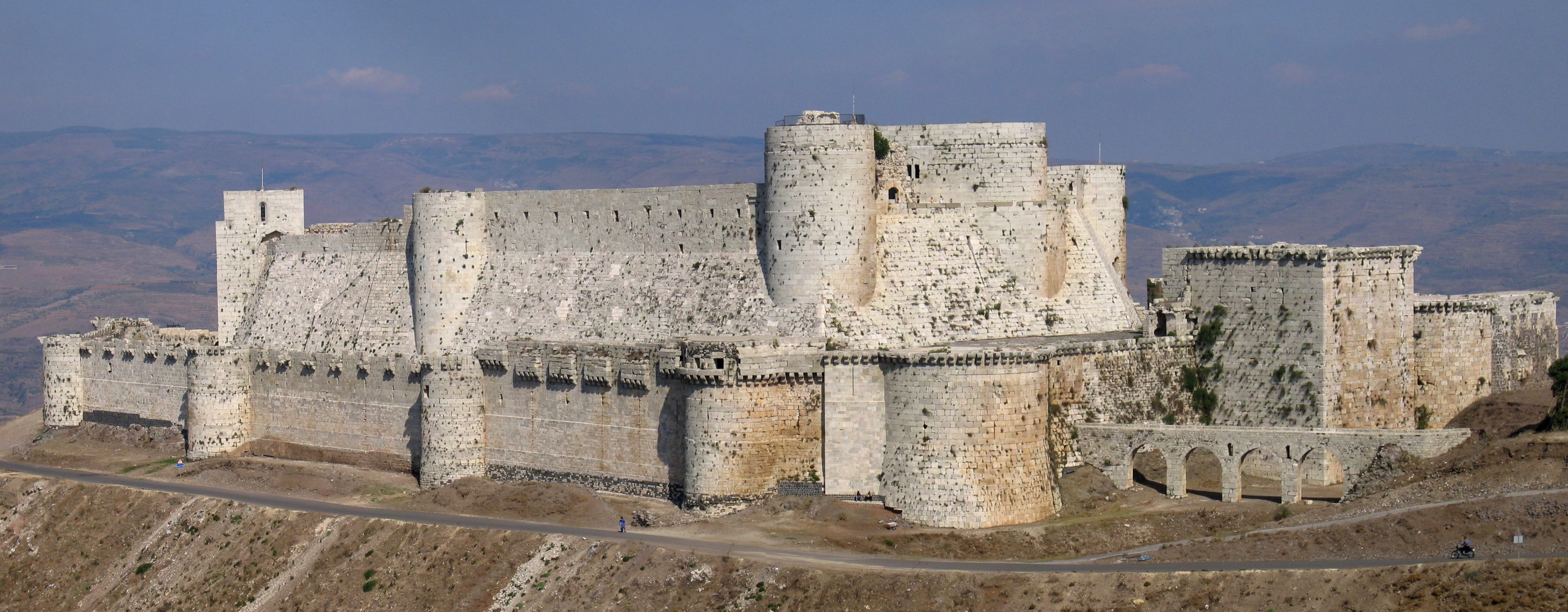
Crac Des Chevaliers Syria
''Crac'' is a 1981 animated short film produced, written and directed by Frédéric Back. Plot The story follows the experiences of a rocking chair, from its creation from a tree through its time as a member of a Canadian farming family. Reception and legacy ''Crac'' won the 1981 Academy Award for Best Animated Short Film The Academy Award for Best Animated Short Film is an award given by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS) as part of the annual Academy Awards, or Oscars, since the 5th Academy Awards (with different names), covering the year .... It also was part of Animation Show of Shows. Animation critic Charles Solomon named it as one of the best animated films of the 1980s. References External links * {{Authority control 1981 films 1981 animated films 1980s animated short films Best Animated Short Academy Award winners Canadian animated short films Films scored by Normand Roger Films directed by Frédéric Back Animated films wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saladin Tithe
The Saladin tithe, or the Aid of 1188, was a tax, or more specifically a tallage, levied in England and to some extent in France in 1188, in response to the capture of Jerusalem by Saladin in 1187. Background In July 1187, the Kingdom of Jerusalem's army was defeated by Saladin at the Battle of Hattin, and in October Saladin captured Jerusalem itself. When news of this reached Europe at the end of the year, a new crusade was promulgated. In January 1188, Henry II of England and Philip II of France discussed the crusade at Le Mans, with Joscius, Archbishop of Tyre in attendance, and on February 11, Henry began to organize the preaching of the crusade in England at Geddington. There he also discussed the "Saladin tithe." Collection of the tithe The Saladin tithe was a literal tithe of 10% on revenues and movable properties.Tyerman, Christopher. God's War: A New History of the Crusades Reprinted in Roy C. Cave & Herbert H. Coulson, A Source Book for Medieval Economic History, (Milwauk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
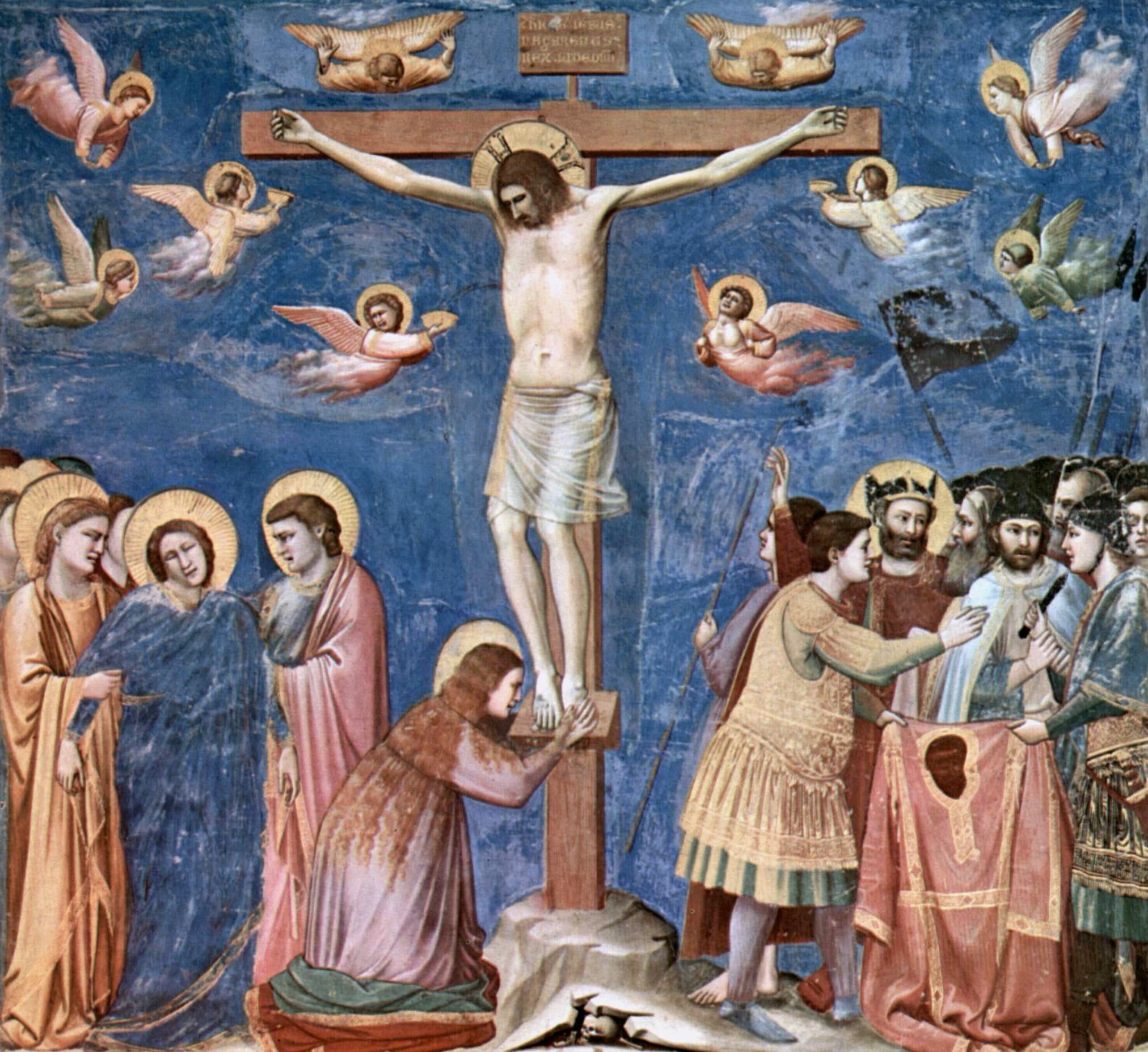
Church Of The Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem. According to traditions dating back to the 4th century, it contains the two holiest sites in Christianity: the site where Jesus was crucified, at a place known as Calvary or Golgotha, and Jesus's empty tomb, which is where he was buried and resurrected. Each time the church was rebuilt, some of the antiquities from the preceding structure were used in the newer renovation. The tomb itself is enclosed by a 19th-century shrine called the Aedicule. The Status Quo, an understanding between religious communities dating to 1757, applies to the site. Within the church proper are the last four stations of the Cross of the Via Dolorosa, representing the final episodes of the Passion of J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Cross
The True Cross is the cross upon which Jesus was said to have been crucified, particularly as an object of religious veneration. There are no early accounts that the apostles or early Christians preserved the physical cross themselves, although protective use of the sign of the cross was common by at least the 2nd century. Post-Nicene historians such as Socrates of Constantinople relate that Helena, the mother of the Roman emperor ConstantineI, travelled to the Holy Land in the years 326–328, founding churches and establishing relief agencies for the poor. The late 4th-century historians Gelasius of Caesarea and Tyrannius Rufinus claimed that while there she discovered the hiding place of three crosses that were believed to have been used at the crucifixion of Jesus and the two thieves, St. Dismas and Gestas, executed with him. To one cross was affixed the titulus bearing Jesus's name, but according to Rufinus, Helena was not sure until a miracle revealed that this was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestina (region)
Palestine ( el, Παλαιστίνη, ; la, Palaestina; ar, فلسطين, , , ; he, פלשתינה, ) is a geographic region in Western Asia. It is usually considered to include Israel and the State of Palestine (i.e. West Bank and Gaza Strip), though some definitions also include part of northwestern Jordan. The first written records to attest the name of the region were those of the Twentieth dynasty of Egypt, which used the term "Peleset" in reference to the neighboring people or land. In the 8th century, Assyrian inscriptions refer to the region of "Palashtu" or "Pilistu". In the Hellenistic period, these names were carried over into Greek, appearing in the Histories of Herodotus in the more recognizable form of "Palaistine". The Roman Empire initially used other terms for the region, such as Judaea, but renamed the region Syria Palaestina after the Bar Kokhba revolt. During the Byzantine period, the region was split into the provinces of Palaestina Prima, Palaestina S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
May 26
Events Pre-1600 * 17 – Germanicus celebrates a triumph in Rome for his victories over the Cherusci, Chatti, and other German tribes west of the Elbe. * 451 – Battle of Avarayr between Armenian rebels and the Sasanian Empire takes place. The Sasanids defeat the Armenians militarily but guarantee them freedom to openly practice Christianity. * 946 – King Edmund I of England is murdered by a thief whom he personally attacks while celebrating St Augustine's Mass Day. * 961 – King Otto I elects his six-year-old son Otto II as heir apparent and co-ruler of the East Frankish Kingdom. He is crowned at Aachen, and placed under the tutelage of his grandmother Matilda. * 1135 – Alfonso VII of León and Castile is crowned in León Cathedral as ''Imperator totius Hispaniae'' (''Emperor of all of Spain''). * 1293 – An earthquake strikes Kamakura, Kanagawa, Japan, killing about 23,000. * 1328 – William of Ockham, the Franciscan Minister-General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It is a unitary republic that consists of 14 governorates (subdivisions), and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east and southeast, Jordan to the south, and Israel and Lebanon to the southwest. Cyprus lies to the west across the Mediterranean Sea. A country of fertile plains, high mountains, and deserts, Syria is home to diverse ethnic and religious groups, including the majority Syrian Arabs, Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians, Armenians, Circassians, Albanians, and Greeks. Religious groups include Muslims, Christians, Alawites, Druze, and Yazidis. The capital and largest city of Syria is Damascus. Arabs are the largest ethnic group, and Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and Syria. An important figure of the Third Crusade, he spearheaded the Muslim military effort against the Crusader states in the Levant. At the height of his power, Ayyubid territorial control spanned Egypt, Syria, Upper Mesopotamia, the Hejaz, Yemen, the Maghreb, and Nubia. Alongside his uncle Shirkuh, a military general of the Zengid dynasty, Saladin was sent to Egypt under the Fatimid Caliphate in 1164, on the orders of Nur ad-Din. With their original purpose being to help restore Shawar as the to the teenage Fatimid caliph al-Adid, a power struggle ensued between Shirkuh and Shawar after the latter was reinstated. Saladin, meanwhile, climbed the ranks of the Fatimid government by virtue of his military successes against Crusader assault ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick IV, Duke Of Swabia
Frederick IV of Hohenstaufen (1145–1167) was duke of Swabia, succeeding his cousin, Frederick Barbarossa, Holy Roman Emperor, in 1152. He was the son of Conrad III of Germany and his second wife Gertrude von Sulzbach and thus the direct heir of the crown, had there been true heredity. However, on his death bed, Conrad III allegedly advised the only two persons present, his nephew Frederick Barbarossa and the bishop of Bamberg, to nominate Frederick Barbarossa; and handed the Imperial insignia to him. Barbarossa wasted no time in getting the Bavarian clerics to endorse him, and had the archbishop of Cologne convene a hurried election. There the electors of the Empire (minus their "''primus inter pares''", Henry I, Archbishop of Mainz, an ally of the Pope) elected Frederick Barbarossa to be King, instead of his six-year-old cousin Frederick. The younger man became Duke of Swabia instead. Frederick participated in Barbarossa's campaigns in Italy, becoming one of the many casualt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curia Christi
The ''Curia Christi'' ("Court of Christ") or ''Curia Dei'' ("Court of God") was a diet or court day (''Hoftag'') of the Holy Roman Empire held in Mainz on 27 March 1188. It was so called because it was notionally under the presidency of Jesus Christ as king of kings. It was the occasion both for the public resolution of the conflict between Emperor Frederick Barbarossa and Archbishop Philip of Cologne and for the emperor's "taking of the cross", when he vowed to lead an army on the Third Crusade. Sources The ''Curia Christi'' is a well recorded event. It is mentioned in the '' Royal Chronicle of Cologne'', the ''Chronicle'' of Magnus of Reichersberg, the ''Chronicle'' of Otto of Sankt Blasien and the ''Chronicle of the Slavs'' of Arnold of Lübeck. The ''History of the Expedition of the Emperor Frederick'' and the ''History of the Pilgrims'' are the source for the names ''Curia Christi'' and ''Curia Dei'', respectively. The ''History of the Expedition'' includes the text of a let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt on 4 March 1152 and crowned in Aachen on 9 March 1152. He was crowned King of Italy on 24 April 1155 in Pavia and emperor by Pope Adrian IV on 18 June 1155 in Rome. Two years later, the term ' ("holy") first appeared in a document in connection with his empire. He was later formally crowned King of Burgundy, at Arles on 30 June 1178. He was named by the northern Italian cities which he attempted to rule: Barbarossa means "red beard" in Italian; in German, he was known as ', which means "Emperor Redbeard" in English. The prevalence of the Italian nickname, even in later German usage, reflects the centrality of the Italian campaigns to his career. Frederick was by inheritance Duke of Swabia (1147–1152, as Frederick III) before his i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March 27
Events Pre-1600 *1309 – Pope Clement V imposes excommunication and Interdict (Catholic canon law), interdiction on Venice, and a general prohibition of all commercial intercourse with Venice, which had seized on Ferrara, a papal fiefdom. *1329 – Pope John XXII issues his ''In Agro Dominico'' condemning some writings of Meister Eckhart as heretical. *1513 – Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León reaches the northern end of The Bahamas on his first voyage to Florida. 1601–1900 *1625 – Charles I of England, Charles I becomes Monarchy of the United Kingdom, King of England, Scotland and Ireland as well as claiming the title English claims to the French throne, King of France. *1638 – The first of four destructive 1638 Calabrian earthquakes, Calabrian earthquakes strikes southern Italy. Measuring magnitude 6.8 and assigned a Modified Mercalli intensity scale, Mercalli intensity of XI, it kills 10,000–30,000 people. *1782 – The Second Rockingham m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |