|
10th Coast Artillery (United States)
The 10th Coast Artillery Regiment was a Coast Artillery regiment in the United States Army. It primarily served as the Regular Army coast artillery component of the Harbor Defenses (HD) of Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island from 1924 through 1944, when it was relieved and disbanded as part of an Army-wide reorganization.Stanton, p. 456 Lineage Constituted in the Regular Army on 27 February 1924 as 10th Coast Artillery (Harbor Defense), and organized on 1 July 1924 at Fort Adams by redesignating the following companies of the Coast Artillery Corps (CAC): 173rd, 52nd, 97th, 102nd, 110th, 129th, 147th, and 174th. (and 7th CA Band). Only Headquarters and Headquarters Battery (HHB) activated; provided caretaker detachments for HD Narragansett Bay and HD New Bedford.Gaines Regular Army, p. 9 The 243rd Coast Artillery was the Rhode Island National Guard component of HD Narragansett Bay. * 1st, 2nd, and 3rd Battalion and HHB constituted inactive components on 31 January 1935. * Batteries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coast Artillery Corps
The U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps (CAC) was an Corps#Administrative corps, administrative corps responsible for coastal defence and fortification, coastal, harbor, and anti-aircraft Seacoast defense in the United States, defense of the United States and its possessions between 1901 and 1950. The CAC also operated heavy and railway artillery during World War I. History As early as 1882 the need for heavy fixed artillery for seacoast defense was noted in Chester A. Arthur's Second Annual Message to Congress where he noted: In 1885 the Board of Fortifications, Endicott Board was convened under the subsequent Grover Cleveland administration, chaired by Secretary of War William Crowninshield Endicott. This board recommended a large-scale program of harbor defenses at 29 ports, including 12-inch gun M1895, guns, 12-inch coast defense mortar, mortars, and Submarine mines in United States harbor defense, mine fields. Most of their recommendations were implemented and new defenses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Greene (Narragansett, Rhode Island)
Fort Greene is a United States Army Reserve installation in the Point Judith area of Narragansett, Rhode Island. During World War II this was a coastal defense fort, and together with Fort Church in Little Compton, it superseded all previous heavy gun defenses in the Harbor Defenses of Narragansett Bay. It is named for General Nathanael Greene of the Revolutionary War, who was born in Rhode Island. History Fort Greene was built as part of a general modernization of US coast defenses, begun in 1940 with the outbreak of war in Europe and the Fall of France. The goal was to replace all previous heavy weapons, most of which were over 35 years old, with long-range ex-Navy 16"/50 caliber Mark 2 guns. Lighter weapons would be replaced by 6-inch guns on high-angle shielded barbette carriages. Ammunition magazines and the 16-inch guns would be in casemated bunkers to protect against air attack. The fort was intended to protect the approaches to Narragansett Bay as part of the Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distinctive Unit Insignia (U
A distinctive unit insignia (DUI) is a metallic heraldic badge or device worn by soldiers in the United States Army. The DUI design is derived from the coat of arms authorized for a unit. DUIs may also be called "distinctive insignia" (DI) or, imprecisely, a "crest" or a "unit crest" by soldiers or collectors. The U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry is responsible for the design, development and authorization of all DUIs. History Pre-World War I Insignia Distinctive ornamentation of a design desired by the organization was authorized for wear on the Mess Jacket uniform by designated organizations (staff corps, departments, corps of artillery, and infantry and cavalry regiments) per War Department General Order 132 dated December 31, 1902. The distinctive ornamentation was described later as coats of arms, pins and devices. The authority continued until omitted in the Army uniform regulation dated December 26, 1911. Distinctive unit insignia War Department Circular 161 dated 29 Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort McHenry
Fort McHenry is a historical American coastal pentagonal bastion fort on Locust Point, now a neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland. It is best known for its role in the War of 1812, when it successfully defended Baltimore Harbor from an attack by the British navy from the Chesapeake Bay on September 13–14, 1814. It was first built in 1798 and was used continuously by the U.S. armed forces through World War I and by the Coast Guard in World War II. It was designated a national park in 1925, and in 1939 was redesignated a " National Monument and Historic Shrine". During the War of 1812 an American storm flag, , was flown over Fort McHenry during the bombardment. It was replaced early on the morning of September 14, 1814, with a larger American garrison flag, . The larger flag signaled American victory over the British in the Battle of Baltimore. The sight of the ensign inspired Francis Scott Key to write the poem " Defence of Fort M'Henry" that was later set to the tune "To An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coast Defenses Of Narragansett Bay
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in natural ecosystems, often home to a wide range of biodiversity. On land, they harbor important ecosystems such as freshwater or estuarine wetlands, which are important for bird populations and other terrestrial animals. In wave-protected areas they harbor saltmarshes, mangroves or seagrasses, all of which can provide nursery habitat for finfish, shellfish, and other aquatic species. Rocky shores are usually found along exposed coasts and provide habitat for a wide range of sessile animals (e.g. mussels, starfish, barnacles) and various kinds of seaweeds. Along tropical coasts with clear, nutrient-poor water, coral reefs can often be found between depths of . According to a United Nations atlas, 44% of all people live within 5 km (3.3mi) of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Air Defense Artillery Regiment
The 2nd Air Defense Artillery Regiment is an air defense artillery regiment of the United States Army, first formed in 1821 as a field artillery unit. Battery A-2nd ADAR THAAD (Battery A, 2nd Air Defense Artillery Regiment, Terminal High Altitude Area Defense)A-2 THAAD successfully intercepts missile target ''Fort Bliss Bugle'' (20 July 2017) accessdate=2017-07-20 of the 11th Air Defense Artillery (ADA) Brigade successfully intercepted an Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile which was launched near Hawaii on 11 July 2017. The soldiers used the procedures of an act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild Air Force Base
Fairchild Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force base, located in the northwest United States in eastern Washington, approximately southwest of Spokane. The host unit at Fairchild is the 92nd Air Refueling Wing (92 ARW) assigned to the Air Mobility Command's Eighteenth Air Force. The 92 ARW is responsible for providing air refueling, as well as passenger and cargo airlift and aero-medical evacuation missions supporting U.S. and coalition conventional operations as well as U.S. Strategic Command strategic deterrence missions. Fairchild AFB was established in 1942 as the Spokane Army Air Depot. and is named in honor of General Muir S. Fairchild a World War I aviator from the state, he was the Vice Chief of Staff of the Air Force at the time of his death. During the Cold War, Fairchild was a Strategic Air Command (SAC) base for 45 years (1947–1992), with bombers and tankers, as well as missiles for a brief period (1960–1965). , the 92d Air Refueling Wing wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nike Missile
The United States Army's Nike Ajax was the world's first operational guided surface-to-air missile (SAM), entering service in 1954. Nike Ajax was designed to attack conventional bomber aircraft flying at high subsonic speeds and altitudes above . Nike was initially deployed in the US to provide defense against Soviet bomber attacks, and was later deployed overseas to protect US bases, as well as being sold to various allied forces. Some examples remained in use until the 1970s. Originally known simply as Nike, it gained the Ajax as part of a 1956 renaming effort that resulted from the introduction of Hercules. It was initially given the identifier SAM-A-7 (Surface-to-air, Army, design 7) as part of an early tri-service identification system, but later changed to MIM-3 (Mobile Interceptor Missile, design 3) in 1962.Nike was initially designated SAM-G-7, and later changed to SAM-A-7. Originally the Air Force used A while the Army used G, but the Air Force abandoned the 1947 tri-se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th Air Defense Artillery Regiment
The 5th Air Defense Artillery Regiment is an Air Defense Artillery regiment of the United States Army, first formed in 1861 in the Regular Army as the 5th Regiment of Artillery. Lineage On 4 May 1861, in conformity with the proclamation of the President, a new regiment of 12 batteries was added to the artillery arm of service and became known as the Fifth of the series. Congress confirmed this act of the President, 12 July (approved 29 July) of the same year, but all appointments dated from 14 May. The regiment was constituted on 18 June 1861 and organized on 4 July at Camp Greble, Pennsylvania, where the regiment initially assembled and trained. Differing in organization from the older regiments, the new one comprised only field batteries, being in this regard the first entire regiment so equipped in the Regular Army. But it must not be inferred that the Fifth was designated by law as a light artillery regiment. "Nowhere in the act of 29 July do the words 'field or light artill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Army Air & Missile Defense Command
The 10th Army Air and Missile Defense Command (10th AAMDC) is a theater level Army air and missile defense organization and directly subordinated to United States Army Europe. On order, the 10th AAMDC deploys worldwide to conduct joint and combined/coalition air missile defense ops for US European Command. The 10th AAMDC serves as the United States Army in Europe's executive agent for all theater air and missile defense ops and air missile defense force management. Lineage and history The command's lineage dates from the 10th Coast Artillery (Harbor Defense), Fort Adams, Rhode Island. The flashes symbolize the speed and efficiency of the unit while "X" suggests the numerical designation of the unit. The distinctive unit insignia was originally approved for the 10th Artillery Group on 10 November 1969. It was amended to correct the description on 1 December 1969. It was redesignated for the 10th Air Defense Artillery Group on 5 April 1972. It was redesignated for the 10th Ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camp Forrest
Camp Forrest, located in a wooded area east of the city of Tullahoma, Tennessee, was one of the U.S. Army's largest training bases during World War II. It was an active army post between 1941 and 1946. History The camp, named after Civil War cavalry Confederate General Nathan Bedford Forrest, was originally named Camp Peay. Camp Peay was named after the Tennessee Governor Austin Peay and built near Tullahoma as a National Guard Camp in 1926. Camp Peay covered . Camp Forrest covered located just beyond the old Camp Peay. The camp was a training area for infantry, artillery, engineer, signal organizations, and cooks. It also served as a hospital center and temporary encampment area for troops during maneuvers. Major General George Patton brought his 2nd Armored Division from Fort Benning, Georgia for maneuvers. William Northern Field, an air training base, was an addition used as a training site for crews of four-engined B-24 bombers of the Army Air Forces. Incoming troops had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
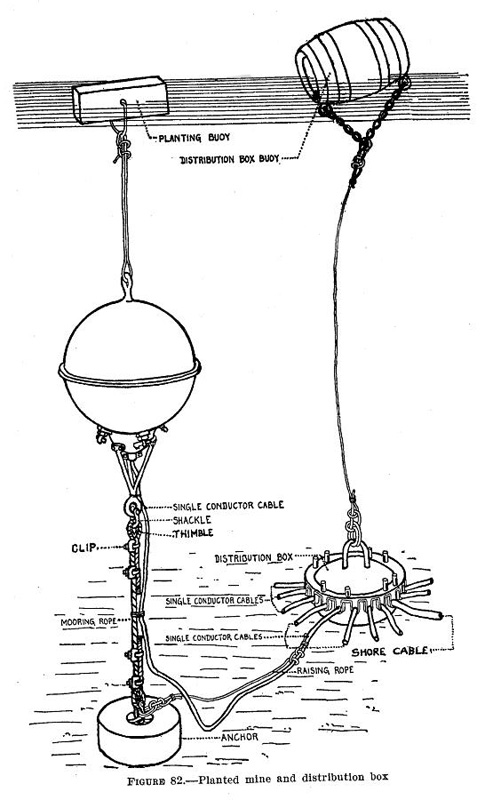
Submarine Mines In United States Harbor Defense
The modern era of defending American harbors with controlled mines or submarine mines (originally referred to as "torpedoes") began in the post-Civil War period, and was a major part of US harbor defenses from circa 1900 to 1947. Brief history In 1866, the United States Army Corps of Engineers established the Engineer School of Application at Willets Point, New York. The first commander of this school, Major Henry Larcom Abbot, was almost single-handedly responsible for designing and supervising the program of research and development that defined the strategy and tactics for the mine defense of American harbors. Abbot experimented with underwater explosives, fuzes, cabling, and electrical equipment for over a decade before publishing the first manuals on the use of mines in coast defense in 1876–77. At least one experimental controlled minefield was emplaced at this time, at Fort Mifflin in Pennsylvania. However, funding of the fortification program of the 1870s was cancell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |