|
103rd Regiment Of Foot (Royal Bombay Fusiliers)
The 103rd Regiment of Foot (Royal Bombay Fusiliers) was a regiment raised in 1662. It transferred to the command of the Honourable East India Company in 1668 and to the command of the British Army in 1862. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 102nd Regiment of Foot (Royal Madras Fusiliers) to form the Royal Dublin Fusiliers in 1881. History Formation The regiment was originally raised in England as independent companies of European soldiers to garrison Bombay in February 1662. It embarked for India later that year and was transferred to the Honourable East India Company as The Bombay Regiment in March 1668. In 1688 it was renamed The Bombay (European) Regiment – "European" indicating it was composed of white soldiers, not Indian sepoys. The regiment saw action at the Battle of Plassey in June 1757 during the Seven Years' War. It also fought at the Battle of Buxar in October 1764 during the Oude Campaign. It next saw action at the siege of Seringapatam in Febr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The British East India Company (1801)
The flag of the East India Company was used to represent the East India Company, which was chartered in England in 1600. The flag was altered as the nation changed from England to Great Britain to the United Kingdom. It was initially a red and white striped ensign with the flag of England in the canton. The flag displayed in the canton was later replaced by the flag of Great Britain and then the flag of the United Kingdom, as the nation developed. Early years Upon receiving a Royal Charter to trade in the Indian Ocean from Queen Elizabeth I in 1600, the English East India Company adopted a flag of red and white stripes (varying from nine to thirteen stripes in total), with the flag of England in the canton. It was reported that the number of stripes was chosen because many of the East India Company's shareholders were Freemasons, and the number thirteen is considered powerful in Freemasonry. However, different reports gave varying initial numbers of stripes. The flag caused p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Sir William Wyllie
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry. In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The term ''general'' is used in two ways: as the generic title for all grades of general officer and as a specific rank. It originates in the 16th century, as a shortening of ''captain general'', which rank was taken from Middle French ''capitaine général''. The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. Today, the title of ''general'' is known in some countries as a four-star rank. However, different countries use different systems of stars or other insignia for senior ranks. It has a NATO rank scal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
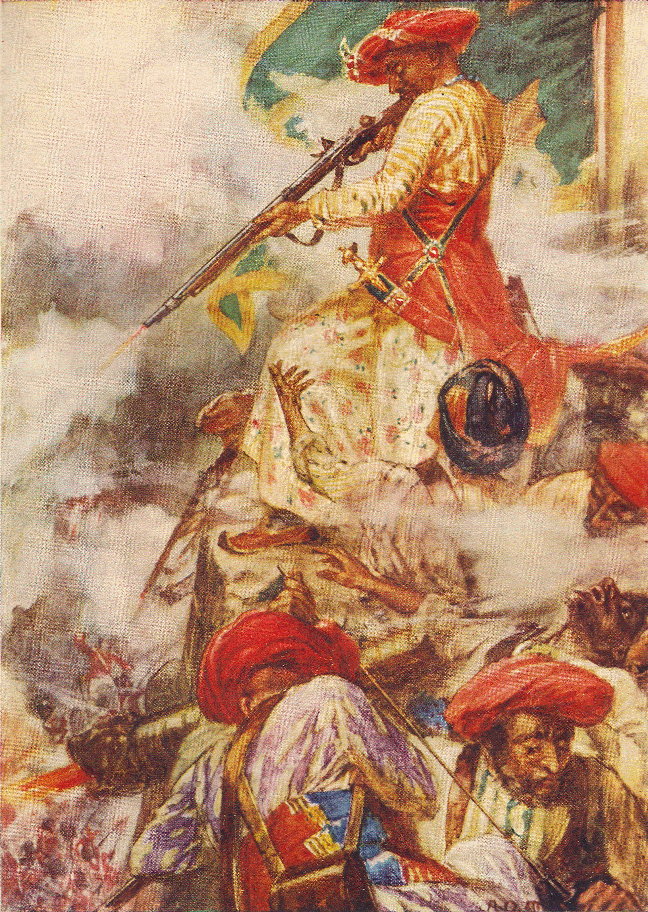
Beni Boo Alli (battle Honour)
The Bani Bu Ali expedition (1820–21) was a punitive campaign launched by the Sultan of Muscat and the East India Company against an Omani tribe known as the Bani Bu Ali in southeastern Arabia. It consisted of two expeditions. The first was the only land campaign Said bin Sultan conducted in Arabia during his long reign. It included a small allied British force and was defeated. The second, led by a more substantial British component, resulted in a decisive victory over the Bani Bu Ali. Company units engaged in the expedition received the "Beni Boo Alli" battle honour. Background The Bani Bu Ali tribe occupied the fortified village of Belad Bani Bu Ali (Place of the Sons of Ali) in Oman, in the hinterland of the Sultanate of Muscat, whose suzerainty the tribe nominally recognized. They did not, however, respect the good relations of sultan with the Company and engaged in piracy in the Arabian Sea.A. W. H. Lees, "A Forgotten Battle: Belad Beni Bu Ali, 1821", ''Journal of the So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of the Persian Gulf. Oman shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen, while sharing maritime borders with Iran and Pakistan. The coast is formed by the Arabian Sea on the southeast, and the Gulf of Oman on the northeast. The Madha and Musandam exclaves are surrounded by the United Arab Emirates on their land borders, with the Strait of Hormuz (which it shares with Iran) and the Gulf of Oman forming Musandam's coastal boundaries. Muscat is the nation's capital and largest city. From the 17th century, the Omani Sultanate was an empire, vying with the Portuguese and British empires for influence in the Persian Gulf and Indian Ocean. At its peak in the 19th century, Omani influence and control extended ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. At , the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world. Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula includes Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Yemen, as well as the southern portions of Iraq and Jordan. The largest of these is Saudi Arabia. In the classical era, the southern portions of modern-day Syria, Jordan, and the Sinai Peninsula were also considered parts of Arabia (see Arabia Petraea). The Arabian Peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and southwest, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the northeast, the Levant and Mesopotamia to the north and the Arabian S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Khadki
The Battle of Khadki, also known as or The Battle of Ganeshkhind, took place at modern day Khadki, India on 5 November 1817 between the forces of the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire under the leadership of Appasaheb Bhonsle. The Company forces achieved a decisive victory, and Khadki later became a military cantonment under the British rule. Prelude Maratha Empire in decline The Second Anglo-Maratha War, proved disastrous for the Maratha Empire/Confederacy. Due to a titular de-jure Chhatrapati and Peshwas Maratha Sardars took advantage of the reduced strength and command of Emperor over Maharashtra and the Maratha Empire started to decline. The Confederacy was in very high debts (taken for battles and governance) and were not receiving any income from taxes (all Sardars were keeping the all taxes to themselves instead of sending a part of it to the central authority). Mahadji Scindia did restore the Maratha authority in Northern India with the help of his cav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Seringapatam (1799)
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. The art of conducting and resisting sieges is called siege warfare, siegecraft, or poliorcetics. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block the provision of supplies and the reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as " investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, artillery bombardment, mining (also known as sapping), or the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Seedaseer
The Battle of Seedaseer was a battle of the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War on 6 March 1799 at Seedaseer (near present-day Siddapura, Karnataka), a hill and pass on the border of the Coorg and Mysore country seven miles from Piriyapatna and with a view almost as far as Seringapatam. Battle Lieutenant-General James Stuart and the Bombay Army of 6,500 under his command advanced from Cannanore, aiming to cross the Western Ghats and converge at Seringapatam with the larger Madras Army advancing from the east. He then took up a defensive position on the Anglo-Mysore frontier to await further orders from General Harris, placing his right brigade in an advanced position at Seedaseer on 2 March so as to better receive Harris's orders. This was under Lieutenant-Colonel Montressor and was made up of what are now the 1st and 2nd Maratha Light Infantry battalions and the now-defunct 1st Bombay Pioneers. He kept his other 2 brigades, the main body of his force, at Siddapura and Ahmootenaar 8 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Seringapatam (1792)
The 1792 Siege of Seringapatam was a battle and siege of the Mysorean capital city of Seringapatam (Srirangapatna) at the end of the Third Anglo-Mysore War. An army led by Charles, Earl Cornwallis, consisting of British East India Company and British Army forces, along with allied forces from the Maratha Empire and the Nizam of Hyderabad, arrived at Seringapatam on 5 February 1792, and after less than three weeks of battle and siege, forced Tipu Sultan to capitulate. With his agreement to the Treaty of Seringapatam on 18 March 1792, the war came to an end. Background The prospects for Tipu Sultan, the Muslim ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore, had declined significantly during the 1791 campaign season of the Third Anglo-Mysore War. Although he had been able to reverse some advances made by forces of the British East India Company forces under General William Medows in 1790, he had lost ground on all fronts in 1791, and only a slash-and-burn policy to deprive his opponents of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Buxar
The Battle of Buxar was fought between 22 and 23 October 1764, between the forces under the command of the British East India Company, led by Hector Munro, and the combined armies of Mir Qasim, Nawab of Bengal till 1764; the Nawab of Awadh, Shuja-ud-Daula; and the Mughal Emperor, Shah Alam II. The battle was fought at Buxar, a "strong fortified town" within the territory of Bihar, located on the banks of the Ganga river about west of Patna; it was a challenging victory for the British East India Company. The war was brought to an end by the Treaty of Allahabad in 1765. Battle The British army engaged in the fighting numbered 17,072 comprising 1,859 British regulars, 5,297 Indian sepoys and 9,189 Indian cavalry. The alliance army's numbers were estimated to be over 40,000. According to other sources, the combined army of the Mughals, Awadh and Mir Qasim consisting of 10 ,000 men was defeated by a British army comprising 10,000 men. The Nawabs had gained their military p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey was a decisive victory of the British East India Company over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies on 23 June 1757, under the leadership of Robert Clive. The victory was made possible by the defection of Mir Jafar, who was Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah's commander in chief. The battle helped the British East India Company take control of Bengal. Over the next hundred years, they seized control of most of the rest of the Indian subcontinent, including Burma. The battle took place at Palashi (Anglicised version: ''Plassey'') on the banks of the Hooghly River, about north of Calcutta (now Kolkata) and south of Murshidabad in West Bengal, then capital of Bengal Subah (now in Nadia district in West Bengal). The belligerents were the Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah, the last independent Nawab of Bengal , and the British East India Company. He succeeded Alivardi Khan (his maternal grandfather). Siraj-ud-Daulah had become the Nawab of Bengal the year before, and he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepoy
''Sepoy'' () was the Persian-derived designation originally given to a professional Indian infantryman, traditionally armed with a musket, in the armies of the Mughal Empire. In the 18th century, the French East India Company and its other European counterparts employed locally recruited soldiers within India, mainly consisting of infantry designated as "sepoys". The largest sepoy force, trained along European lines, served the British East India Company The term "sepoy" continues in use in the modern Indian, Pakistan and Nepalese armies, where it denotes the rank of private. Etymology In Persian (Aspa) means horse and Ispahai is also the word for cavalrymen. The term ''sepoy'' is derived from the Persian word () meaning the traditional "infantry soldier" in the Mughal Empire. In the Ottoman Empire the term was used to refer to cavalrymen. History The sepoys of the Mughal Empire were infantrymen usually armed with a musket and a talwar, although they so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)