|
100,000 Year Problem
The 100,000-year problem ("100 ky problem", "100 ka problem") of the Milankovitch theory of orbital forcing refers to a discrepancy between the reconstructed geologic temperature record and the reconstructed amount of incoming solar radiation, or insolation over the past 800,000 years. Due to variations in the Earth's orbit, the amount of insolation varies with periods of around 21,000, 40,000, 100,000, and 400,000 years. Variations in the amount of incident solar energy drive changes in the climate of the Earth, and are recognised as a key factor in the timing of initiation and termination of glaciations. While there is a Milankovitch cycle in the range of 100,000 years, related to Earth's orbital eccentricity, its contribution to variation in insolation is much smaller than those of precession and obliquity. The 100,000-year-problem refers to the lack of an obvious explanation for the periodicity of ice ages at roughly 100,000 years for the past million years, but n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope Fractionation
Isotope fractionation describes fractionation processes that affect the relative abundance of isotopes, phenomena which are taken advantage of in isotope geochemistry and other fields. Normally, the focus is on stable isotopes of the same element. Isotopic fractionation can be measured by isotope analysis, using isotope-ratio mass spectrometry or cavity ring-down spectroscopy to measure ratios of isotopes, an important tool to understand geochemical and biological systems. For example, biochemical processes cause changes in ratios of stable carbon isotopes incorporated into biomass. Definition Stable isotopes partitioning between two substances ''A'' and ''B'' can be expressed by the use of the isotopic fractionation factor (alpha): where ''R'' is the ratio of the heavy to light isotope (e.g., 2H/1H or 18O/16O). Values for alpha tend to be very close to 1. McGlynn, Shawn E.; "Biological Isotope Fractionation and Earth History: From Enzymes to Cells to Ecosystems" pp 59-79 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium-3
Helium-3 (3He see also helion) is a light, stable isotope of helium with two protons and one neutron (the most common isotope, helium-4, having two protons and two neutrons in contrast). Other than protium (ordinary hydrogen), helium-3 is the only stable isotope of any element with more protons than neutrons. Helium-3 was discovered in 1939. Helium-3 occurs as a primordial nuclide, escaping from Earth's crust into its atmosphere and into outer space over millions of years. Helium-3 is also thought to be a natural nucleogenic and cosmogenic nuclide, one produced when lithium is bombarded by natural neutrons, which can be released by spontaneous fission and by nuclear reactions with cosmic rays. Some of the helium-3 found in the terrestrial atmosphere is also an artifact of atmospheric and underwater nuclear weapons testing. Much speculation has been made over the possibility of helium-3 as a future energy source. Unlike most nuclear fusion reactions, the fusion of helium-3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Precession
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar energy is rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
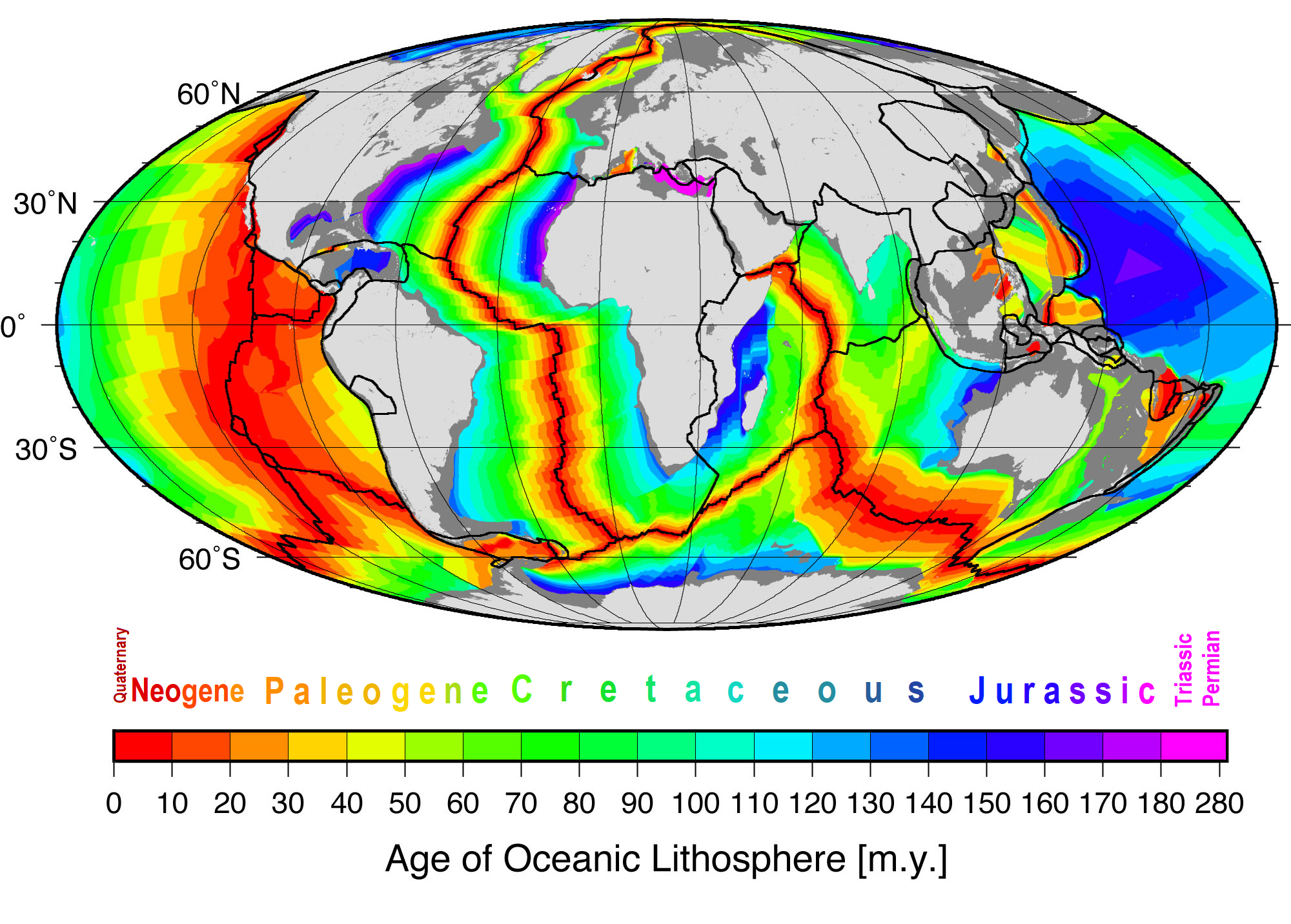
Sea Floor Spreading
Seafloor spreading or Seafloor spread is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. History of study Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener and Alexander du Toit of continental drift postulated that continents in motion "plowed" through the fixed and immovable seafloor. The idea that the seafloor itself moves and also carries the continents with it as it spreads from a central rift axis was proposed by Harold Hammond Hess from Princeton University and Robert Dietz of the U.S. Naval Electronics Laboratory in San Diego in the 1960s. The phenomenon is known today as plate tectonics. In locations where two plates move apart, at mid-ocean ridges, new seafloor is continually formed during seafloor spreading. Significance Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics. When oceanic plates diverge, tensional stress causes fractures to occur in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Drift
Continental drift is the hypothesis that the Earth's continents have moved over geologic time relative to each other, thus appearing to have "drifted" across the ocean bed. The idea of continental drift has been subsumed into the science of plate tectonics, which studies the movement of the continents as they ride on plates of the Earth's lithosphere. The speculation that continents might have 'drifted' was first put forward by Abraham Ortelius in 1596. A pioneer of the modern view of mobilism was the Austrian geologist Otto Ampferer.Helmut W. Flügel: Die virtuelle Welt des Otto Ampferer und die Realität seiner Zeit'. In: Geo. Alp., Vol. 1, 2004. The concept was independently and more fully developed by Alfred Wegener in 1912, but the hypothesis was rejected by many for lack of any motive mechanism. The English geologist Arthur Holmes later proposed mantle convection for that mechanism. History Early history Abraham Ortelius , Theodor Christoph Lilienthal (1756), A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillating force is applied at a resonant frequency of a dynamic system, the system will oscillate at a higher amplitude than when the same force is applied at other, non-resonant frequencies. Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are also known as resonant frequencies or resonance frequencies of the system. Small periodic forces that are near a resonant frequency of the system have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations in the system due to the storage of vibrational energy. Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, orbital resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron spin resonance (ESR) and reso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Obliquity Range
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar energy is rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deglaciation
Deglaciation is the transition from full glacial conditions during ice ages, to warm interglacials, characterized by global warming and sea level rise due to change in continental ice volume. Thus, it refers to the retreat of a glacier, an ice sheet or frozen surface layer, and the resulting exposure of the Earth's surface. The decline of the cryosphere due to ablation can occur on any scale from global to localized to a particular glacier. After the Last Glacial Maximum (ca. 21,000 years ago), the last deglaciation begun, which lasted until the early Holocene. Around much of Earth, deglaciation during the last 100 years has been accelerating as a result of climate change, partly brought on by anthropogenic changes to greenhouse gases. The previous deglaciation took place from approximately 22 ka until 11.5 ka. This occurred when there was an annual mean atmospheric temperature on the earth that increased by roughly 5 °C, which was also accompanied by regional hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Shackleton
Sir Nicholas John Shackleton (23 June 1937 – 24 January 2006) was an English geologist and paleoclimatologist who specialised in the Quaternary Period. He was the son of the distinguished field geologist Robert Millner Shackleton and great-nephew of the explorer Ernest Shackleton. Education and employment Educated at Cranbrook School, Kent (thanks to the generosity of a person he called his "fairy godmother" as she paid his school fees) Shackleton went on to read natural sciences at Clare College, Cambridge. He graduated with the Bachelor of Arts degree in 1961, promoted in 1964 to Master of Arts. In 1967 Cambridge awarded him a PhD degree, for a thesis entitled "The Measurement of Paleotemperatures in the Quaternary Era". Apart from periods abroad as Visiting Professor or Research Associate, Shackleton's entire scientific career was spent at Cambridge. He became Ad hominem Professor in 1991, in the Department of Earth Sciences, working in the Godwin Institute for Quater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramanifera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a "test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and Textularia in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthic), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA. Foraminifera typically produce a test, or shell, which can have either one or multiple chambers, some becoming quite elaborate in st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_0.002_K_region.png)