|
1998 In Science
The year 1998 in science and technology involved many events, some of which are included below. Astronomy and space exploration * January–September – Cosmologists from the Supernova Cosmology Project led by Saul Perlmutter and the High-z Supernova Search Team led by Adam Riess and Brian Schmidt publish evidence that the expansion rate of the universe is increasing. * January 6 – The Lunar Prospector spacecraft is launched into orbit around the Moon and later finds evidence for frozen water on the Moon's surface. * February 26 – Total solar eclipse * March 2 – Data sent from the Galileo space probe indicates that Jupiter's moon Europa has a liquid ocean under a thick crust of ice. * March 5 – NASA announces that the Clementine probe orbiting the Moon has found enough water in polar craters to support a human colony and rocket-fuelling station. * March 13 – Penumbral lunar eclipse * July 5 – Japan launches a probe to Mars, and thus joins the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmologist
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in Latin by German philosopher Christian Wolff, in ''Cosmologia Generalis''. Religious or mythological cosmology is a body of beliefs based on mythological, religious, and esoteric literature and traditions of creation myths and eschatology. In the science of astronomy it is concerned with the study of the chronology of the universe. Physical cosmology is the study of the observable universe's origin, its large-scale structures and dynamics, and the ultimate fate of the universe, including the laws of science that govern these areas. It is investigated by scientists, such as astronomers and physicists, as well as philosophers, such as metaphysicians, philosophers of physics, and philosophers of space and time. Because of this shared scope with philosophy, theori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March 1998 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Friday, March 13, 1998, the first of three lunar eclipses in 1998. Visibility Related eclipses Eclipses of 1998 * A total solar eclipse on February 26. * A penumbral lunar eclipse on March 13. * A penumbral lunar eclipse on August 8. * An annular solar eclipse on August 22. * A penumbral lunar eclipse on September 6. Lunar year series This is the last of four lunar year eclipses at the ascending node of the moon's orbit. Half-Saros cycle A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, ''The half-saros'' This lunar eclipse is related to two partial solar eclipses of Solar Saros 149. Tzolkinex * Preceded: Lunar eclipse of January 30, 1991 * Followed: Lunar eclipse of April 24, 2005 See also *List of lunar eclipses *List of 20th-century lunar eclipses A total of 229 lunar eclipses took place in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIH Virus
CIH, also known as Chernobyl or Spacefiller, is a Microsoft Windows 9x computer virus that first emerged in 1998. Its payload is highly destructive to vulnerable systems, overwriting critical information on infected system drives and, in some cases, destroying the system BIOS. Chen Ing-hau (陳盈豪, pinyin: ''Chén Yíngháo''), a student at Tatung University in Taiwan, created the virus.ithome.com.tw 從CIH「重裝駭客」變身「除錯超人」. 2006-08-25. It was believed to have infected sixty million computers internationally, resulting in an estimated US$1 billion in commercial damages. Chen claimed to have written the virus as a challenge against bold claims of antiviral efficiency by antivirus software developers.parenting.com.tw從駭電腦到愛旅行─昔日網路小子陳盈豪 Chen stated that after classmates at Tatung University spread the virus, he apologized to the school and made an antivirus program available for public download. Weng Shi-hao (翁世豪 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro Paranal
{{Antofagasta-geo-stub ...
Cerro Paranal is a mountain in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile and is the home of the Paranal Observatory. Prior to the construction of the observatory, the summit was a horizontal control point with an elevation of ; now it is above sea level. It is the site of the Very Large Telescope and the VLT Survey Telescope. It is located south of Antofagasta and north of Taltal, as well as inland and west of highway B-710. Gallery Up high Cerro Paranal.jpg, Milky Way pictured above Cerro Paranal. Zodiacal Light Seen from Paranal.jpg, Zodiacal Light seen from Paranal. References External links Cerro Paranal Paranal Paranal Cerro Paranal is a mountain in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile and is the home of the Paranal Observatory. Prior to the construction of the observatory, the summit was a horizontal control point with an elevation of ; now it is above sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Southern Observatory
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, commonly referred to as the European Southern Observatory (ESO), is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental research organisation made up of 16 member states for ground-based astronomy. Created in 1962, ESO has provided astronomers with state-of-the-art research facilities and access to the southern sky. The organisation employs about 730 staff members and receives annual member state contributions of approximately €162 million. Its observatories are located in northern Chile. ESO has built and operated some of the largest and most technologically advanced telescopes. These include the 3.6 m New Technology Telescope, an early pioneer in the use of active optics, and the Very Large Telescope (VLT), which consists of four individual 8.2 m telescopes and four smaller auxiliary telescopes which can all work together or separately. The Atacama Large Millimeter Array observes the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
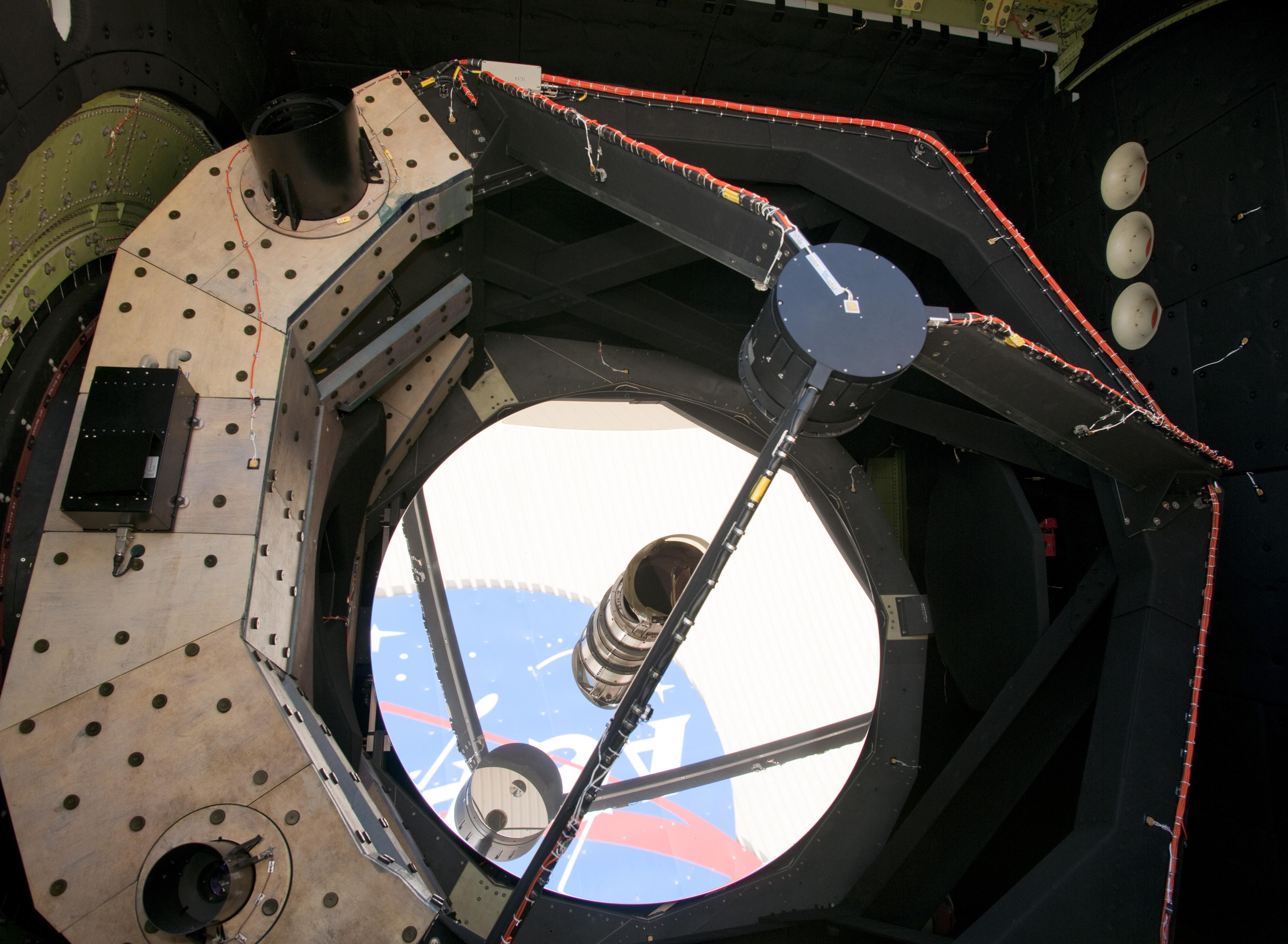
Very Large Telescope
The Very Large Telescope (VLT) is a telescope facility operated by the European Southern Observatory on Cerro Paranal in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile. It consists of four individual telescopes, each with a primary mirror 8.2 m across, which are generally used separately but can be used together to achieve very high angular resolution. The four separate optical telescopes are known as ''Antu'', ''Kueyen'', ''Melipal'', and ''Yepun'', which are all words for astronomical objects in the Mapuche language. The telescopes form an array complemented by four movable Auxiliary Telescopes (ATs) of 1.8 m aperture. The VLT operates at visible and infrared wavelengths. Each individual telescope can detect objects roughly four billion times fainter than can be detected with the naked eye, and when all the telescopes are combined, the facility can achieve an angular resolution of about 0.002 arcsecond. In single telescope mode of operation angular resolution is about 0.05 arcs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflecting Telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Many variant forms are in use and some employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a catoptric telescope. From the time of Newton to the 1800s, the mirror itself was made of metal usually speculum metal. This type included Newton's first designs and even the larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest Modular design, modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), European Space Agency, ESA (Europe), and Canadian Space Agency, CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which Scientific research on the International Space Station, scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The International Space Station programme, ISS programme evolved from the Space Station Freedom, Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zarya (ISS Module)
''Zarya'' (russian: Заря, , Dawn), also known as the Functional Cargo Block or FGB (from the russian: "Функционально-грузовой блок", , ''Funktsionalno-gruzovoy blok'' or ''ФГБ''), is the first module of the International Space Station to have been launched.NASA, International Space StationZarya(accessed 19 Apr. 2014) The FGB provided electrical power, storage, propulsion, and guidance to the ISS during the initial stage of assembly. With the launch and assembly in orbit of other modules with more specialized functionality, it is primarily used for storage, both inside the pressurized section and in the externally mounted fuel tanks. The ''Zarya'' is a descendant of the TKS spacecraft designed for the Russian ''Salyut'' program. The name ''Zarya'' ("Dawn") was given to the FGB because it signified the dawn of a new era of international cooperation in space. Although it was built by a Russian company, it is owned by the United States. Construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Glenn
John Herschel Glenn Jr. (July 18, 1921 – December 8, 2016) was an American Marine Corps aviator, engineer, astronaut, businessman, and politician. He was the third American in space, and the first American to orbit the Earth, circling it three times in 1962. Following his retirement from NASA, he served from 1974 to 1999 as a Democratic United States Senator from Ohio; in 1998, he flew into space again at age 77. Before joining NASA, Glenn was a distinguished fighter pilot in World War II, the Chinese Civil War and the Korean War. He shot down three MiG-15s, and was awarded six Distinguished Flying Crosses and eighteen Air Medals. In 1957, he made the first supersonic transcontinental flight across the United States. His on-board camera took the first continuous, panoramic photograph of the United States. He was one of the Mercury Seven, military test pilots selected in 1959 by NASA as the nation's first astronauts. On February 20, 1962, Glenn flew the '' Fri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Discovery
Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' ( Orbiter Vehicle Designation: OV-103) is one of the orbiters from NASA's Space Shuttle program and the third of five fully operational orbiters to be built. Its first mission, STS-41-D, flew from August 30 to September 5, 1984. Over 27 years of service it launched and landed 39 times, aggregating more spaceflights than any other spacecraft to date. The Space Shuttle launch vehicle has three main components: the Space Shuttle orbiter, a single-use central fuel tank, and two reusable solid rocket boosters. Nearly 25,000 heat-resistant tiles cover the orbiter to protect it from high temperatures on re-entry. ''Discovery'' became the third operational orbiter to enter service, preceded by ''Columbia'' and '' Challenger''. It embarked on its final mission, STS-133, on February 24, 2011, and touched down for the last time at Kennedy Space Center on March 9, having spent a cumulative total of nearly a full year in space. ''Discovery'' performed both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
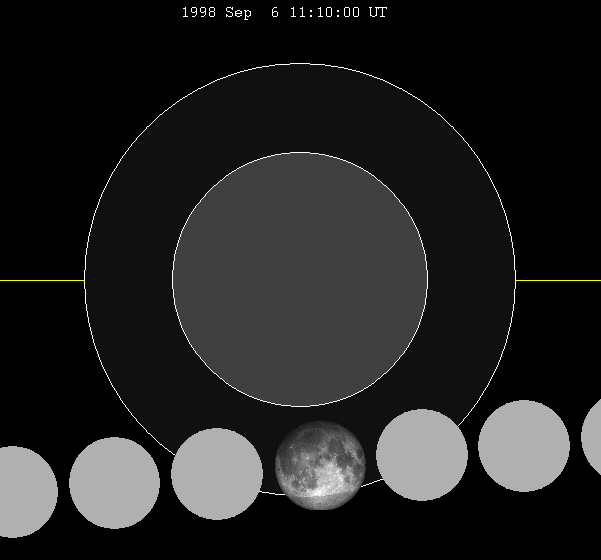
September 1998 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Sunday, September 6, 1998, the last of three lunar eclipses in 1998. Visibility Related eclipses Eclipses of 1998 * A total solar eclipse on February 26. * A penumbral lunar eclipse on March 13. * A penumbral lunar eclipse on August 8. * An annular solar eclipse on August 22. * A penumbral lunar eclipse on September 6. Lunar year series This is the last of four lunar year eclipses at the descending node of the moon's orbit. Half-Saros cycle A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, ''The half-saros'' This lunar eclipse is related to two partial solar eclipses of Solar Saros 154. See also *List of lunar eclipses *List of 20th-century lunar eclipses A total of 229 lunar eclipses took place in the 20th century: 83 penumbral, 65 partial and 81 total. See also: Lists of lunar eclipses, List of 19th-cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)