|
1979–80 South-West Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 1979–80 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season was an above-average cyclone season. The season officially ran from November 1, 1979, to April 30, 1980. Systems Tropical Cyclone Tony On 26 August, the BoM reported that a tropical low had developed on a shear line about to the northwest of Cocos Island. Over the next couple of days the depression gradually developed further before at 1800 UTC on 27 August, TCWC Perth estimated that it had become a tropical cyclone and named it Tony. During the next couple of days, the system moved towards the west-southwest before on 29 August it reached its peak intensity of and a peak pressure of as it approached the edge of TCWC Perth's area of responsibility. During the next day, Tony moved into the South West Indian Ocean and weakened gradually before it dissipated during 31 August. Neither the Mauritius or Reunion meteorological services monitored Tony as a tropical cyclone while it was active, while it was not included in the JTWC' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1977–78 South-West Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 1977–78 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season was an above average cyclone season. The season officially ran from November 1, 1977, to April 30, 1978. Systems Intense Tropical Cyclone Aurore Moderate Tropical Storm Babette Moderate Tropical Storm Sam–Celimene Tropical Depression Dulcinee Moderate Tropical Storm Esther Tropical Cyclone Fleur Cyclone Fleur passed just east of Mauritius on January 20, producing wind gusts of , which damaged crops. Heavy rainfall occurred on neighboring Réunion, reaching at Foc Foc. Moderate Tropical Storm Huberte The storm passed near Rodrigues. Moderate Tropical Storm Georgia Severe Tropical Storm Irena Moderate Tropical Storm Jacqueline Moderate Tropical Storm Kiki On March 7, Kiki reformed near Mauritius and latter passed just southeast of Réunion. Rainfall reached , which flooded coastal roads, damaged bridges, and killed two people. Tropical Depression Lucie Moderate Tropical Storm Maryl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Franc
The franc (, ; sign: F or Fr), also commonly distinguished as the (FF), was a currency of France. Between 1360 and 1641, it was the name of coins worth 1 livre tournois and it remained in common parlance as a term for this amount of money. It was reintroduced (in decimal form) in 1795. After two centuries of inflation, it was redenominated in 1960, with each (NF) being worth 100 old francs. The NF designation was continued for a few years before the currency returned to being simply the franc. Many French residents, though, continued to quote prices of especially expensive items in terms of the old franc (equivalent to the new centime), up to and even after the introduction of the euro (for coins and banknotes) in 2002. The French franc was a commonly held international reserve currency of reference in the 19th and 20th centuries. Between 1998 and 2002, the conversion of francs to euros was carried out at a rate of 6.55957 francs to 1 euro. History The French Franc tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South-West Indian Ocean Cyclone Seasons
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each separated by 90 degrees, and secondarily divided by four ordinal (intercardinal) directions—northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest—each located halfway between two cardinal directions. Some disciplines such as meteorology and navigation further divide the compass with additional azimuths. Within European tradition, a fully defined compass has 32 'points' (and any finer subdivisions are described in fractions of points). Compass points are valuable in that they allow a user to refer to a specific azimuth in a colloquial fashion, without having to compute or remember degrees. Designations The names of the compass point directions follow these rules: 8-wind compass rose * The four cardinal directions are north (N), east (E), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979–80 South-West Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 1979–80 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season was an above-average cyclone season. The season officially ran from November 1, 1979, to April 30, 1980. Systems Tropical Cyclone Tony On 26 August, the BoM reported that a tropical low had developed on a shear line about to the northwest of Cocos Island. Over the next couple of days the depression gradually developed further before at 1800 UTC on 27 August, TCWC Perth estimated that it had become a tropical cyclone and named it Tony. During the next couple of days, the system moved towards the west-southwest before on 29 August it reached its peak intensity of and a peak pressure of as it approached the edge of TCWC Perth's area of responsibility. During the next day, Tony moved into the South West Indian Ocean and weakened gradually before it dissipated during 31 August. Neither the Mauritius or Reunion meteorological services monitored Tony as a tropical cyclone while it was active, while it was not included in the JTWC' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1980 North Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 1980 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was part of the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD. __TOC__ Systems There were 14 depressions during the season. The first depression lasted from May 15–19, moving from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 North Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 1979 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was part of the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD. __TOC__ Systems Cyclone One (1B) The system formed on 6 May close to the coast of Sri Lanka. It moved towards northwest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1980 Pacific Typhoon Season
The 1980 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1980, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Tropical storms which formed in the entire west Pacific basin were assigned a name by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility are assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can often result in the same storm having two names. A total of 28 tropical depressions formed this year in the Western Pacific, of which 24 became tropical storms. Beginning in March, tropical cyclones formed in each subsequent month through December. Of the 28, 15 storms reached typhoon intensity, of which 2 reached super typhoon strength. Seven tropical cyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 Pacific Typhoon Season
The 1979 Pacific typhoon season featured the largest and most intense tropical cyclone recorded globally, Typhoon Tip. The season also experienced slightly above-average tropical cyclone activity. The season had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1979, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the international date line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 1979 Pacific hurricane season. Tropical storms formed in the entire west Pacific basin were assigned a name by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Tropical depressions in this basin have the "W" suffix added to their number. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1980 Pacific Hurricane Season
The 1980 Pacific hurricane season officially started May 15, 1980, in the eastern Pacific and June 1, 1980, in the central Pacific, lasting until November 30, 1980. These dates conventionally delimit each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern and central Pacific Ocean. This season was relatively uneventful; since no tropical cyclones made landfall, there were no reports of casualties or damage. Overall, the 1980 season was slightly below the long-term average, with 16 tropical cyclones forming. Of those, 15 were named, 7 reached hurricane intensity, and only 3 became major hurricanes by attaining category 3 status or higher on the Saffir–Simpson scale. All eastern Pacific systems this year formed in the eastern Pacific proper and two storms crossed into the central Pacific: Carmen from the west and Kay from the east. The season had an early start when Carmen crossed over the International Date Line in April. The strongest storm of this season is Hurricane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 Pacific Hurricane Season
The 1979 Pacific hurricane season was an inactive season, featuring 10 named storms, 6 hurricanes, and 4 major hurricanes. It featured zero tropical cyclones in the Central Pacific, the most recent occurrence on record as of 2021. An average year sees four to five tropical cyclones in that basin. Seasonal activity in 1979 remained within the confines of a traditional hurricane season, which begins on May 15 and ends on November 30 in the East Pacific basin. Those dates conventionally delimit the period during each year when most tropical cyclones occur. The season's first system, Andres, developed on May 31, while the year's final cyclone, Jimena, dissipated on November 18. In early June, Andres moved onshore Mexico as a minimal hurricane, while in late October, Ignacio struck the coastline as a tropical depression. Impacts from those storms were minimal, as were the effects of the preponderance of systems during the season. No casualties or damage were reporte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
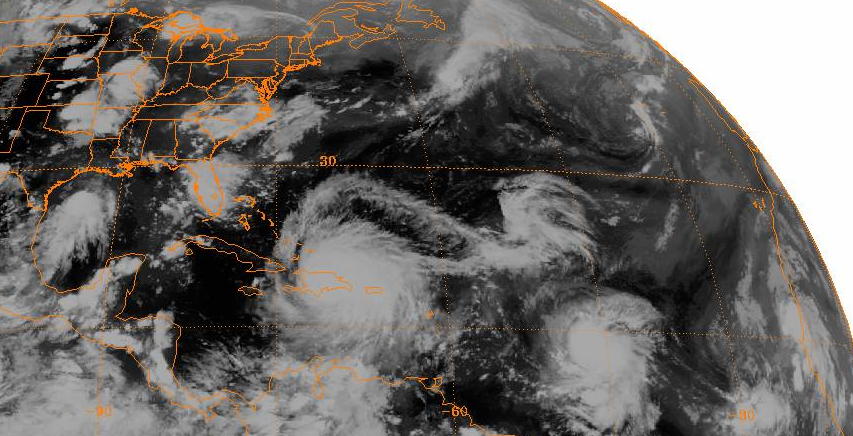
1980 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1980 Atlantic hurricane season featured nine hurricanes, the most since 1969. The season officially began on June 1, 1980, and lasted until November 30, 1980. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean. The season was fairly active, with sixteen tropical cyclones forming, eleven of which intensified into a tropical storm. It was the first time since the 1971 season that there were no active tropical cyclones in the Atlantic basin during the month of June. The season occurred during an ENSO-neutral phase, having neither an El Niño nor a La Niña. Three tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean in 1980 were notable. Hurricane Allen was the then-earliest Category 5 hurricane on record, reaching that intensity on August 5. The storm devastated portions of the Caribbean, Mexico, and the United States. Overall, Allen caused about $2.57 billion and at least 269 deaths. Tropical St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1979 Atlantic hurricane season was the first season to include both male and female names, as well as the common six-year rotating lists of tropical cyclone names. The season officially began on June 1, and lasted until November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. It was slightly below average, with nine systems reaching tropical storm intensity. The first system, an unnumbered tropical depression, developed north of Puerto Rico on June 9. Two days later, Tropical Depression One formed and produced severe flooding in Jamaica, with 40 deaths and about $27 million (1979 USD) in damage. Tropical Storm Ana caused minimal impact in the Lesser Antilles. Hurricane Bob spawned tornadoes and produced minor wind damage along the Gulf Coast of the United States, primarily in Louisiana, while the remnants caused flooding, especially in Indiana. Tropical Storm Claudette caused e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |