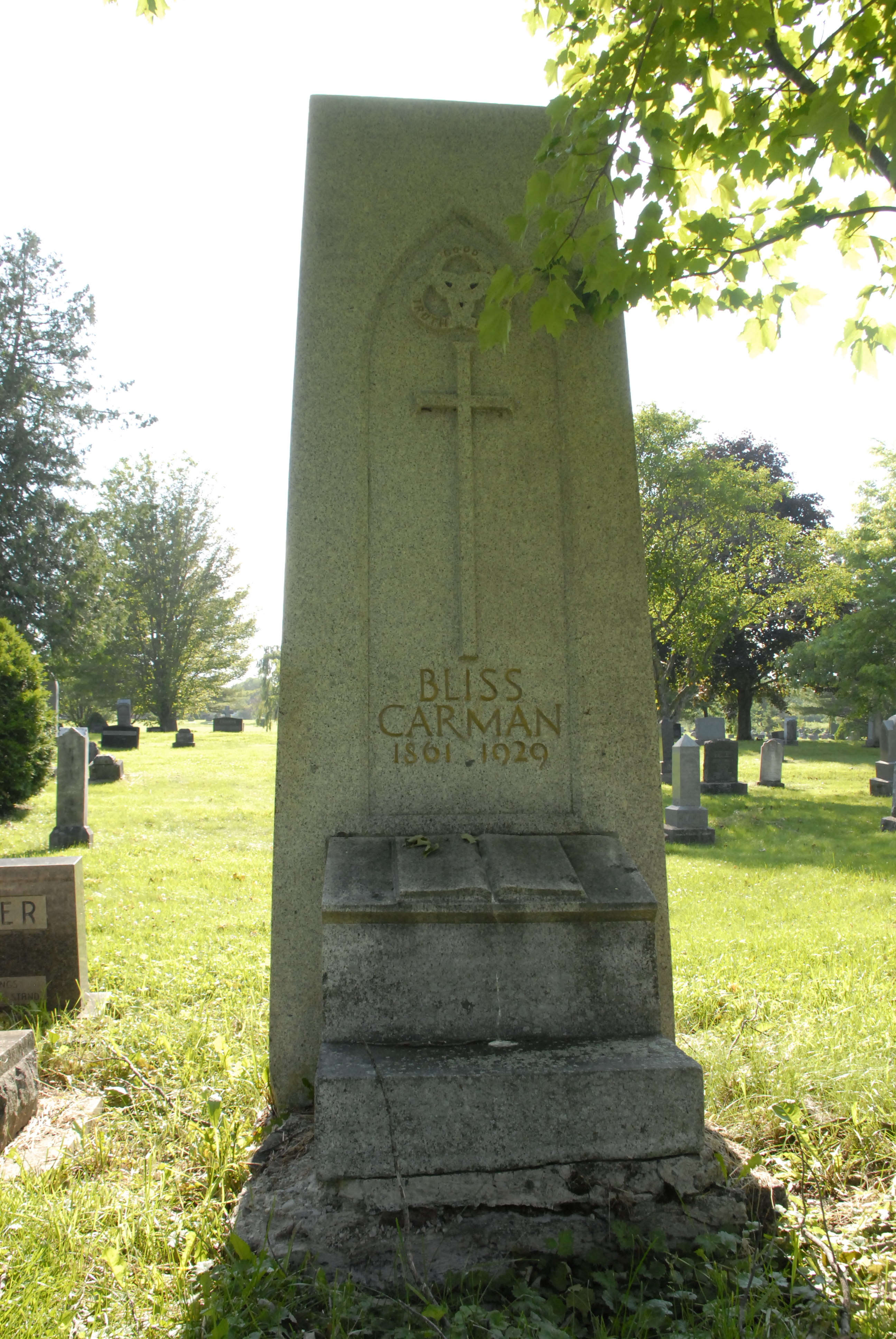|
1896 In Poetry
— closing lines of Rudyard Kipling's ''If—'', first published this year Nationality words link to articles with information on the nation's poetry or literature (for instance, Irish or France). Events * July 7 – Charles Thomas Wooldridge is hanged at Reading Gaol in England for uxoricide, inspiring fellow-prisoner C.3.3. Oscar Wilde's ''The Ballad of Reading Gaol'' (1897). * William Morris publishes the Kelmscott Press edition of Chaucer's works Works published in English Australia * John Le Gay Brereton: ** ''Perdita, A Sonnet Record'' ** ''The Song of Brotherhood and Other Verses'' * Edward Dyson, ''Rhymes from the Mines and Other Lines'' * Henry Lawson: ** ''In the Days When the World was Wide and Other Verses''"Lawson, Henry (1867 - 1922)" article, ''Australian Dictionary of Biography Online Edition'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work. Kipling's works of fiction include the ''Jungle Book'' duology ('' The Jungle Book'', 1894; '' The Second Jungle Book'', 1895), ''Kim'' (1901), the '' Just So Stories'' (1902) and many short stories, including "The Man Who Would Be King" (1888). His poems include " Mandalay" (1890), " Gunga Din" (1890), "The Gods of the Copybook Headings" (1919), " The White Man's Burden" (1899), and "If—" (1910). He is seen as an innovator in the art of the short story.Rutherford, Andrew (1987). General Preface to the Editions of Rudyard Kipling, in "Puck of Pook's Hill and Rewards and Fairies", by Rudyard Kipling. Oxford University Press. His children's books are classics; one critic noted "a versatile and luminous narrative gift".Rutherford, Andrew ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Lawson
Henry Archibald Hertzberg Lawson (17 June 1867 – 2 September 1922) was an Australian writer and bush poet. Along with his contemporary Banjo Paterson, Lawson is among the best-known Australian poets and fiction writers of the colonial period and is often called Australia's "greatest short story writer". A vocal nationalist and republican, Lawson regularly contributed to '' The Bulletin'', and many of his works helped popularise the Australian vernacular in fiction. He wrote prolifically into the 1890s, after which his output declined, in part due to struggles with alcoholism and mental illness. At times destitute, he spent periods in Darlinghurst Gaol and psychiatric institutions. After he died in 1922 following a cerebral haemorrhage, Lawson became the first Australian writer to be granted a state funeral. He was the son of the poet, publisher and feminist Louisa Lawson. Family and early life Henry Lawson was born 17 June 1867 in a town on the Grenfell goldfields of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Poetry
This article focuses on poetry from the United Kingdom written in the English language. The article does not cover poetry from other countries where the English language is spoken, including Republican Ireland after December 1922. The earliest surviving English poetry, written in Anglo-Saxon, the direct predecessor of modern English, may have been composed as early as the 7th century. The earliest English poetry The earliest known English poem is a hymn on the creation; Bede attributes this to Cædmon ( fl. 658–680), who was, according to legend, an illiterate herdsman who produced extemporaneous poetry at a monastery at Whitby. This is generally taken as marking the beginning of Anglo-Saxon poetry. Much of the poetry of the period is difficult to date, or even to arrange chronologically; for example, estimates for the date of the great epic ''Beowulf'' range from AD 608 right through to AD 1000, and there has never been anything even approaching a consensus. It is pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Joseph Sherman
Francis Joseph Sherman (February 3, 1871 – June 15, 1926) was a Canadian poet. He published a number of books of poetry during the last years of the nineteenth century, including ''Matins'' and ''In Memorabilia Mortis'' (a collection of sonnets in memory of William Morris). Life Sherman was born in Fredericton, New Brunswick, the son of Alice Maxwell Myshrall and Louis Walsh Sherman. He attended Fredericton Collegiate School, where he came under the influence of headmaster George R. Parkin, "an Oxonian with an enthusiasm for the poetry of Rossetti, Swinburne, and, notably, Morris,"Karen Herbert,'There Was One Thing He Could Not See' William Morris in the Writing of Archibald Lampman and Francis Sherman," ''Canadian Poetry: Studies/Documents/Reviews'' No. 37, UWO, Web, May 11, 2011. who had also taught Bliss Carman and Charles G.D. Roberts. For a short time, Carman was one of Sherman's teachers.Tammy Armstrong,Francis Joseph Sherman," New Brunswick Literary Encyclopedia, STU. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duncan Campbell Scott
Duncan Campbell Scott (August 2, 1862 – December 19, 1947) was a Canadian civil servant and poet and prose writer. With Charles G.D. Roberts, Bliss Carman, and Archibald Lampman, he is classed as one of Canada's Confederation Poets. A career civil servant, Scott served as deputy superintendent of the Department of Indian Affairs from 1913 to 1932. Life and legacy Scott was born in Ottawa, Ontario, the son of Rev. William Scott, a Methodist preacher, and Janet MacCallum. He was educated at Stanstead Wesleyan College. Early in life, he became an accomplished pianist. Scott wanted to be a doctor, but family finances were precarious, so in 1879 he joined the federal civil service. William Scott might not have money uthe had connections in high places. Among his acquaintances was the prime minister, Sir John A. Macdonald, who agreed to meet with Duncan. As chance would have it, when Duncan arrived for his interview, the prime minister had a memo on his desk from the Indian B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Sangster
Charles Sangster (July 16, 1822 – December 9, 1893) was a Canadian poet. He was the first poet to write poetry which was substantially about Canadian subjects. ''The Dictionary of Canadian Biography'' calls him "the best of the pre-confederation poets."Frank M. Tierney,Sangster, Charles" Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online. Web., October 15, 2010. Life Sangster was born at the Navy Yard on Point Frederick (now the site of Royal Military College of Canada), near Kingston, Ontario,John Garvin,Charles Sangster" ''Canadian Poets'' (Toronto: McClelland, Goodchild & Stewart, 1916), 9-18, UPenn.edu, Web, October 15, 2010. the son of Ann Ross and James Sangster. A twin sister died in infancy. His father, a "joiner" or shipbuilder who worked for the British Navy around the Great Lakes, died at Penetanguishene just before Charles turned 2. His mother raised Charles and his 4 siblings on her own. Sangster was an indifferent student, and showed little interest in the school curricul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles G
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was '' Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in ''Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as '' Carolus''. Some Germanic languages, for example Dutch and German, have retained the word in two separate senses. In the particular case of Dutch, ''Karel'' refers to the given name, whereas the noun ''kerel'' means "a bloke, fellow, man". Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as churl (< Old English ''ċeorl''), which developed its depr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Poetry
American poetry refers to the poetry of the United States. It arose first as efforts by American colonists to add their voices to English poetry in the 17th century, well before the constitutional unification of the Thirteen Colonies (although a strong oral tradition often likened to poetry already existed among Native American societies). Unsurprisingly, most of the early colonists' work relied on contemporary English models of poetic form, diction, and Theme (literary), theme. However, in the 19th century, a distinctive American Common parlance, idiom began to emerge. By the later part of that century, when Walt Whitman was winning an enthusiastic audience abroad, List of poets from the United States, poets from the United States had begun to take their place at the forefront of the English-language ''avant-garde''. Much of the American poetry published between 1910 and 1945 remains lost in the pages of small circulation political periodicals, particularly the ones on the far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Hovey
Richard Hovey (May 4, 1864 – February 24, 1900) was an American poet. Graduating from Dartmouth College in 1885, he is known in part for penning the school Alma Mater, '' Men of Dartmouth''. Biography Hovey was born in Normal, Illinois, the son of Major General Charles Edward Hovey and Harriet Spofford Hovey. He grew up in North Amherst, Massachusetts, and in Washington, D.C., before attending Dartmouth. His first volume of poems was privately published in 1880. He collaborated with Canadian poet Bliss Carman on three volumes of "tramp" verse: ''Songs from Vagabondia'' (1894), ''More Songs from Vagabondia'' (1896), and ''Last Songs from Vagabondia'' (1900), the last being published after Hovey's death. Hovey and Carman were members of the "Visionists" social circle along with F. Holland Day and Herbert Copeland, who published the "Vagabondia" series. Some twenty-nine poets have attempted to write sequels for Byron's ''Don Juan''. Hovey was one of them. Samuel Chew praised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bliss Carman
William Bliss Carman (April 15, 1861 – June 8, 1929) was a Canadian poet who lived most of his life in the United States, where he achieved international fame. He was acclaimed as Canada's poet laureate during his later years. In Canada, Carman is classed as one of the Confederation Poets, a group which also included Charles G.D. Roberts (his cousin), Archibald Lampman, and Duncan Campbell Scott. "Of the group, Carman had the surest lyric touch and achieved the widest international recognition. But unlike others, he never attempted to secure his income by novel writing, popular journalism, or non-literary employment. He remained a poet, supplementing his art with critical commentaries on literary ideas, philosophy, and aesthetics." Life William Bliss Carman was born on April 15, 1861 in Fredericton, New Brunswick. "Bliss" was his mother's maiden name. He was the great grandson of United Empire Loyalists who fled to Nova Scotia after the American Revolution, settling in New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Poetry
Canadian poetry is poetry of or typical of Canada. The term encompasses poetry written in Canada or by Canadian people in the official languages of English and French, and an increasingly prominent body of work in both other European and Indigenous languages. Although English Canadian poetry began to be written soon after European colonization began, many of English-speaking Canada’s first celebrated poets come from the Confederation period of the mid to late 19th century. In the 20th century, Anglo-Canadian poets embraced European and American poetic innovations, such as Modernism, Confessional poetry, Postmodernism, New Formalism, Concrete and Visual poetry, and Slam, but always turned to a uniquely Canadian perspective. The minority French Canadian poetry, primarily from Quebec, blossomed in the 19th century, moving through Modernism and Surrealism in the 20th century, to develop a unique voice filled with passion, politics and vibrant imagery. Montreal, with its exposure t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mulga Bill's Bicycle
"Mulga Bill's Bicycle" is a poem written in 1896 by Banjo Paterson. It was originally published on the 25th of July 1896 edition of the ''Sydney Mail'', and later appeared in the poet's second poetry collection ''Rio Grande's Last Race and Other Verses''. The poem is a ballad. Each line is a fourteener, having fourteen syllables and seven iambic feet. Synopsis It tells the tragic tale of Mulga Bill, a man whose pride in his riding skill causes him to purchase, ride and crash a bicycle. Although Mulga Bill claims expertise in riding all things his ineptitude and subsequent accident suggest that he may only know how to ride a horse. The poem was first published in ''The Sydney Mail'' on 25 July 1896 and was illustrated by Norman Hardy. It is amongst Paterson's most popular works. A 1973 reprinting of the poem illustrated by Kilmeny & Deborah Niland has been continuously in print since publication and won the 1973 ABPA Book Design Award and the 1974 Visual Arts Board Award. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)