|
1837 Great Plains Smallpox Epidemic
The 1837 Great Plains smallpox epidemic spanned 1836 through 1840, but reached its height after the spring of 1837 when an American Fur Company steamboat, the S.S. ''St. Peter'', carried infected people and supplies into the Missouri Valley.''Rationalizing Epidemics: Meanings and Uses of American Indian Mortality Since 1600''; David S. Jones; Harvard University Press; 2004; Pg. 76 More than 17,000 Indigenous people died along the Missouri River alone, with some bands becoming nearly extinct. Having witnessed the effects of the epidemic on the Mandan tribe, fur trader Francis Chardon wrote, "the small-pox had never been known in the civilized world, as it had been among the poor Mandans and other Indians. Only ''twenty-seven'' Mandans were left to tell the tale." The Commissioner of Indian Affairs in 1839 reported on the casualties: "No attempt has been made to count the victims, nor is it possible to reckon them in any of these tribes with accuracy; it is believed that if he numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) certified the global eradication of the disease in 1980, making it the only human disease to be eradicated. The initial symptoms of the disease included fever and vomiting. This was followed by formation of ulcers in the mouth and a skin rash. Over a number of days, the skin rash turned into the characteristic fluid-filled blisters with a dent in the center. The bumps then scabbed over and fell off, leaving scars. The disease was spread between people or via contaminated objects. Prevention was achieved mainly through the smallpox vaccine. Once the disease had developed, certain antiviral medication may have helped. The risk of death was about 30%, with higher rates among babies. Often, those who survived had extensive scarring of their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Vaccination Act Of 1832
The Indian Vaccination Act is a US federal law was passed by the US Congress in 1832. The purpose of the act was to vaccinate the American Indians against smallpox to prevent the spread of the disease. History The act was first passed on May 5, 1832. Lewis Cass, Secretary of War, designed the act. Members of Congress appropriated US$12,000 dollars (approximately $ in current money) to vaccinate them. By February 1, 1833, more than 17,000 Indians had been vaccinated. Congress allocated $12,000 for the entire program, to be administered by Indian agents and sub-agents. Some US army surgeons refused to participate due to the lack of funds, leaving agents themselves and others with no medical training to produce and administer vaccines.However, not everyone was included. As a result, a few years later, smallpox killed 90% of the Mandan Indians, who had been excluded from the act. It also excluded Hidatsas and Arikara Arikara (), also known as Sahnish, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1837 In The United States
Events from the year 1837 in the United States of America. Incumbents Federal Government * President: Andrew Jackson ( D-Tennessee) (until March 4), Martin Van Buren ( D- New York) (starting March 4) * Vice President: Martin Van Buren ( D- New York) (until March 4), Richard M. Johnson ( D-Kentucky) (starting March 4) * Chief Justice: Roger B. Taney (Maryland) * Speaker of the House of Representatives: James K. Polk ( D-Tennessee) * Congress: 24th (until March 4), 25th (starting March 4) Events * January 6 – DePauw University founded in Greencastle, Indiana. * January 26 – Michigan is admitted as the 26th U.S. state (see History of Michigan). * February 4 – Seminoles attack Fort Foster. * February 8 – Richard Johnson becomes the only Vice President of the United States chosen by the United States Senate. * February 15 – Knox College founded in Galesburg, Illinois. * February 16 - Lake County was organized by the Indiana General Assembly. * February 25 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1830s In The United States
Year 183 ( CLXXXIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Victorinus (or, less frequently, year 936 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 183 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * An assassination attempt on Emperor Commodus by members of the Senate fails. Births * January 26 – Lady Zhen, wife of the Cao Wei state Emperor Cao Pi (d. 221) * Hu Zong, Chinese general, official and poet of the Eastern Wu state (d. 242) * Liu Zan (Zhengming), Chinese general of the Eastern Wu state (d. 255) * Lu Xun Zhou Shuren (25 September 1881 – 19 October 1936), better known by his pen name Lu Xun (or Lu Sun; ; Wade–Giles: Lu Hsün), was a Chinese writer, essayist, poet, and literary cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Cheyenne Exodus
The Northern Cheyenne Exodus, also known as Dull Knife's Raid, the Cheyenne War, or the Cheyenne Campaign, was the attempt of the Northern Cheyenne to return to the north, after being placed on the Southern Cheyenne reservation in the Indian Territory, and the United States Army operations to stop them. The period lasted from 1878 to 1879. Background Following the Battle of the Little Bighorn attempts by the U.S. Army to subdue the Northern Cheyenne intensified. In 1877, after the Dull Knife Fight, when Crazy Horse surrendered at Fort Robinson a few Cheyenne chiefs and their people surrendered as well. The Cheyenne chiefs that surrendered at the fort were Dull Knife, Little Wolf, Standing Elk, and Wild Hog with nearly one thousand Cheyenne. On the other hand, Two Moon surrendered at Fort Keogh with three hundred Cheyenne in 1877. The Cheyenne wanted and expected to live on the reservation with the Sioux in accordance with an April 29, 1868 treaty of Fort Laramie of which both Dul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yavapai Wars
The Yavapai Wars, or the Tonto Wars, were a series of armed conflicts between the Yavapai and Tonto tribes against the United States in the Arizona Territory. The period began no later than 1861, with the arrival of American settlers on Yavapai and Tonto land. At the time, the Yavapai were considered a band of the Western Apache people due to their close relationship with tribes such as the Tonto and Pinal. The war culminated with the Yavapai's removal from the Camp Verde Reservation to San Carlos on February 27, 1875, an event now known as Exodus Day. Settler–Yavapai conflict With the Mohave people's power greatly diminished, Tolkepaya saw that they needed to make new alliances to protect their safety. In April 1863, Quashackama, a well-known Tolkepaya, met with Arizona Territory superintendent of Indian affairs Charles Poston, along with representatives of the Pimas, Mohaves, Maricopas and Chemehuevis, at Fort Yuma, to sign an agreement intended "to promote the commerce in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
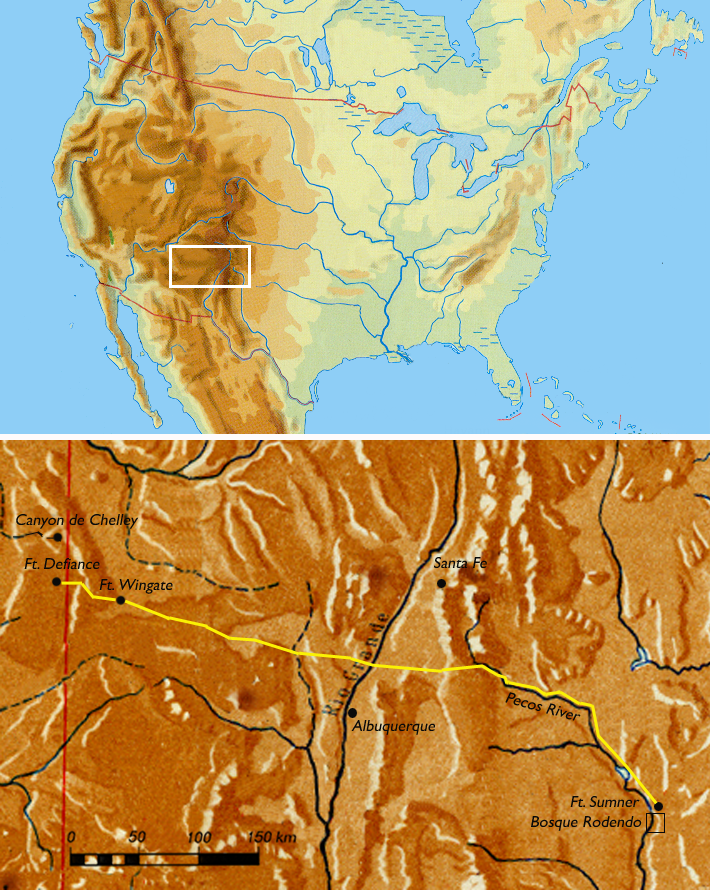
Long Walk Of The Navajo
The Long Walk of the Navajo, also called the Long Walk to Bosque Redondo ( nv, Hwéeldi), was the 1864 deportation and attempted ethnic cleansing of the Navajo people by the United States federal government. Navajos were forced to walk from their land in what is now Arizona to eastern New Mexico. Some 53 different forced marches occurred between August 1864 and the end of 1866. Some anthropologists claim that the "collective trauma of the Long Walk...is critical to contemporary Navajos' sense of identity as a people". Introduction The traditional Navajo homeland spans from Arizona through western New Mexico, where the Navajo had houses, planted crops and raised livestock. There was a long historical pattern in the Southwest of groups or bands raiding and trading with each other, with treaties being made and broken. This included interactions between Navajo, Spanish, Mexican, Pueblos, Apache, Comanche, Ute, and later European Americans. Individual civilians and Native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trail Of Tears
The Trail of Tears was an ethnic cleansing and forced displacement of approximately 60,000 people of the "Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government. As part of the Indian removal, members of the Cherokee, Muscogee (Creek), Seminole, Chickasaw, and Choctaw nations were forcibly removed from their ancestral homelands in the Southeastern United States to newly designated Indian Territory west of the Mississippi River after the passage of the Indian Removal Act in 1830. The Cherokee removal in 1838 (the last forced removal east of the Mississippi) was brought on by the discovery of gold near Dahlonega, Georgia, in 1828, resulting in the Georgia Gold Rush. The relocated peoples suffered from exposure, disease, and starvation while en route to their newly designated Indian reserve. Thousands died from disease before reaching their destinations or shortly after. Some historians have said that the event constituted a genocide, although this label ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Genocide
The California genocide was the killing of thousands of indigenous peoples of California by United States government agents and private citizens in the 19th century. It began following the American Conquest of California from Mexico, and the influx of settlers due to the California Gold Rush, which accelerated the decline of the indigenous population of California. Between 1846 and 1873, it is estimated that non-Natives killed between 9,492 and 16,094 California Natives. Hundreds to thousands were additionally starved or worked to death. Acts of enslavement, kidnapping, rape, child separation and displacement were widespread. These acts were encouraged, tolerated, and carried out by state authorities and militias. The 1925 book ''Handbook of the Indians of California'' estimated that the indigenous population of California decreased from perhaps as many as 150,000 in 1848 to 30,000 in 1870 and fell further to 16,000 in 1900. The decline was caused by disease, low birth rates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arikara
Arikara (), also known as Sahnish, ''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011) Arikaree, Ree, or Hundi, are a tribe of Native Americans in . Today, they are enrolled with the and the as the |