|
1833 In New Zealand
The following lists events that happened during 1833 in New Zealand. Incumbents Regal and viceregal *Head of State – King William IV *Governor of New South Wales – Major-General Sir Richard Bourke Government and law * British Resident in New Zealand – James Busby Events *10 May – James Busby arrives in the Bay of Islands on HMS ''Imogene''. *16 May – James Busby meets 22 leading chiefs at Paihia and reads them a message from King William IV. *October/November ** – Alfred Nesbitt Brown along with Henry Williams, John Morgan and William Fairburn visit the Thames Valley and reach Matamata.(see also 1834 & 1835) *November/December ** – A mission is established at Puriri. Undated *The building of the house for James Busby is begun. After the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi there in 1840 it will be known as the Treaty House. *The keystone above the door of the Stone Store in Kerikeri is carved. *Late in the year Louisa, daughter of John and Elizabeth Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1833
Events January–March * January 3 – Reassertion of British sovereignty over the Falkland Islands (1833), Reassertion of British sovereignty over the Falkland Islands in the South Atlantic. * February 6 – His Royal Highness Prince Otto Friedrich Ludwig of Bavaria assumes the title Otto of Greece, His Majesty Othon the First, by the Grace of God, King of Greece, Prince of Bavaria. * February 16 – The United States Supreme Court hands down its landmark decision of Barron v. Baltimore, Barron v. Mayor and City Council of Baltimore. * March 4 – Andrew Jackson is Second inauguration of Andrew Jackson, sworn in for his second term as President of the United States. April–June * April 1 – General Antonio López de Santa Anna is elected President of Mexico by the legislatures of 16 of the 18 Mexican states. During his frequent absences from office to fight on the battlefield, Santa Anna turns the duties of government over to his vice president, Valentín Gómez Farías. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puriri, New Zealand
Puriri is a small locality on the Hauraki Plains of New Zealand. It lies approximately 14 km south-east of Thames, New Zealand. Puriri was originally a Ngāti Maru settlement, which the Rev. Henry Williams visited in October 1833, when the Church Missionary Society (CMS) missionaries, William Thomas Fairburn, John Alexander Wilson, John Morgan and James Preece established a mission station in the settlement, In 1835 James Stack was appointed to Puriri. However, the missionaries withdrew from the mission that same year as the result of fighting in the Waikato. Fairburn returned to the Puriri Mission at the end of the fighting. Preece took over the mission in 1834 with the assistance of the Rev. James Hamlin. In 1838 the station was transferred to Parawai (part of the present town of Thames). In 1868 Puriri was the location for an official goldfield during the Thames-Coromandel gold rush. Puriri railway station was to the west of the village from Morrinsville and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bryce
John Bryce (14 September 1833 – 17 January 1913) was a New Zealand politician from 1871 to 1891 and Minister of Native Affairs from 1879 to 1884. In his attitudes to Māori land questions, he favoured strict legal actions against Māori opposed to alienation, and he personally directed the invasion of Parihaka and the arrest of the leaders of the movement. Described as being stubborn and embittered to Māori questions, Bryce was the public face of a harsh policy towards Māori, but his actions were supported by the Premier and other members of his cabinet. Early life John Bryce arrived in New Zealand as a child in 1840, and had little formal education. After a short time in the Australian gold-fields in 1851, he purchased a farm near Wanganui and remained a farmer for the next fifty years. Early political career In 1859, Bryce started his political career. By 1862 he was representing his area in the Wellington Provincial Council, and by 1866 was the Member of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Boyle, 7th Earl Of Glasgow
David Boyle, 7th Earl of Glasgow, (31 May 1833 – 13 December 1915), was a British naval commander and colonial governor. He served as Governor of New Zealand between 1892 and 1897. Background Boyle was the son of Patrick Boyle (eldest son of David Boyle, Lord Boyle, by his first wife, Elizabeth Montgomerie). His mother was Mary Frances Elphinstone-Dalrymple, daughter of Sir Robert Dalrymple-Horn-Elphinstone, 1st Baronet. He succeeded in the earldom in 1890. Royal Navy Boyle served with the Royal Navy during the Crimean and Second Opium Wars. He was commander of when the ship wrecked in 1874. He retired with the rank of captain. Governor of New Zealand Boyle was the Governor of New Zealand from 1892 to 1897. He was the cousin of another Governor, Sir James Fergusson James Fergusson may refer to: Politics *Sir James Fergusson, 6th Baronet (1832–1907), Governor of South Australia, New Zealand and Bombay *Sir James Fergusson, 8th Baronet (1904–1973), Lord Lieutenant of Ayr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Larnach
William James Mudie Larnach (27 January 1833 – 12 October 1898) was a New Zealand businessman and politician. He is known for his extravagant incomplete house near Dunedin called Larnach's castle by his opponents and now known as Larnach Castle. He is also remembered for his suicide within parliament buildings when faced with bankruptcy and consequent loss of his seat in parliament. Early career Larnach was born in the Hunter Region, north of Sydney, Australia, the son of John Larnach, a station owner and Emily daughter of James Mudie. He was well-connected. For example his uncle Donald Larnach became a director of the Australian board of the Bank of New South Wales in 1846 and after his retirement to England became one of the leading financial authorities in the City of London. Larnach was also a family friend of W. J. T. Clarke, said at that time to be the richest man in Australasia. In his late twenties, after his 1859 marriage to Eliza Jane Guise, daughter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
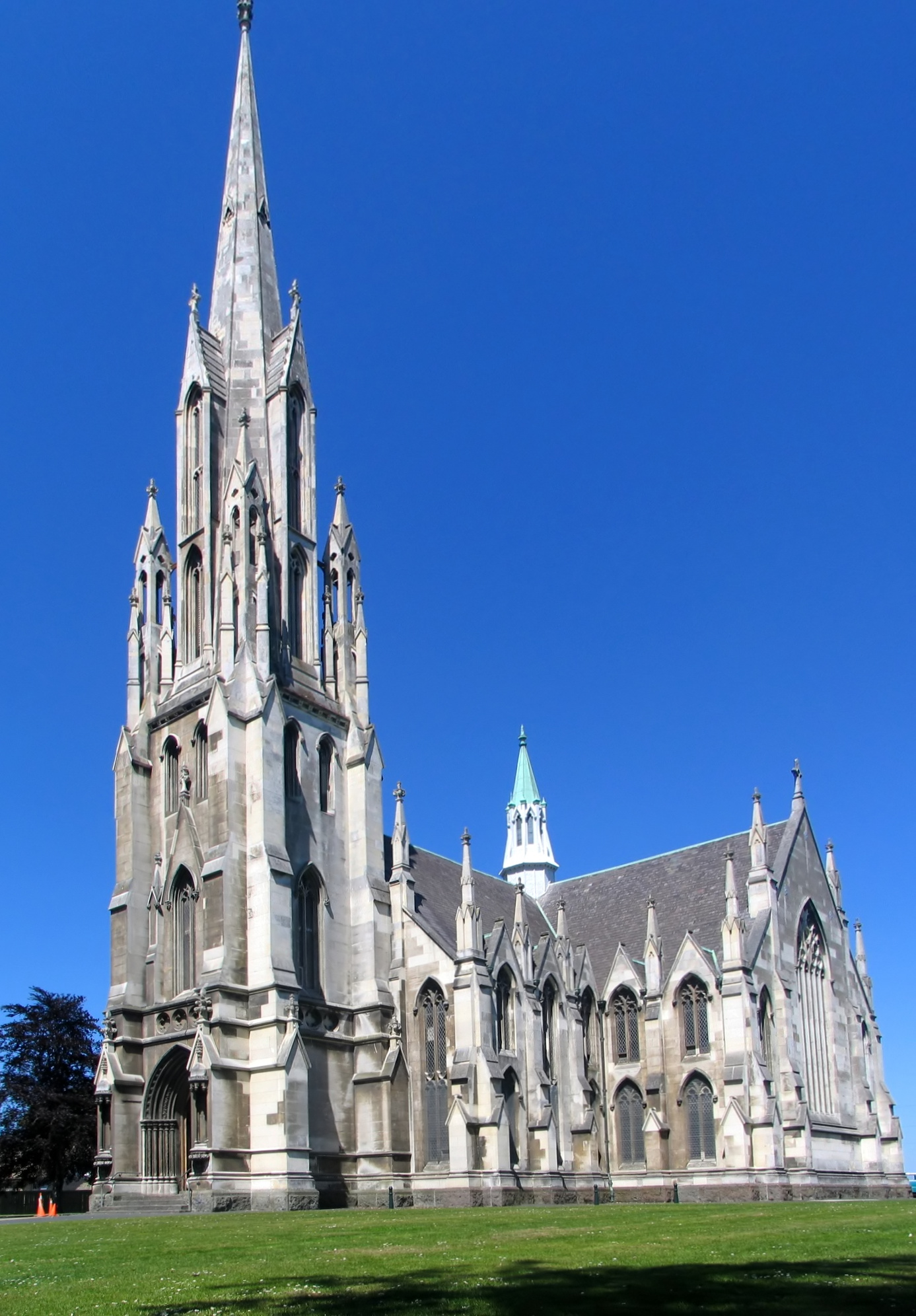
Robert Lawson (architect)
Robert Arthur Lawson (1 January 1833 – 3 December 1902) was one of New Zealand's pre-eminent 19th century architects. It has been said he did more than any other designer to shape the face of the Victorian era architecture of the city of Dunedin. He is the architect of over forty churches, including Dunedin's First Church for which he is best remembered, but also other buildings, such as Larnach Castle, a country house, with which he is also associated. Born at Newburgh, in Fife, Scotland, he emigrated in 1854 to Australia and then in 1862 to New Zealand. He died aged 69 in Canterbury, New Zealand. Lawson is acclaimed for his work in both the Gothic revival and classical styles of architecture. He was prolific, and while isolated buildings remain in Scotland and Australia, it is in the Dunedin area that most surviving examples can now be found. Today he is held in high esteem in his adopted country. However, at the time of his death his reputation was at a low ebb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Island
The South Island, also officially named , is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, and to the south and east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers , making it the world's 12th-largest island. At low altitude, it has an oceanic climate. The South Island is shaped by the Southern Alps which run along it from north to south. They include New Zealand's highest peak, Aoraki / Mount Cook at . The high Kaikōura Ranges lie to the northeast. The east side of the island is home to the Canterbury Plains while the West Coast is famous for its rough coastlines such as Fiordland, a very high proportion of native bush and national parks, and the Fox and Franz Josef Glaciers. The main centres are Christchurch and Dunedin. The economy relies on agriculture and fishing, tourism, and general manufacturing and services. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Underwood
Te Whanganui / Port Underwood is a sheltered harbour which forms the north-east extension of Te Koko-o-Kupe / Cloudy Bay at the northeast of New Zealand's South Island, on the east coast of the Marlborough Sounds.Wises New Zealand Guide, 7th Edition, 1979. p.457. With only a relatively narrow entrance to the south-south-east it is sheltered from almost all winds. Originally considered part of Cloudy Bay, the port was named after Joseph Underwood of the shipping firm Kabel and Underwood in the early 19th century. There is evidence of a large Māori population at various times prior to European arrival in New Zealand. In the 1820s the local Rangitane were defeated by the Ngāti Toa chief Te Rauparaha. Sealers first visited about 1826 and were followed immediately by whalers.Wises New Zealand Guide, 7th Edition, 1979. p.67. John Guard, who had started a whaling station in Tory Channel the previous year, set up a subsidiary station at Kakapo Bay in 1828. By 1840 there were approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Guard
John 'Jacky' Guard (ca. 1791/92 – 1857) was an English convict sent to Australia who was one of the first European settlers in the South Island of New Zealand, working as a whaler and trader. Early life Guard was born in London in 1791 or 1792. On 17 March 1813 at age 21, the stonecutter was convicted of stealing a quilt"Jack Guard and his Family" , Te Papa and sentenced to transportation and five years hard labour. At the end of his sentence, he worked as a sealer, and after five or six years had his own boat and crew. New Zealand Guard can lay credit to a number of European firsts in New Zealand's |
Kerikeri
Kerikeri () is the largest town in Northland, New Zealand. It is a tourist destination north of Auckland and north of the northern region's largest city, Whangarei. It is sometimes called the Cradle of the Nation, as it was the site of the first permanent mission station in the country, and it has some of the most historic buildings in the country. A rapidly expanding centre of subtropical and allied horticulture, Kerikeri is in the Far North District of the North Island and lies at the western extremity of the Kerikeri Inlet, a northwestern arm of the Bay of Islands, where fresh water of the Kerikeri River enters the Pacific Ocean. The village was established by New Zealand's pioneering missionaries, who called it Gloucester Town, but the name did not endure. The Māori word ''Kerikeri'' was interpreted by said missionaries as Keddi Keddi or Kiddeekiddee, before the romanisation methods they used were revised to what is used today. In 1814, Samuel Marsden acquired lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Store
The Stone Store at Kerikeri in the Bay of Islands is New Zealand’s oldest surviving stone building. Part of the second Church Missionary Society station in New Zealand, the store was designed by John Hobbs to replace an earlier wooden storehouse. The Stone Store was erected between 1832 and 1836 by a mason, William Parrott, a carpenter, Ben Nesbitt, and a team of Māori. Construction was of sandstone from Australia, local volcanic rocks, and burnt shell mortar. Iron ties and window bars were forged by James Kemp, though these corroded the sandstone. Initially the building had a wooden belfry on one side. The Stone Store was intended to be the base of the Church Missionary Society’s trading post, selling produce from the farms at the te Waimate mission to ships, and European goods to Māori. Marsden planned to build a flour mill on the adjacent Kerikeri River, but this was eventually built at te Waimate instead. Stone was used to protect wheat from rats, for defence aga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keystone (architecture)
A keystone (or capstone) is the wedge-shaped stone at the apex of a masonry arch or typically round-shaped one at the apex of a vault. In both cases it is the final piece placed during construction and locks all the stones into position, allowing the arch or vault to bear weight. In arches and vaults (such as quasi-domes) keystones are often enlarged beyond the structural requirements and decorated. A variant in domes and crowning vaults is a lantern. Keystones, as a hallmark of strength or good architecture, or their suggested form are sometimes placed in the centre of the flat top of doors, recesses and windows for decorative effect, so as to form an upward projection of a lintel. Although a masonry arch or vault cannot be self-supporting until the keystone is placed, the keystone experiences the least stress of any of the voussoirs, due to its position at the apex. Old keystones can decay due to vibration, a condition known as bald arch. Architecture In a rib-vaulted c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

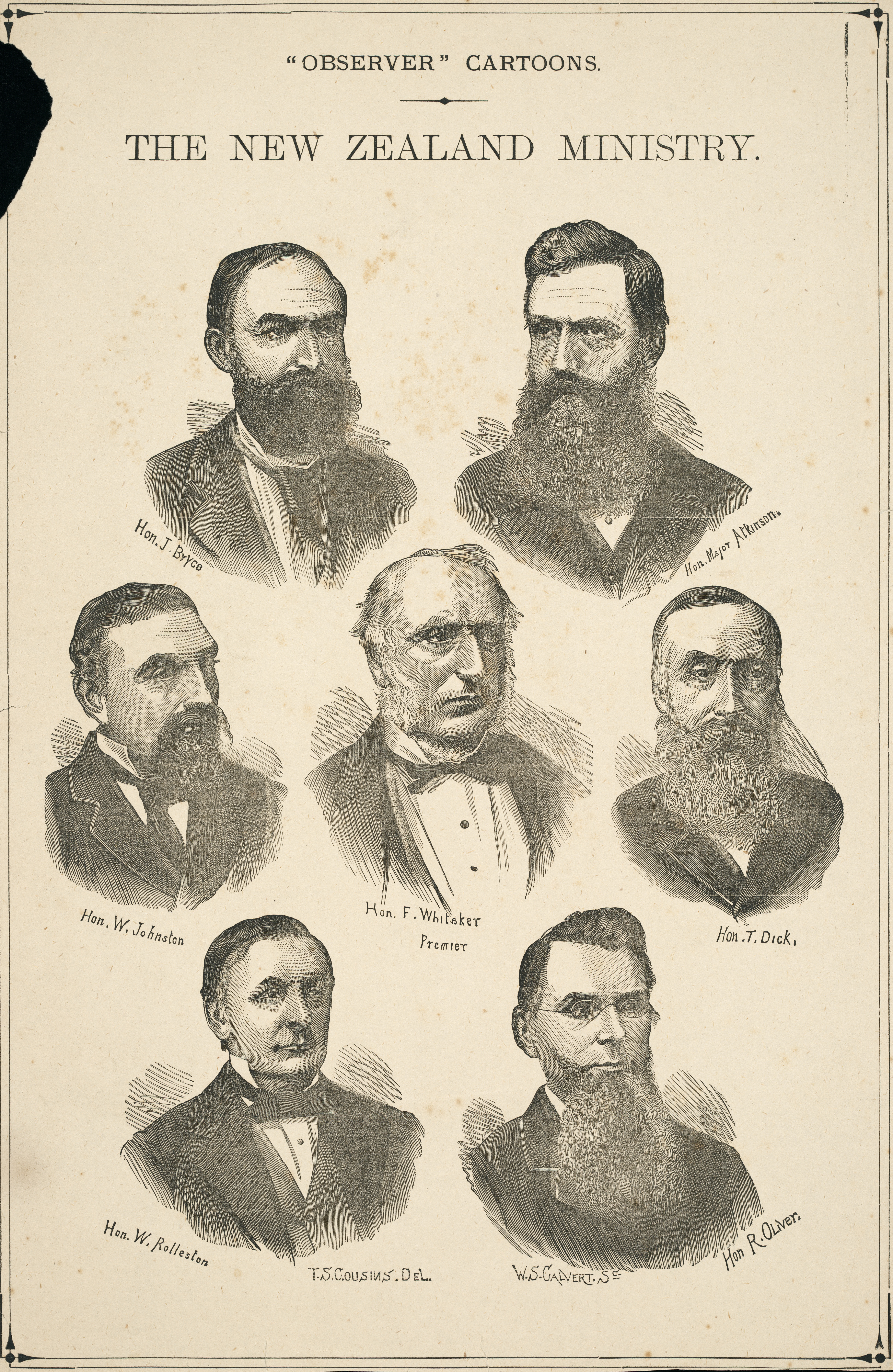


.png)