|
1814 In Scotland
Events from the year 1814 in Scotland. Incumbents Law officers * Lord Advocate – Archibald Colquhoun (politician), Archibald Colquhoun * Solicitor General for Scotland – Alexander Maconochie, Lord Meadowbank, Alexander Maconochie Judiciary * Lord President of the Court of Session – Charles Hope, Lord Granton, Lord Granton * Lord Justice General – James Graham, 3rd Duke of Montrose, The Duke of Montrose * Lord Justice Clerk – David Boyle, Lord Boyle, Lord Boyle Events * From midyear – Highland Clearances: Patrick Sellar begins mass expulsion of Croft (land), crofting tenants from Strathnaver at Grummore to make way for sheep farming as Factor (agent), factor for the George Leveson-Gower, 1st Duke of Sutherland, Marquess and Elizabeth Leveson-Gower, Duchess of Sutherland, Marchioness of Stafford. * 7 July – Walter Scott's ''Waverley (novel), Waverley'', his first prose fiction and one of the first significant historical novels in English, set during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Leveson-Gower, 1st Duke Of Sutherland
George Granville Leveson-Gower, 1st Duke of Sutherland KG, PC (9 January 175819 July 1833), known as Viscount Trentham from 1758 to 1786, as Earl Gower from 1786 to 1803 and as the Marquess of Stafford from 1803 to 1833, was an English politician, diplomat, landowner and patron of the arts from the Leveson-Gower family. He was the wealthiest man in Britain during the latter part of his life. He remains a controversial figure for his role in the Highland Clearances. Background Sutherland was the eldest son of the Granville Leveson-Gower, 1st Marquess of Stafford, by his second wife, Lady Louisa, daughter of Scroop Egerton, 1st Duke of Bridgwater. Granville Leveson-Gower, 1st Earl Granville, was his half-brother. He was educated at Westminster and at Christ Church, Oxford, where he graduated MA in 1777. Earlier political career Sutherland sat as Member of Parliament for Newcastle-under-Lyme from 1779 to 1784 and for Staffordshire from 1787 to 1799. The latter year he was summo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
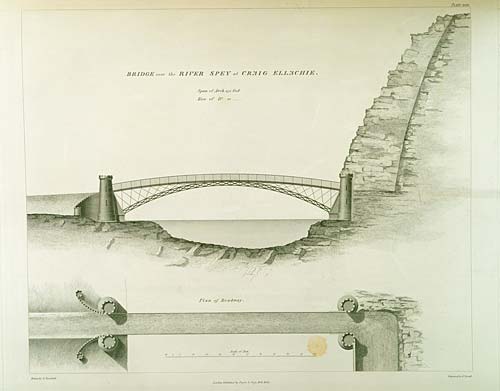
Craigellachie Bridge
Craigellachie Bridge is a cast iron arch bridge across the River Spey at Craigellachie, Moray, Craigellachie, near to the village of Aberlour in Moray, Scotland. It was designed by the renowned civil engineer Thomas Telford and built from 1812 to 1814. It is a Category A listed structure. Construction The bridge has a single Span (architecture), span of approximately and was revolutionary for its time, in that it used an extremely slender arch which was not possible using traditional masonry construction. The ironwork was cast at the Plas Kynaston iron foundry at Cefn Mawr, near Ruabon in Denbighshire (historic), Denbighshire by William Hazledine, who cast a number of Telford bridges. The ironwork was transported from the foundry through the Ellesmere Canal and Pontcysyllte Aqueduct then by sea to Speymouth, where it was loaded onto wagons and taken to the site. Testing in the 1960s revealed that the cast-iron had an unusually high tensile strength. This was probably specified b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cast Iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impurities which allow cracks to pass straight through, grey cast iron has graphite flakes which deflect a passing crack and initiate countless new cracks as the material breaks, and ductile cast iron has spherical graphite "nodules" which stop the crack from further progressing. Carbon (C), ranging from 1.8 to 4 wt%, and silicon (Si), 1–3 wt%, are the main alloying elements of cast iron. Iron alloys with lower carbon content are known as steel. Cast iron tends to be brittle, except for malleable cast irons. With its relatively low melting point, good fluidity, castability, excellent machinability, resistance to deformation and wear resistance, cast irons have become an engineering material with a wide range of applications and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Beauly
The River Beauly ( gd, Abhainn nam Manach, ) is a river in the Scottish Highlands, about 15 km west of the city of Inverness. It is about 25 km long, beginning near the village of Struy, at the confluence of the River Farrar and the River Glass (). The river meanders as it flows east, passing to the south of the village of Beauly and into the Beauly Firth. The river was first bridged in about 1817, when Thomas Telford constructed the five arched Lovat Bridge about 1 km south west of Beauly. Sabre Roads, Retrieved 25 March 2017 This bridge carried the A9, the main route north, until the |
Thomas Telford
Thomas Telford FRS, FRSE, (9 August 1757 – 2 September 1834) was a Scottish civil engineer. After establishing himself as an engineer of road and canal projects in Shropshire, he designed numerous infrastructure projects in his native Scotland, as well as harbours and tunnels. Such was his reputation as a prolific designer of highways and related bridges, he was dubbed ''The Colossus of Roads'' (a pun on the Colossus of Rhodes), and, reflecting his command of all types of civil engineering in the early 19th century, he was elected as the first President of the Institution of Civil Engineers, a post he held for 14 years until his death. The town of Telford in Shropshire was named after him. Early career Telford was born on 9 August 1757, at Glendinning, a hill farm east of Eskdalemuir Kirk, in the rural parish of Westerkirk, in Eskdale, Dumfriesshire. His father John Telford, a shepherd, died soon after Thomas was born. Thomas was raised in poverty by his mother Janet Jac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh University Library
Edinburgh University Library is the main library of the University of Edinburgh and one of the most important libraries of Scotland. The University Library was moved in 1827 to William Playfair's Upper Library in the Old College building. The collections in Edinburgh University Old College were moved in 1967 to the purpose-built eight-storey Main Library building at George Square, one of the largest academic libraries in the world. Today, Edinburgh's university-wide library system holds over 3.8m books, e-books and e-journals in total. History The University was founded by Royal Charter from King James VI in 1582 and opened in 1583, however the library pre-dated this by three years. The initial collection was a bequest of 276 theological books from Clement Littill, an advocate who left his collection to the town in 1580. Until 1708, the teaching staff consisted of four regents and the Principal, the former taking each class through a year's part of the whole arts curriculum o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth. Edinburgh is Scotland's List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city, after Glasgow, and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous city in the United Kingdom. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament and the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland. The city's Holyrood Palace, Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarchy in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scots law, Scottish law, literature, philosophy, the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archibald Constable
Archibald David Constable (24 February 1774 – 21 July 1827) was a Scottish publisher, bookseller and stationer. Life Constable was born at Carnbee, Fife, son of the land steward to the Earl of Kellie. In 1788 Archibald was apprenticed to Peter Hill, an Edinburgh bookseller, but in 1795 he started in business for himself as a dealer in rare books. He bought the rights to publish the ''Scots Magazine'' in 1801, and John Leyden, the orientalist, became its editor. In 1800 Constable began the ''Farmer's Magazine'', and in November 1802 he issued the first number of the ''Edinburgh Review'', under the nominal editorship of Sydney Smith; Lord Jeffrey, was, however, the guiding spirit of the review, having as his associates Lord Brougham, Sir Walter Scott, Henry Hallam, John Playfair and afterwards Lord Macaulay. Constable made a new departure in publishing by the generosity of his terms to authors. Writers for the ''Edinburgh Review'' were paid at an unprecedented rate, and Consta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobite Rising Of 1745
The Jacobite rising of 1745, also known as the Forty-five Rebellion or simply the '45 ( gd, Bliadhna Theàrlaich, , ), was an attempt by Charles Edward Stuart to regain the Monarchy of Great Britain, British throne for his father, James Francis Edward Stuart. It took place during the War of the Austrian Succession, when the bulk of the British Army was fighting in mainland Europe, and proved to be the last in Jacobite risings, a series of revolts that began in Jacobite rising of 1689, 1689, with major outbreaks in 1708, Jacobite rising of 1715, 1715 and Jacobite rising of 1719, 1719. Charles launched the rebellion on 19 August 1745 at Glenfinnan in the Scottish Highlands, capturing Edinburgh and winning the Battle of Prestonpans in September. At a council in October, the Scots agreed to invade England after Charles assured them of substantial support from English Jacobitism, Jacobites and a simultaneous French landing in Southern England. On that basis, the Jacobite Army (1745) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Novel
Historical fiction is a literary genre in which the plot takes place in a setting related to the past events, but is fictional. Although the term is commonly used as a synonym for historical fiction literature, it can also be applied to other types of narrative, including theatre, opera, cinema, and television, as well as video games and graphic novels. An essential element of historical fiction is that it is set in the past and pays attention to the manners, social conditions and other details of the depicted period. Authors also frequently choose to explore notable historical figures in these settings, allowing readers to better understand how these individuals might have responded to their environments. The historical romance usually seeks to romanticize eras of the past. Some subgenres such as alternate history and historical fantasy insert intentionally ahistorical or speculative elements into a novel. Works of historical fiction are sometimes criticized for lack of authe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waverley (novel)
''Waverley; or, 'Tis Sixty Years Since'' is a historical novel by Walter Scott (1771–1832). Scott was already famous as a poet, and chose to publish it anonymously in 1814 as his first venture into prose fiction. It is often regarded as one of the first historical novels in the Western tradition. Edward Waverley, an English gentleman of honour, chooses an occupation in the army at the time just before the Jacobite uprising of 1745 on advice of his father. He has an officer's commission. On leave from army training, he visits friends of his family in Scotland, as he is not far from their place. He enjoys their Scottish hospitality. His head is full of the romantic notions of his unstructured education, including much reading, and he is startled to find himself in the midst of loyalists who support the return of the House of Stuart and the Stuart prince, known as Bonnie Prince Charlie and the Young Chevalier to his supporters and as the Younger Pretender to his foes. His honou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




.jpg)