|
1805 In Science
Significant events in 1805 in science and technology are listed. Biology * Jean Henri Jaume Saint-Hilaire publishes ''Exposition des Familles naturelles et de la Germination des Plantes, contentant la description de 2337 genres et d'environ 4000 espèces, 112 planches dont les figures ont ete dessinées par l'auteur'', popularising the Jussiaean classification system. * Marie Jules César Savigny publishes ''Histoire naturelle et mythologique de l'Ibis'' in Paris, the first illustrated monograph on the ibis. Chemistry * John Dalton's list of molecular weights is first published. * Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac discovers that water is composed of two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen by volume. * Jane Marcet's elementary textbook for young people, ''Conversations on Chemistry'' ("intended more especially for the female sex"), is published anonymously in London. It proves extremely popular on both sides of the Atlantic, running through at least forty editions. Exploration * April 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrien-Marie Legendre
Adrien-Marie Legendre (; ; 18 September 1752 – 9 January 1833) was a French mathematician who made numerous contributions to mathematics. Well-known and important concepts such as the Legendre polynomials and Legendre transformation are named after him. Life Adrien-Marie Legendre was born in Paris on 18 September 1752 to a wealthy family. He received his education at the Collège Mazarin in Paris, and defended his thesis in physics and mathematics in 1770. He taught at the École Militaire in Paris from 1775 to 1780 and at the École Normale Supérieure, École Normale from 1795. At the same time, he was associated with the Bureau des Longitudes. In 1782, the Prussian Academy of Sciences, Berlin Academy awarded Legendre a prize for his treatise on projectiles in resistant media. This treatise also brought him to the attention of Lagrange. The ''Académie des sciences'' made Legendre an adjoint member in 1783 and an associate in 1785. In 1789, he was elected a Fellow of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir William Congreve, 2nd Baronet
Sir William Congreve, 2nd Baronet KCH FRS (20 May 1772 – 16 May 1828) was an English soldier, publisher and inventor. He pioneered rocket artillery and was renowned for his development and deployment of Congreve rockets. He was also a Tory Member of Parliament (MP). Biography He was the eldest son of Rebeca Elmston and Lt. General Sir William Congreve, 1st Baronet, the Comptroller of the Royal Laboratories at the Royal Arsenal and raised in Kent, England. He was educated at Newcome's school in Hackney, Wolverhampton Grammar School and Singlewell School in Kent. He then studied law at Trinity College, Cambridge, graduating BA in 1793 and MA in 1796. In 1814 he succeeded his father as second Baronet Congreve. In 1803 he was a volunteer in the London and Westminster Light Horse, and was a London businessman who published a polemical newspaper, the ''Royal Standard and Political Register'', which was Tory, pro-government and anti-Cobbett. Following a damaging libel action agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Beaufort
Rear-Admiral Sir Francis Beaufort (; 27 May 1774 – 17 December 1857) was an Irish hydrographer, rear admiral of the Royal Navy, and creator of the Beaufort cipher and the Beaufort scale. Early life Francis Beaufort was descended from French Protestant Huguenots, who fled the French Wars of Religion in the sixteenth century. His parents moved to Ireland from London. His father, Daniel Augustus Beaufort, was a Protestant clergyman from Navan, County Meath, Ireland, and a member of the learned Royal Irish Academy. His mother Mary was the daughter and co-heiress of William Waller, of Allenstown House. Francis was born in Navan on 27 May 1774. He had an older brother, William Louis Beaufort and three sisters, Frances, Harriet, and Louisa. His father created and published a new map of Ireland in 1792. Francis grew up in Wales and Ireland until age fourteen. He left school and went to sea, but never stopped his education. By later in life, he had become sufficiently self ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Speed
In meteorology, wind speed, or wind flow speed, is a fundamental atmospheric quantity caused by air moving from high to low pressure, usually due to changes in temperature. Wind speed is now commonly measured with an anemometer. Wind speed affects weather forecasting, aviation and maritime operations, construction projects, growth and metabolism rate of many plant species, and has countless other implications. Note that wind direction is usually almost parallel to isobars (and not perpendicular, as one might expect), due to Earth's rotation. Units Metres per second (m/s) is the SI unit for velocity and the unit recommended by the World Meteorological Organization for reporting wind speeds, and is amongst others used in weather forecasts in the Nordic countries. Since 2010 the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) also recommends meters per second for reporting wind speed when approaching runways, replacing their former recommendation of using kilometres per h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaufort Scale
The Beaufort scale is an empirical measure that relates wind speed to observed conditions at sea or on land. Its full name is the Beaufort wind force scale. History The scale was devised in 1805 by the Irish hydrographer Francis Beaufort (later Rear Admiral), a Royal Navy officer, while serving on . The scale that carries Beaufort's name had a long and complex evolution from the previous work of others (including Daniel Defoe the century before) to when Beaufort was Hydrographer of the Navy in the 1830s, when it was adopted officially and first used during the voyage of HMS ''Beagle'' under Captain Robert FitzRoy, who was later to set up the first Meteorological Office (Met Office) in Britain giving regular weather forecasts. In the 18th century, naval officers made regular weather observations, but there was no standard scale and so they could be very subjective – one man's "stiff breeze" might be another's "soft breeze". Beaufort succeeded in standardising the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Birth
Water birth is labor and sometimes delivery that occurs in water, usually a birthing pool. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists does not recommend birthing in water as the safety has not been determined. Proponents believe childbirth in water results in a more relaxed, less painful experience that promotes a midwife-led model of care. Critics argue that the safety of waterbirth has not been scientifically proven and that a wide range of adverse neonatal outcomes have been documented, including increased mother or child infections and the possibility of infant drowning. A 2018 Cochrane Review of water immersion in the first stages of labor found evidence of fewer epidurals and few adverse effects but insufficient information regarding giving birth in water. Benefits A moderate to weak level of evidence indicates that water immersion during the first stage of childbirth reduces the pain of labor. A 2018 Cochrane Review found that immersion at this stage reduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Parkinson
James Parkinson (11 April 175521 December 1824) was an English surgeon, apothecary, geologist, palaeontologist and political activist. He is best known for his 1817 work ''An Essay on the Shaking Palsy'', in which he was the first to describe "paralysis agitans", a condition that would later be renamed Parkinson's disease by Jean-Martin Charcot. Early life James Parkinson was born April 11, 1755 in Shoreditch, London, England. He was the son of John Parkinson, an apothecary and surgeon practising in Hoxton Square in London, and the oldest of five siblings, including his brother William and his sister Mary Sedgwick. In 1784 Parkinson was approved by the City of London Corporation as a surgeon. On 21 May 1783, he married Mary Dale, with whom he subsequently had eight children; two did not survive past childhood. Soon after he was married, Parkinson succeeded his father in his practice in 1 Hoxton Square. Politics In addition to his flourishing medical practice, Parkinson had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urology (journal)
''Urology'', also known as ''The Gold Journal'', is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering urology and nephrology. It is published by Elsevier on behalf of the Société Internationale d'Urologie and the editor-in-chief is Eric A. Klein. It was established in 1973. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Current Contents, EMBASE, MEDLINE, and Scopus. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', ''Urology'' has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 2.649. References External links *Société Internationale d'Urologie website {{DEFAULTSORT:Urology (journal) Publications established in 1973 Elsevier academic journals Monthly journals English-language journals Urology journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
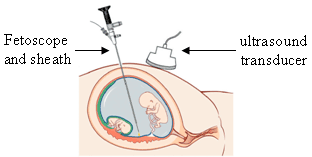
Endoscope
An endoscope is an inspection instrument composed of image sensor, optical lens, light source and mechanical device, which is used to look deep into the body by way of openings such as the mouth or anus. A typical endoscope applies several modern technologies including optics, ergonomics, precision mechanics, electronics, and software engineering. With an endoscope, it is possible to observe lesions that cannot be detected by X-ray, making it useful in medical diagnosis. Endoscopes use tubes which are only a few millimeters thick to transfer illumination in one direction and high-resolution images in real time in the other direction, resulting in minimally invasive surgeries. It is used to examine the internal organs like the throat or esophagus. Specialized instruments are named after their target organ. Examples include the cystoscope (bladder), nephroscope (kidney), bronchoscope (bronchus), arthroscope (joints) and colonoscope (colon), and laparoscope (abdomen or pelvis). They c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philipp Bozzini
Philipp Bozzini (May 25, 1773 – April 4, 1809) was born in Mainz, Germany. On June 12, 1797 he was awarded the degree of doctor of medicine. From 1804 onwards, Bozzini devoted himself virtually completely to develop his instrument, Lichtleiter or "Light Conductor", a primitive endoscope to allow for inspecting the ear, urethra, rectum, female bladder, cervix, mouth, nasal cavity, or wounds. Philipp Bozzini, using the modest means available at the beginning of the 19th century, was able to show to the medical profession the way to endoscopy. With his instrument and ideas, he was three quarters of a century ahead of the technical and scientific possibilities of his time. Historians agree that this instrument using artificial light and various mirrors and specula was the beginning of a large family of endoscopes. Early life Philipp Bozzini was born on May 25, 1773 in Mainz, Germany. His father, Nicolaus Maria Bozzini de Bozza, came from a well-to-do Italian family that had to escape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |