|
1760 In Science
The year 1760 in science and technology involved some significant events. Chemistry * Louis Claude Cadet de Gassicourt investigates inks based on cobalt salts and isolates cacodyl from cobalt mineral containing arsenic, pioneering work in organometallic chemistry. Geology * John Michell suggests earthquakes are caused by one layer of rocks rubbing against another. Medicine * April 30 – Swiss mathematician Daniel Bernoulli presents a paper at the French Academy of Sciences in Paris in which "a mathematical model was used for the first time to study the population dynamics of infectious disease." * Samuel-Auguste Tissot publishes ''L'Onanisme'' in Lausanne, a treatise on the supposed ill-effects of masturbation. Physics * Johann Heinrich Lambert publishes ''Photometria'', a pioneering work in photometry, including a formulation of the Beer–Lambert law on light absorption and the introduction of the albedo as a reflection coefficient. Technology * Liègeois mechanician J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Heinrich Lambert
Johann Heinrich Lambert (; ; 26 or 28 August 1728 – 25 September 1777) was a polymath from the Republic of Mulhouse, at that time allied to the Switzerland, Swiss Confederacy, who made important contributions to the subjects of mathematics, physics (particularly optics), philosophy, astronomy and map projections. Biography Lambert was born in 1728 into a Huguenot family in the city of Mulhouse, nowadays in Alsace, France, at that time a city-state allied to the Swiss Confederacy. Some sources give 26 August as his birth date and others 28 August. Leaving school at 12, he continued to study in his free time while undertaking a series of jobs. These included assistant to his father (a tailor), a clerk at a nearby iron works, a private tutor, secretary to the editor of ''Basler Zeitung'' and, at the age of 20, private tutor to the sons of Count Salis in Chur. Travelling Europe with his charges (1756–1758) allowed him to meet established mathematicians in the German states, Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Beddoes
Thomas Beddoes (13 April 176024 December 1808) was an English physician and scientific writer. He was born in Shifnal, Shropshire and died in Bristol fifteen years after opening his medical practice there. He was a reforming practitioner and teacher of medicine, and an associate of leading scientific figures. He worked to treat tuberculosis. Beddoes was a friend of Samuel Taylor Coleridge, and, according to E. S. Shaffer, an important influence on Coleridge's early thinking, introducing him to the higher criticism. The poet Thomas Lovell Beddoes was his son. A painting of him by Samson Towgood Roch is in the National Portrait Gallery, London. Early life and education Beddoes was born in Shifnal, Shropshire, on April 13, 1760, at Balcony House. He was educated at Bridgnorth Grammar School and Pembroke College, Oxford. He enrolled in the University of Edinburgh's medical course in the early 1780s. There he was taught chemistry by Joseph Black and natural history by John Walker (n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Wilson (painter)
Benjamin Wilson (21 June 1721 – 6 June 1788) was a British painter, printmaker and scientist (natural philosopher). Life He was the 14th child of Major Wilson, a wealthy York clothier whose house was decorated by the French history painter, Jacques Parmentier (d 1730). His father's business failed and Wilson moved to London, where he became a legal clerk and began to study painting, with the encouragement of William Hogarth, taking life-drawing classes at St. Martin's Lane Academy. For two weeks in 1746 and again from 1748 to 1750 he was in Dublin, where he practised successfully as a Portrait, portrait painter and electrical scientist. On his return to London he settled into Godfrey Kneller's old house in Great Queen Street and built up a lucrative portrait practice, competing with the young Joshua Reynolds. He obtained an introduction to Prince Edward, Duke of York and Albany (1739–67), who favoured him in numerous ways, possibly through one of his sitters, Sir John Savile, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copley Medal
The Copley Medal is the most prestigious award of the Royal Society of the United Kingdom, conferred "for sustained, outstanding achievements in any field of science". The award alternates between the physical sciences or mathematics and the biological sciences. It is arguably the highest United Kingdom, British and Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth award for scientific achievement, and has often been included among the most distinguished international scientific awards. Given annually, the medal is the oldest Royal Society medal awarded and the oldest surviving scientific award in the world, having first been given in 1731 to Stephen Gray (scientist), Stephen Gray, for "his new Electrical Experiments: – as an encouragement to him for the readiness he has always shown in obliging the Society with his discoveries and improvements in this part of Natural Knowledge". The medal is made of silver-gilt and awarded with a £25,000 prize. It is awarded to "senior scientists" irres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louise Of Brandenburg-Schwedt
Louise Henriette Wilhelmine of Brandenburg-Schwedt (24 September 1750 in Różanki – 21 December 1811 in Dessau), was a Margravine of Brandenburg by birth and by marriage a princess, and later Duchess, of Anhalt-Dessau. Early life Louise was the daughter of Margrave Frederick Henry, Margrave of Brandenburg-Schwedt and his wife, Princess Leopoldine Marie of Anhalt-Dessau. By birth, Louise Henriette belonged to Brandenburg-Schwedt line of the House of Hohenzollern. Biography She was educated in Prussia, together with her sister, Friederike Charlotte of Brandenburg-Schwedt. Between 1760 and 1762, the mathematician Leonhard Euler sent her sister numerous letters in French about mathematical and philosophical subjects. These letters were published between 1769 and 1773 under the title ''Letters to a German Princess'' and were printed in Leipzig and St. Petersburg. The French edition was printed twelve times. She befriended Jenny Voigts who was a life-long friend of Loui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friederike Charlotte Of Brandenburg-Schwedt
Friederike Charlotte Leopoldine Louise of Brandenburg-Schwedt (also often referred to as the Princess of Prussia; 18 August 1745 in Schwedt – 23 January 1808 in Altona) was a German aristocrat who lived as a secular canoness and ruled as the last Princess-abbess of Herford Abbey. Life Friederike Charlotte was a member of the Brandenburg-Schwedt line of the Prussian royal family, the daughter of Frederick Henry, Margrave of Brandenburg-Schwedt and his wife Leopoldine Marie of Anhalt-Dessau. After the breakup of her parents' marriage, King Frederick II of Prussia sent her mother to Kołobrzeg in Pomerania and Friederike Charlotte received a place in Herford Abbey. In 1755, she became coadjutor to Abbess Hedwig Sophie of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp, whom she later succeeded. Friederike Charlotte was partly educated in Prussia, together with her sister Louise. Between 1760 and 1762, the mathematician Leonhard Euler sent her numerous letters in French about mathematical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letters To A German Princess
''Letters to a German Princess, On Different Subjects in Physics and Philosophy'' (French: ''Lettres à une princesse d'Allemagne sur divers sujets de physique et de philosophie'') were a series of 234 letters written by the mathematician Leonhard Euler between 1760 and 1762 addressed to Friederike Charlotte of Brandenburg-Schwedt and her younger sister Louise. Contents Euler started the first letter with an explanation of the concept of "size". Starting with the definition of a foot, he defined the mile and the diameter of the earth as a unit in terms of foot and then calculated the distance of the planets of the Solar System in terms of the diameter of the earth. Publication The first two volumes of the 234 letters originally written in French appeared in print in Saint Petersburg in 1768 and the third in Frankfurt in 1774. The letters were later reprinted in Paris with the first volume in 1787, the second in 1788 and the third in 1789. The publication of the book was supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonhard Euler
Leonhard Euler ( ; ; ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss polymath who was active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, logician, geographer, and engineer. He founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made influential discoveries in many other branches of mathematics, such as analytic number theory, complex analysis, and infinitesimal calculus. He also introduced much of modern mathematical terminology and Mathematical notation, notation, including the notion of a mathematical function. He is known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy, and music theory. Euler has been called a "universal genius" who "was fully equipped with almost unlimited powers of imagination, intellectual gifts and extraordinary memory". He spent most of his adult life in Saint Petersburg, Russia, and in Berlin, then the capital of Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia. Euler is credited for popularizing the Greek letter \pi (lowercase Pi (letter), pi) to denote Pi, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roller Skates
Roller skates are boots with wheels mounted to the bottom, allowing the user to travel on hard surfaces similarly to an ice skater on ice. The first roller skate was an inline skate design, effectively an ice skate with a line of wheels replacing the blade. In modern usage, the term typically refers to skates with two pairs of wheels on shared axles like those of skateboards (early versions of which were made using roller skate parts). Skates with this configuration are also known as "quad skates" or "quads" and, like skateboards, steer by tilting the skate to one side, which causes the axles to turn inward. History While the first reported use of wheeled skates was on a London stage in 1743, the first patented "roller skate" was introduced in 1760 by Belgian inventor John Joseph Merlin. They were hard to steer and stopping was difficult due to the fact that they did not have any type of braking mechanism and as such they failed to gain popularity. Merlin demonstrated his i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Joseph Merlin
John Joseph Merlin (born Jean-Joseph Merlin, 6 September 1735 – 8 May 1803) was a Freemason, clock-maker, musical-instrument maker, and inventor from the Prince-Bishopric of Liège in the Holy Roman Empire. He moved to England in 1760. By 1766 he was working with James Cox (inventor), James Cox and creating automatons such as Cox's timepiece and the Silver Swan (automaton), Silver Swan. By 1773 he was designing and making innovative keyboard instruments. In 1783 he opened Merlin's Mechanical Museum in Princes Street, Hanover Square, London, a meeting-place for the gentry and nobility. In addition to his clocks, musical instruments and automata, Merlin is credited with the invention of inline skates in the 1760s. He was referred to by contemporaries as "The Ingenious Mechanic". He was friendly with composer Joseph Haydn. Life Jean-Joseph Merlin was born on 6 September 1735, in Huy, in what was then the Prince-Bishopric of Liège and is now in Belgium, Wallonia. His parents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
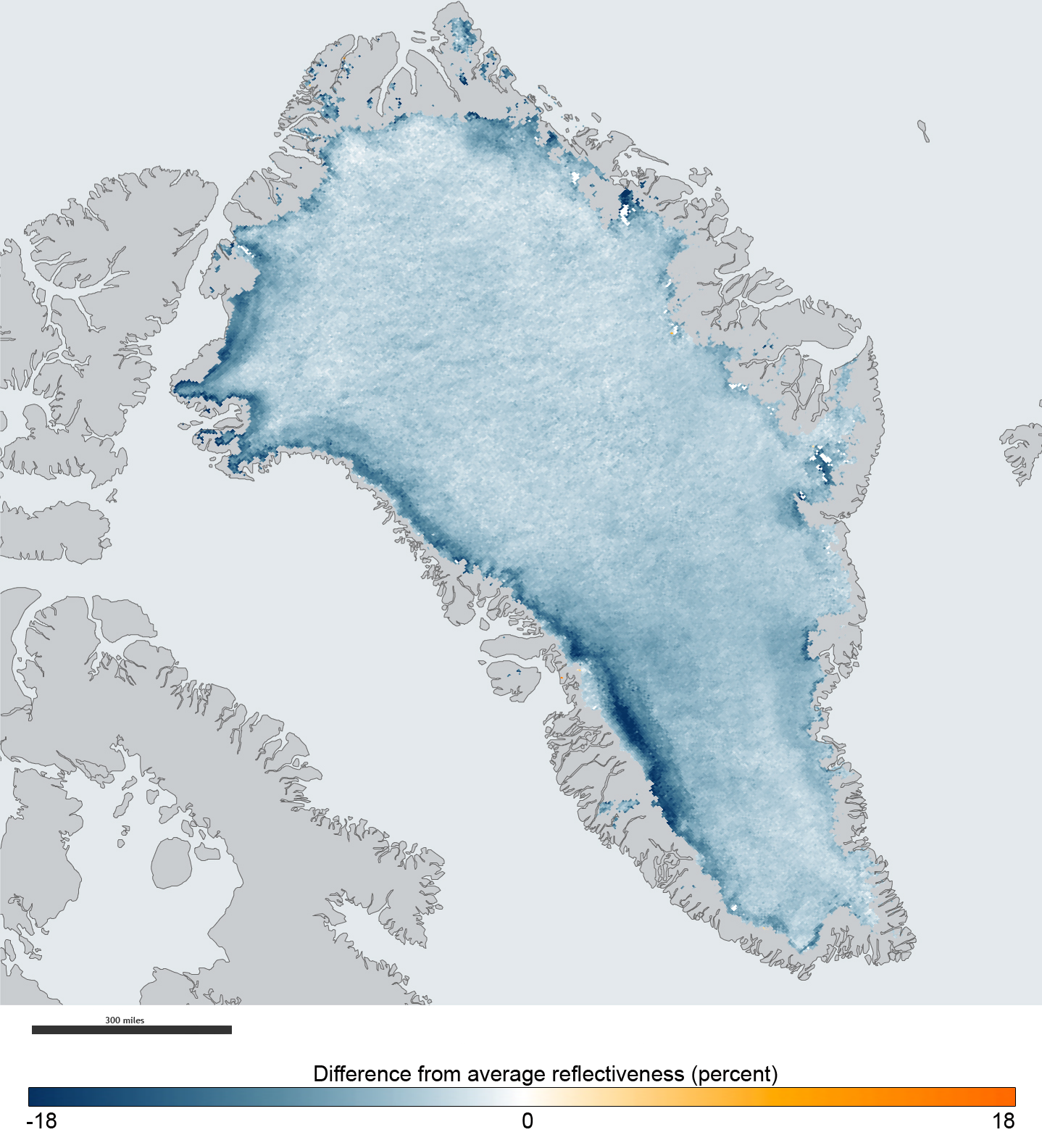
Albedo
Albedo ( ; ) is the fraction of sunlight that is Diffuse reflection, diffusely reflected by a body. It is measured on a scale from 0 (corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation) to 1 (corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation). ''Surface albedo'' is defined as the ratio of Radiosity (radiometry), radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While directional-hemispherical reflectance factor is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |