|
1716 Algiers Earthquake
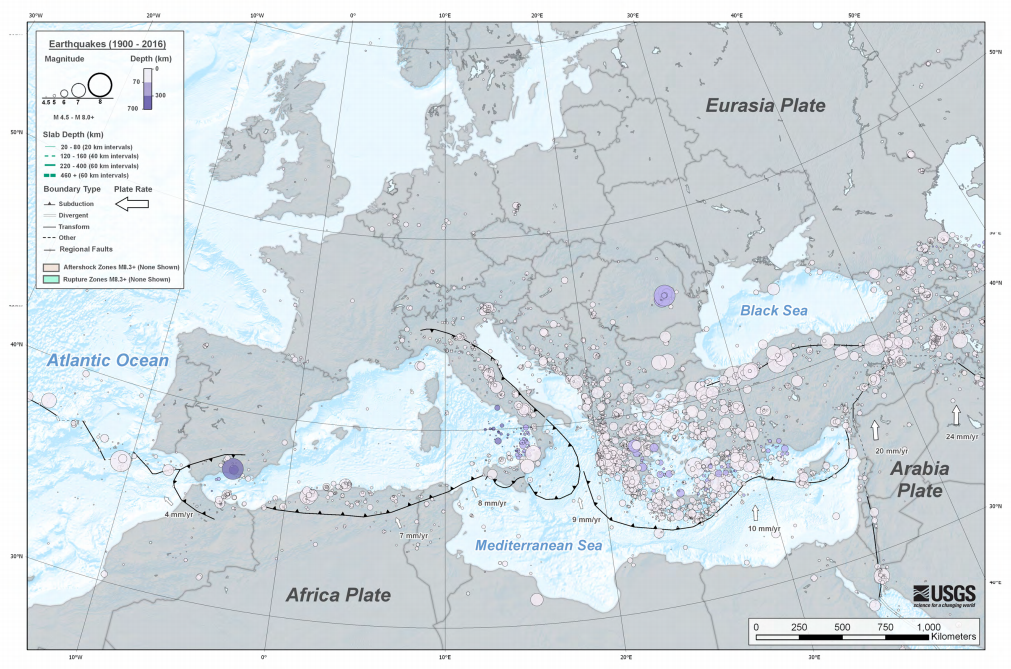
The 1716 Algiers earthquake was part of a seismic sequence which began in February and ended in May 1716. The largest and most destructive shock occurred on February 3 with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.0. The earthquakes with an epicenter thought to be in the Algiers region had a maximum European macroseismic scale (EMS-98) intensity of IX (''Destructive''), killing approximately 20,000 people. The earthquake was felt in Catania and Syracuse on the Italian island Sicily. Tectonic setting The nation of Algeria lie near a complex and poorly defined convergent plate boundary separating the African Plate from the Eurasian Plate. The converging plates create a zone of compression in northern Algeria, which are accommodated by mainly thrust and reverse faults onshore and inland. Thrusting of strata due to compression formed the Atlas Mountains in Algeria and Morocco. The tectonic situation of Algeria also makes the country vulnerable to large and deadly seismic events with magn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algeria
) , image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Algiers , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , religion = , official_languages = , languages_type = Other languages , languages = Algerian Arabic (Darja) French , ethnic_groups = , demonym = Algerian , government_type = Unitary semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Abdelmadjid Tebboune , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Aymen Benabderrahmane , leader_title3 = Council President , leader_name3 = Salah Goudjil , leader_title4 = Assembly President , leader_name4 = Ibrahim Boughali , legislature = Parliament , upper_house = Council of the Nation , lower_house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
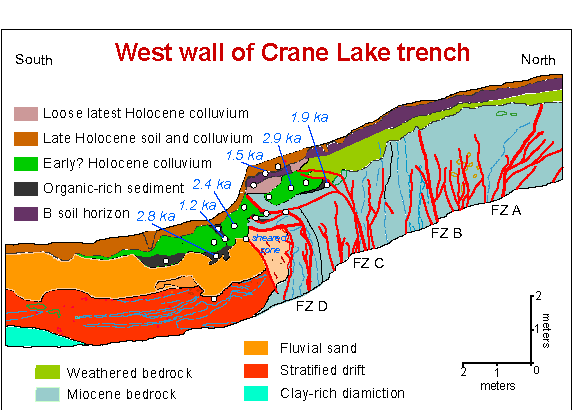
Paleoseismology
Paleoseismology looks at geologic sediments and rocks, for signs of ancient earthquakes. It is used to supplement seismic monitoring, for the calculation of seismic hazard. Paleoseismology is usually restricted to geologic regimes that have undergone continuous sediment creation for the last few thousand years, such as swamps, lakes, river beds and shorelines. In this typical example, a trench is dug in an active sedimentation regime. Evidence of thrust faulting can be seen in the walls of the trench. It becomes a matter of deducting the relative age of each fault, by cross-cutting patterns. The faults can be dated in absolute terms, if there is dateable carbon, or human artifacts. Many notable discoveries have been made using the techniques of paleoseismology. For example, there is a common misconception that having many smaller earthquakes can somehow 'relieve' a major fault such as the San Andreas Fault, and reduce the chance of a major earthquake. It is now known (u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1710s Earthquakes
Year 171 ( CLXXI) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Severus and Herennianus (or, less frequently, year 924 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 171 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Marcus Aurelius forms a new military command, the ''praetentura Italiae et Alpium''. Aquileia is relieved, and the Marcomanni are evicted from Roman territory. * Marcus Aurelius signs a peace treaty with the Quadi and the Sarmatian Iazyges. The Germanic tribes of the Hasdingi (Vandals) and the Lacringi become Roman allies. * Armenia and Mesopotamia become protectorates of the Roman Empire. * The Costoboci cross the Danube (Dacia) and ravage Thrace in the Balkan Peninsula. They reach Eleusis, near Athens, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquakes In Algeria
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques de l'Algérie (web). and in 2020 was estimated to be around 4,500,000. Algiers is located on the Mediterranean Sea and in the north-central portion of Algeria. Algiers is situated on the west side of a bay of the Mediterranean Sea. The modern part of the city is built on the level ground by the seashore; the old part, the ancient city of the deys, climbs the steep hill behind the modern town and is crowned by the Casbah or citadel (a UNESCO World Heritage Site), above the sea. The casbah and the two quays form a triangle. Names The city's name is derived via French and Catalan ''Origins of Algiers'' by Louis Leschi, speech delivered June 16, 1941, published in ''El Djezair Sheets'', July 194History of Algeria . from the Arabic name ''al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1716 Disasters
Events January–March * January 16 – The application of the Nueva Planta decrees to Catalonia make it subject to the laws of the Crown of Castile, and abolishes the Principality of Catalonia as a political entity, concluding the unification of Spain under Philip V. * January 27 – The Tugaloo massacre changes the course of the Yamasee War, allying the Cherokee nation with the British province of South Carolina against the Creek Indian nation. * January 28 – The town of Crieff, Scotland, is burned to the ground by Jacobites returning from the Battle of Sheriffmuir. * February 3 – The 1716 Algiers earthquake sequence began with an 7.0 mainshock that caused severe damage and killed 20,000 in Algeria. * February 10 – James Edward Stuart flees from Scotland to France with a handful of supporters, following the failure of the Jacobite rising of 1715. * February 24 – Jacobite leaders James Radclyffe, 3rd Earl of Derwentwater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Earthquakes In Algeria
Earthquakes in Algeria occur in the north part of the country, usually north of 35° N. latitude, and occasionally as submarine earthquakes in the Mediterranean Sea. On at least one occasion, this type of event has generated a destructive tsunami. Earthquakes See also * Geology of Algeria References Sources * Further reading * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Earthquakes In Algeria Algeria ) , image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Algiers , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , relig ... * Lists of events in Algeria Tsunamis in Algeria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Historical Earthquakes
Historical earthquakes is a list of significant earthquakes known to have occurred prior to the beginning of the 20th century. As the events listed here occurred before routine Seismometer, instrumental recordings, they rely mainly on the analysis of written sources. There is often significant uncertainty in location and magnitude and sometimes date for each earthquake. The number of fatalities is also often highly uncertain, particularly for the older events. Pre-11th century 11th–18th centuries 19th century Source for all events with 'USGS' labelled as the source United States Geological Survey (USGS''Note: Magnitudes are generally estimations from intensity data. When no magnitude was available, the Mercalli intensity scale, maximum intensity, written as a Roman numeral from I to XII, is given.'' See also * :Articles on pre-1900 earthquakes * List of 20th-century earthquakes * List of 21st-century earthquakes * List of tsunamis * Lists of earthquakes * List of megath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dar Aziza
Dar Aziza is a 16th-century Moorish palace located in the Casbah of Algiers in Algeria. Today, it houses the National Agency of Archaeology and Protection of Historic Sites and Monuments. Dar Aziza, arguably the most iconic surviving building of its era in Algiers, was part of a large governmental compound known as Janina Palace, which existed before the arrival of Turkish corsairs. History Dar Aziza was part of a large governmental compound known as Janina Palace, which existed before the arrival of Turkish corsairs. It is believed to have been built at some time in the 16th century, though its surrounding environment was significantly modified after the advent of French colonial rule. In the Ottoman period, it would have served to lodge foreign embassies and, in particular, the Fathers of the Order of Mercy who came to negotiate the redemption of Christian captives. According to a 1721 document, the building had three floors before losing one in the 1716 earthquake. Accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
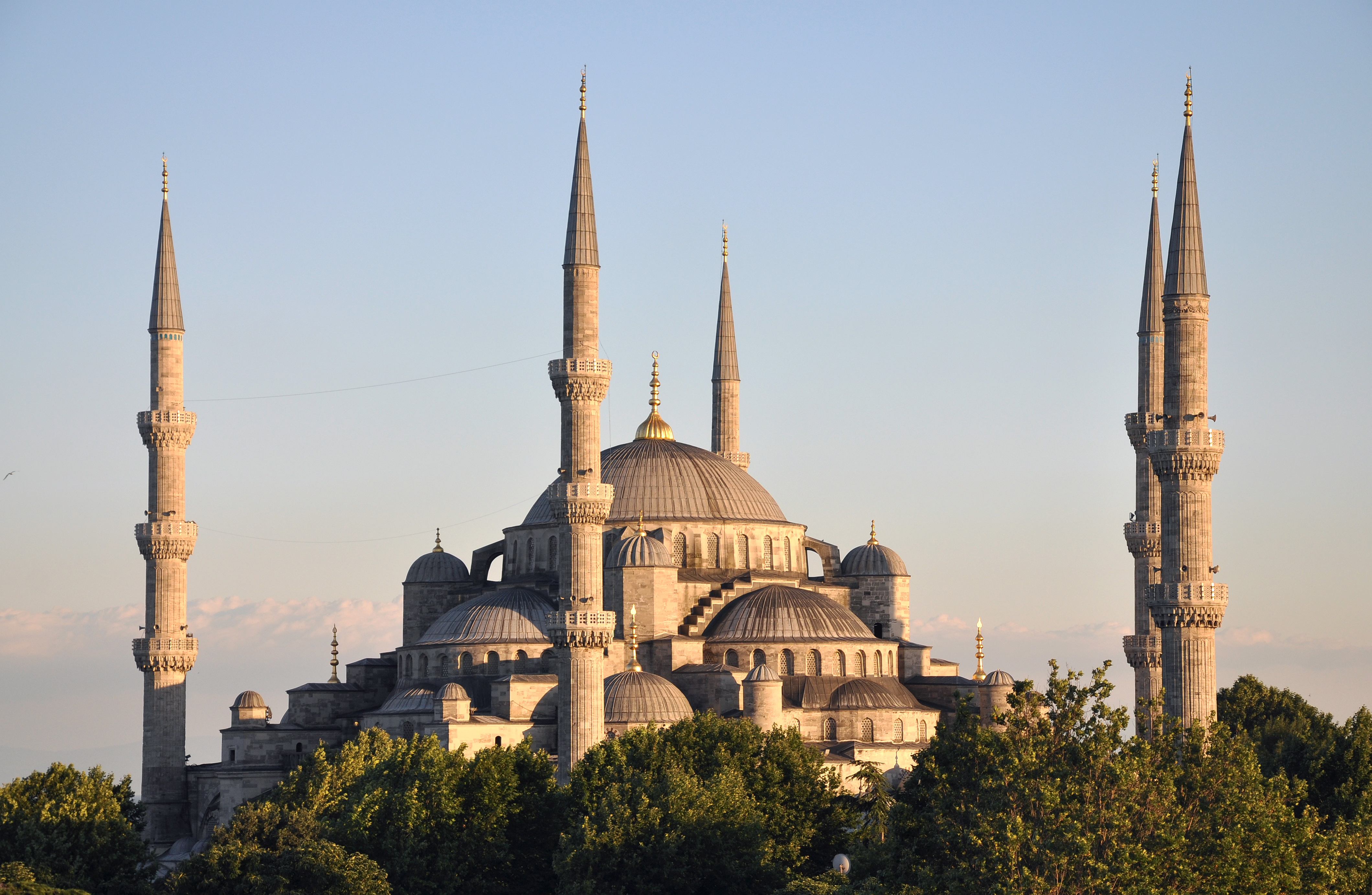
Mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, including outdoor courtyards. The first mosques were simple places of prayer for Muslims, and may have been open spaces rather than buildings. In the first stage of Islamic architecture, 650-750 CE, early mosques comprised open and closed covered spaces enclosed by walls, often with minarets from which calls to prayer were issued. Mosque buildings typically contain an ornamental niche ('' mihrab'') set into the wall that indicates the direction of Mecca (''qiblah''), Wudu, ablution facilities. The pulpit (''minbar''), from which the Friday (jumu'ah) sermon (''khutba'') is delivered, was in earlier times characteristic of the central city mosque, but has since become common in smaller mosques. Mosques typically have Islam and gender se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time In Algeria
Algeria Standard Time or DPRA Standard Time is the time zone for Algeria. It is 1 hour ahead of GMT/ UTC ( UTC+01:00) and is co-linear with neighboring Tunisia. IANA time zone database The IANA time zone database The tz database is a collaborative compilation of information about the world's time zones, primarily intended for use with computer programs and operating systems. Paul Eggert is its current editor and maintainer, with the organizational backi ... contains one zone for Algeria in the file zone.tab. References {{Measurement-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, called charcoal burning, often by forming a charcoal kiln, the heat is supplied by burning part of the starting material itself, with a limited supply of oxygen. The material can also be heated in a closed retort. Modern "charcoal" briquettes used for outdoor cooking may contain many other additives, e.g. coal. This process happens naturally when combustion is incomplete, and is sometimes used in radiocarbon dating. It also happens inadvertently while burning wood, as in a fireplace or wood stove. The visible flame in these is due to combustion of the volatile gases exuded as the wood turns into charcoal. The soot and smoke commonly given off by wood fires result from incomplete combustion of those volatiles. Charcoal burns at a higher temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |