|
1703 In Literature
Events from the year 1703 in literature. Events *July 29– 31 – Daniel Defoe is pilloried at Temple Bar, London, as part of a sentence for seditious libel, after publishing his satirical pamphlet '' The Shortest Way with the Dissenters'' (1702). He is released from Newgate Prison in mid-November. *''unknown date'' – Richard Mead is appointed physician at St Thomas's Hospital, London. New books Prose *Joseph Addison – ''A Letter from Italy'' *Abel Boyer – ''The History of the Reign of Queen Anne'' *Gilbert Burnet – ''A Third Collection of Several Tracts and Discourses'' * Edmund Calamy – ''A Defence of Moderate Non-Conformity'' *Jeremy Collier – ''Mr Collier's Dissuasive from the Play-House'' *William Dampier – ''A Voyage to New Holland, &c. in the Year 1699'' *Daniel Defoe **''A Brief Explanation of a Late Pamphlet, entitled, The Shortest Way with the Dissenters'' **''A Dialogue Between a Dissenter and the Observator'' **''A Hymn to the Funeral Sermon'' **''Hym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
July 29
Events Pre-1600 * 587 BC – The Neo-Babylonian Empire sacks Jerusalem and destroys the First Temple. * 615 – Pakal ascends the throne of Palenque Palenque (; Yucatec Maya language, Yucatec Maya: ), also anciently known in the Itza Language as Lakamhaʼ ("Big Water or Big Waters"), was a Maya city City-state, state in southern Mexico that perished in the 8th century. The Palenque ruins dat ... at the age of 12. * 904 – Sack of Thessalonica (904), Sack of Thessalonica: Saracen raiders under Leo of Tripoli sack Thessaloniki, the Byzantine Empire's second-largest city, after a short siege, and plunder it for a week. * 923 – Battle of Firenzuola: Lombard forces under King Rudolph II of Burgundy, Rudolph II and Adalbert I of Ivrea, Adalbert I, margrave of March of Ivrea, Ivrea, defeat the dethroned Emperor Berengar I of Italy at Firenzuola (Tuscany). *1014 – Byzantine–Bulgarian wars: Battle of Kleidion: List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine empero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeremy Collier
Jeremy Collier (; 23 September 1650 – 26 April 1726) was an English theatre critic, non-juror bishop and theologian. Life Born Jeremiah Collier, in Stow cum Quy, Cambridgeshire, Collier was educated at Caius College, University of Cambridge, receiving the BA (1673) and MA (1676). A supporter of James II, he refused, as a nonjuror (see Nonjuring schism) to take the oath of allegiance to William III and Mary II after the Glorious Revolution. Furthering his obvious disapproval of the new monarchs, he publicly absolved two Jacobites who had conspired to assassinate the King and Queen. In 1713 he was consecrated a non-juror bishop by George Hickes and two Scottish bishops, Archibald Campbell and James Gadderar. Works Collier was the primus of the nonjuring line and a strong supporter of the four usages. (see Nonjuring schism) In the years following the Revolution he wrote a series of tracts questioning the legitimacy of the new monarchs and the deprival of the Non-juror bis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ned Ward
Ned Ward (1667 – 20 June 1731), also known as Edward Ward, was a satirical writer and publican in the late 17th and early 18th century in London. His most famous work, ''The London Spy'', appeared in 18 monthly instalments from November 1698. It was described by its author as a "complete survey" of the London scene and published in book form in 1703. Biography Early life Ned Ward was born in 1667 in Oxfordshire. According to Theophilus Cibber, Ward was "a man of low extraction... who never received any regular education", but he is likely to have been educated at one of the Oxfordshire grammar schools.Howard William Troyer, ''Ned Ward of Grubstreet; a study of sub-literary London in the eighteenth century'', Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard UP, 1946. By 1691 Ward had made his way to London. His first publication, ''The Poet's Ramble After Riches'', describes in humorous Hudibrastic couplets his poverty and his disappointment at not receiving an inheritance. Prose satires that followe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Maundrell
Henry Maundrell (1665–1701) was an academic at Oxford University and later a Church of England clergyman, who served from 20 December 1695 as chaplain to the Levant Company in Syria. His ''Journey from Aleppo to Jerusalem at Easter A.D. 1697'' (Oxford, 1703), which had its origins in the diary he carried with him on his Easter pilgrimage to Jerusalem in 1697, has become an often reprinted "minor travel classic." It was included in compilations of travel accounts from the mid-18th century, and was translated into three additional languages: French (1705), Dutch (1717) and German (1792). By 1749, the seventh edition was printed. Life Maundrell was born at Compton Bassett, near Calne, Wiltshire, in 1665. He attended Exeter College, Oxford, from 1682 and obtained his BA and then in 1688, his MA; at his graduation he was appointed a Fellow of the college, where he would remain until 1689. He accepted a curacy at Brompton, Kent, 1689–95, he was ordained priest by the Bishop of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic (book)
''Arithmetic'' () is a 1703 mathematics textbook by the Russian educator and mathematician Leonty Magnitsky. The book served as the standard Russian mathematics textbook until the mid-18th century. Mikhail Lomonosov was educated on this book, and referred to it as the "gates of my own erudition". It was the first mathematics textbook written in the Russian language that was not a translated edition of a foreign work. It consisted essentially of Magnitsky's own lecture notes, and offered an encyclopedic overview of arithmetic at the time, with sections on navigational astronomy, geodesy, algebra, geometry, and trigonometry. It was organized in instructive question and answer format, and rooted not in the abstract but in practical and demonstrable applications of theories and axioms. The book also contained astronomical tables and coordinate maps for various Russian locales. Production for the School of Navigation The origins of the book lie in Peter the Great Peter I (& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonty Magnitsky
Leonty Filippovich Magnitsky (russian: Леонтий Филиппович Магницкий), born Telyatin (russian: Телятин; June 9, 1669, in Ostashkov – October 19, 1739, in Moscow) was a Russian mathematician and educator.. Biography Magnitsky was born into a peasant family. According to some accounts, he graduated from the Slavic Greek Latin Academy in Moscow. From 1701 and until his death, he taught arithmetic, geometry and trigonometry at the Moscow School of Mathematics and Navigation, becoming its director in 1716. In 1703, Magnitsky wrote his famous ''Arithmetic'' (Арифметика; 2,400 copies), which was used as the principal textbook on mathematics in Russia until the middle of the 18th century. Mikhail Lomonosov was himself taught by this book, which he called the "gates to his own erudition".. In 1703, Magnitsky also produced a Russian edition of Adriaan Vlacq's log tables called ''Таблицы логарифмов и синусов, танге ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean De La Fontaine
Jean de La Fontaine (, , ; 8 July 162113 April 1695) was a French fabulist and one of the most widely read French poets of the 17th century. He is known above all for his ''Fables'', which provided a model for subsequent fabulists across Europe and numerous alternative versions in France, as well as in French regional languages. After a long period of royal suspicion, he was admitted to the French Academy and his reputation in France has never faded since. Evidence of this is found in the many pictures and statues of the writer, later depictions on medals, coins and postage stamps. Life Early years La Fontaine was born at Château-Thierry in France. His father was Charles de La Fontaine, maître des eaux et forêts – a kind of deputy-ranger – of the Duchy of Château-Thierry; his mother was Françoise Pidoux. Both sides of his family were of the highest provincial middle class; though they were not noble, his father was fairly wealthy. Jean, the eldest child, was educa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard De Mandeville
Bernard Mandeville, or Bernard de Mandeville (; 15 November 1670 – 21 January 1733), was an Anglo-Dutch philosopher, political economist and satirist. Born in Rotterdam, Netherlands, he lived most of his life in England and used English for most of his published works. He became famous for ''The Fable of the Bees''. Life Mandeville was born on 15 November 1670, at Rotterdam in the Netherlands, where his father was a prominent physician of Huguenot origin. On leaving the Erasmus school at Rotterdam he showed his ability by an ''Oratio scholastica de medicina'' (1685), and at Leiden University in 1689 he produced the thesis ''De brutorum operationibus'', in which he advocated the Cartesian theory of automatism among animals. In 1691 he took his medical degree, pronouncing an inaugural disputation, ''De chylosi vitiata''. He moved to England to learn the language, and succeeded so remarkably that many refused to believe he was a foreigner. His father had been banished from Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
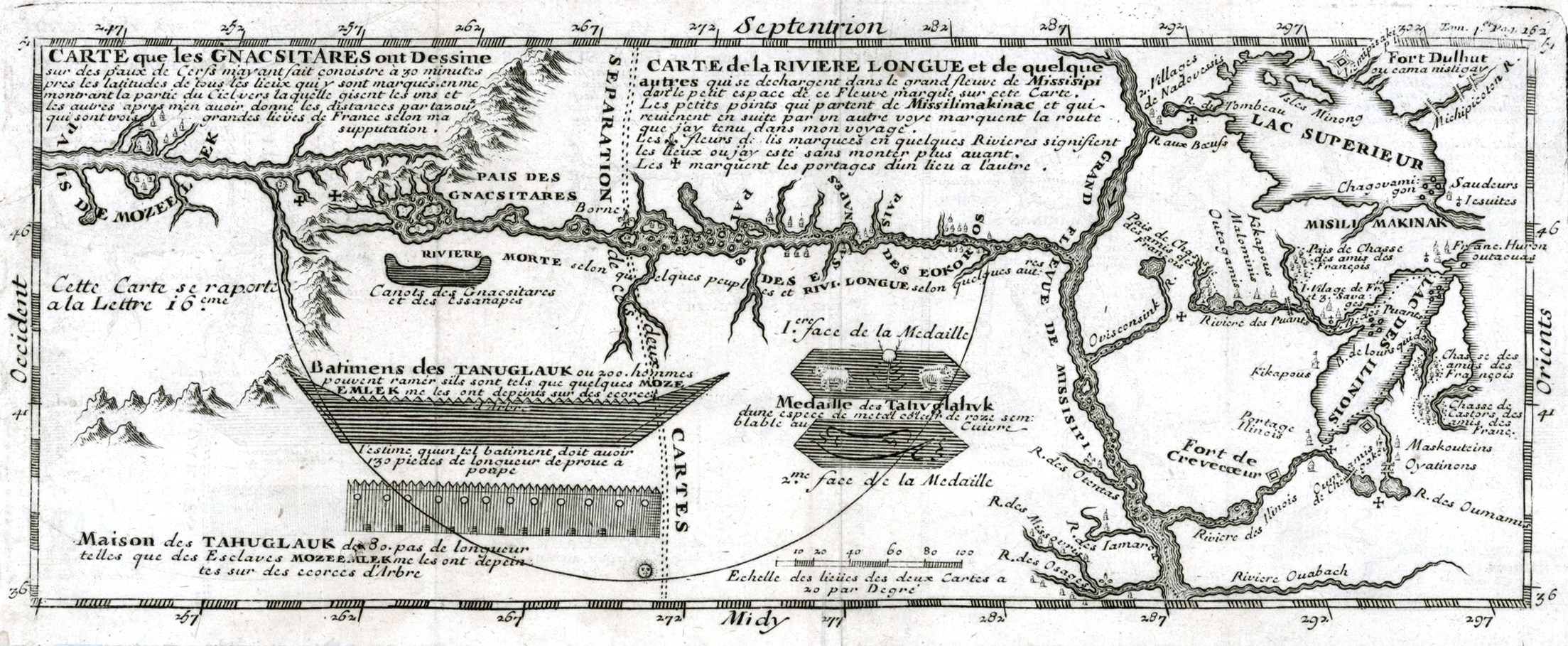
New Voyages To North America
''New Voyages to North America'' is a book by Louis-Armand de Lom d'Arce de Lahontan, Baron de Lahontan, Louis Armand de Lom d’Arce, baron de Lahontan that chronicles his nine years exploring New France as a soldier in the French Army. Published in two volumes in 1703 as ''Nouveaux Voyages de M. le Baron de Lahontan dans l’Amérique Septentrionale'', it was translated into English the same year. Considered the best work on 17th century New France for its detailed descriptions of the environment and North American native society, the book includes accounts of the two winters Lahontan spent hunting with a group of the Algonquin people. Lahontan expresses his opinions of New France and the natives, as well as of European society, through dialogue between himself and "Adario", a fictional native based on the Huron chief Kondiaronk. The volumes provide historical perspective on the landscape, the native peoples, and the developing economic, social, and political involvements of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Armand De Lom D'Arce De Lahontan, Baron De Lahontan
Louis Armand, Baron de Lahontan (9 June 1666 – prior to 1716) served in the French military in Canada where he traveled extensively in the Wisconsin and Minnesota region and the upper Mississippi Valley. Upon his return to Europe he wrote an enormously popular travelogue. In it he recounted his voyage up the "Long River," now thought to be the Missouri. He wrote at length and in very positive terms about Native American culture, portraying Indian people as free, rational, and generally admirable. Early life He was born into the aristocracy and inherited the title Baron Lahontan upon his father's death in 1674. De Lahontan joined the troupes de la marine and was sent to New France in 1683 at age 17 along with two other officers and three companies of troops.Lanctôt, Gustave. The Oakes Collection. Ottawa: J.O. Patenaude, 1940. 11. After arriving at Quebec in November and settling in Beaupré, he would lead his company in 1684 on an unsuccessful offense against the Iroquois from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Hoadly
Benjamin Hoadly (14 November 1676 – 17 April 1761) was an English clergyman, who was successively Bishop of Bangor, of Hereford, of Salisbury, and finally of Winchester. He is best known as the initiator of the Bangorian Controversy. Life He was educated at St Catharine's College, Cambridge and ordained a priest in 1700. He was rector of St Peter-le-Poer, London, from 1704 to 1724, and of St Leonard's, Streatham, from 1710 to 1723. His participation in controversy began at the beginning of his career, when he advocated conformity of the religious rites from the Scottish and English churches for the sake of union. He became a leader of the low church and found favour with the Whig party. He battled with Francis Atterbury, who was the spokesman for the high church group and Tory leader on the subject of passive obedience and non-resistance (i.e. obedience of divines that would not involve swearing allegiance or changing their eucharistic rites but would also not invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Hickes (divine)
George Hickes (20 June 1642 O.S. – 15 December 1715 O.S.) was an English divine and scholar. Biography Hickes was born at Newsham, near Thirsk, Yorkshire, in 1642. After going to school at Thirsk he went to Northallerton Grammar School in 1652 where he was a classmate of Thomas Rymer. In 1659 he entered St John's College, Oxford, whence after the Restoration he removed to Magdalen College and then to Magdalen Hall. In 1664 he was elected fellow of Lincoln College, and in the following year proceeded M.A. In 1673 he graduated in divinity, and in 1675 he was appointed rector of St Ebbes, Oxford. In 1676, as private chaplain, he accompanied the Duke of Lauderdale, the royal commissioner, to Scotland, and shortly afterwards received the degree of D.D. from St Andrews. In 1680 he became vicar of All Hallows, Barking, London; and after having been made chaplain to the king in 1681, he was in 1683 promoted to the deanery of Worcester. He opposed both James II's declaration of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |