|
0 To 60 Mph
The time it takes a vehicle to accelerate from 0 to 60 miles per hour (0 to 97 km/h or 0 to 27 m/s), often said just "zero to sixty", is a commonly used performance measure for automotive acceleration in the United States and the United Kingdom. In the rest of the world, 0 to 100 km/h (0 to 62.1 mph) is used. Present performance cars are capable of going from 0 to 60 mph in under 5 seconds, while exotic cars can do 0 to 60 mph in between 2 and 3 seconds, whereas motorcycles have been able to achieve these figures with sub-500 cc since the 1990s. The fastest automobile in 2015 was the Porsche 918 Spyder, which is a hybrid vehicle taking 2.2 seconds to accelerate from 0 to 60 mph. In June 2021, the Tesla Model S was measured to accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in 1.98 seconds, not including first foot of rollout. Methods Measuring the 0 to 60 mph speed of vehicles is usually done in a closed setting such as a race car track or closed lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilometres Per Hour
The kilometre per hour ( SI symbol: km/h; non-standard abbreviations: kph, km/hr) is a unit of speed, expressing the number of kilometres travelled in one hour. History Although the metre was formally defined in 1799, the term "kilometres per hour" did not come into immediate use – the myriametre () and myriametre per hour were preferred to kilometres and kilometres per hour. In 1802 the term "''myriamètres par heure''" appeared in French literature. The Dutch on the other hand adopted the kilometre in 1817 but gave it the local name of the ''mijl'' ( Dutch mile). Notation history The SI representations, classified as symbols, are "km/h", "" and "". Several other abbreviations of "kilometres per hour" have been used since the term was introduced and many are still in use today; for example, dictionaries list "kph", "kmph" and "km/hr" as English abbreviations. While these forms remain widely used, they are explicitly disallowed by the International Bureau of Weights and Measur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jalopnik
G/O Media Inc. is an American media holding company that runs ''Gizmodo'', ''Kotaku'', ''Jalopnik'', '' Deadspin'', ''Lifehacker'', '' Jezebel'', '' The Root'', '' The A.V. Club'', ''The Takeout'', '' The Onion'', and ''The Inventory''. History G/O was formed in April 2019 when Great Hill Partners, a private equity firm, purchased the websites from Univision for $20.6 million. Prior to the sale, the former Gawker Media properties had operated as Gizmodo Media Group after being acquired by Univision following the conclusion of the '' Bollea v. Gawker'' lawsuit and subsequent bankruptcy in 2016. Former ''Forbes'' executive Jim Spanfeller became the CEO of G/O Media. Conflict with leadership G/O Media's leadership, introduced after the purchase from Univision, has been subject to frequent criticism by employees. Complaints include closer advertiser relationships, a lack of diversity, and suppression of reporting about the company itself. In October 2019 Deadspin's editor-in-ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorcycle Testing And Measurement
Motorcycle testing and measurement includes a range of more than two dozen statistics giving the specifications of the motorcycle, and the actual performance, expressed by such things as the output of the engine, and the top speed or acceleration of the motorcycle. Most parameters are uncontroversial and claims made by manufacturers are generally accepted without verification. These might include simple measurements like rake, trail, or wheelbase, or basic features, such as the type of brakes or ignition system. Other measurements are often doubted or subject to misunderstandings, and the motorcycling press serves as an independent check on sometimes unrealistic sales and marketing claims. Many of these numbers are subject to variable methods of measurements, or disagreement as to the definition of the statistic. The parameters most often in contention for motorcycles are the weight, the engine output (power and torque), and the overall performance, especially acceleration, top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicular Metrics
There are a broad range of metrics that denote the relative capabilities of various vehicle A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles (motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles (trains, trams), ...s. Most of them apply to all vehicles while others are type-specific. See also * * * * * * References External linksCar Performance Meters {{DEFAULTSORT:Vehicle Metrics Vehicles Metrics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
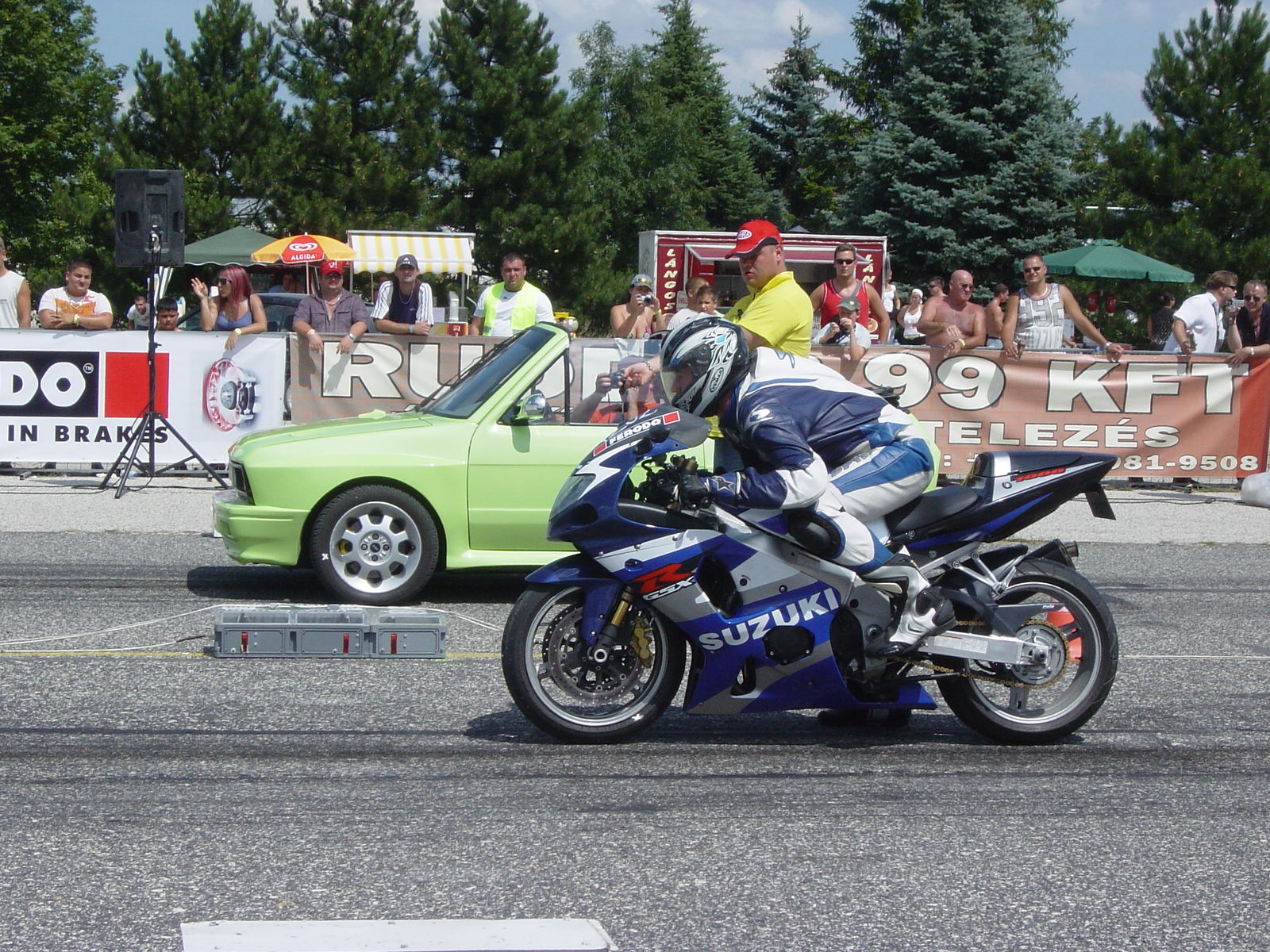
List Of Fastest Production Motorcycles By Acceleration
This is a list of street legal production motorcycles ranked by acceleration from a standing start, limited to 0 to 60 mph times of under 3.5 seconds, and -mile times of under 12 seconds. Concept, custom, modified, and one-off motorcycles of any kind are not listed, nor are racing-only motorcycles. The widely varying testing methodologies mean that, even between identical motorcycles, the acceleration times vary. Some of these differences include: rider skill and launching technique, measuring equipment, track surface conditions, weather, air temperature, and altitude. By 0–60 mph, 3.5 seconds or less Notes specify if test was or . For comparison, an object in free fall, without any air resistance, near the Earth's surface accelerates from 0–100 km/h in 2.83 seconds and from 0–60 mph in 2.73 seconds. *Note model year 2013-2016 documented 0-60 mph times for Ducati Diavel is marked 2.5-2.8 seconds depending on source. If more reliable/consistent sources be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fastest Production Cars By Acceleration
This list is limited to unmodified production cars which meet the eligibility criteria below. All entries must be able to be verified from reliable sources. Up to one percent decline from start to finish is allowed. Times driven privately or by manufacturers need the presence of an independent, reliable source or at least some video footage to confirm the car and tire condition to qualify as independent. Eligible cars Because of the inconsistencies with the various definitions of production cars, dubious claims by manufacturers and self-interested groups, and inconsistent or changing application of the definitions, this list has a defined set of requirements. For further explanation of how these were arrived at see the links above. Production car definition For the purposes of this list a production car is defined as: # Being constructed principally for retail sale to consumers for their personal use, and to transport people on public roads (no commercial or industrial vehicles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-foot Rollout
Rollout or rollout allowance in North-American drag racing is the difference between actual acceleration time and measured acceleration time. For the published 0 to 60 mph acceleration time in North America, a rolling start is used, beginning after the initial standing start position. The method approximates the behaviour of dragstrip measurement equipment for 1/4 mile racing, which was historically limited to only recording after the vehicle had passed over a start line. This leads to a 0.2–0.3-second apparent difference, with larger wheel sizes giving a larger exaggeration in timing. History Historically acceleration measurement took place using dragstrip equipment placed over a measured distance, with a light gate at the start and end. These light gates measured the point in time at which a vehicle passed the measurement point, rather than the point at which movement (acceleration) first occurred leading to a slightly faster apparent time. Standardization With the advent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling Start
A rolling start is one of two modes of initiating or restarting an auto race; the other mode is the standing start. In a rolling start, the cars are ordered on the track and are led on a certain number of laps (parade or caution laps) at a pre-determined safe speed by the safety car. Procedure When race conditions are ready, the safety car will leave the track, and the race marshal will show the green flag, indicating that the field is allowed to accelerate. The safety car typically leaves the track some distance before the finish line, and a few seconds may elapse between the safety car's departure and the showing of the green flag. Cars must wait for the green flag to accelerate to race speeds. In the past, drivers would need to look for the flag, but in modern times this information is typically communicated to drivers via two-way radio, or at the proper acceleration zone, marked by a line or cone, determined at the pre-race drivers and mechanics briefing. In international-le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exotic Car
A supercar – also called exotic car – is a loosely defined description of street-legal, high-performance sports cars. Since the 2010s, the term hypercar has come into use for the highest performing supercars. Supercars commonly serve as the flagship model within a vehicle manufacturer's line-up of sports cars and typically feature various performance-related technology derived from motorsports. Some examples include the Ferrari 458 Italia, Lamborghini Aventador, and McLaren 720S. In the United States, muscle cars were often referred to as "supercars" during the 1960s. History Europe The Lamborghini Miura, produced from 1966–1973, is often said to be the first supercar. By the 1970s and 1980s the term was in regular use, if not precisely defined. One interpretation up until the 1990s was to use it for mid-engine two-seat cars with at least eight cylinders (but typically a V12 engine), a power output of at least and a top speed of at least . Other interpretations stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
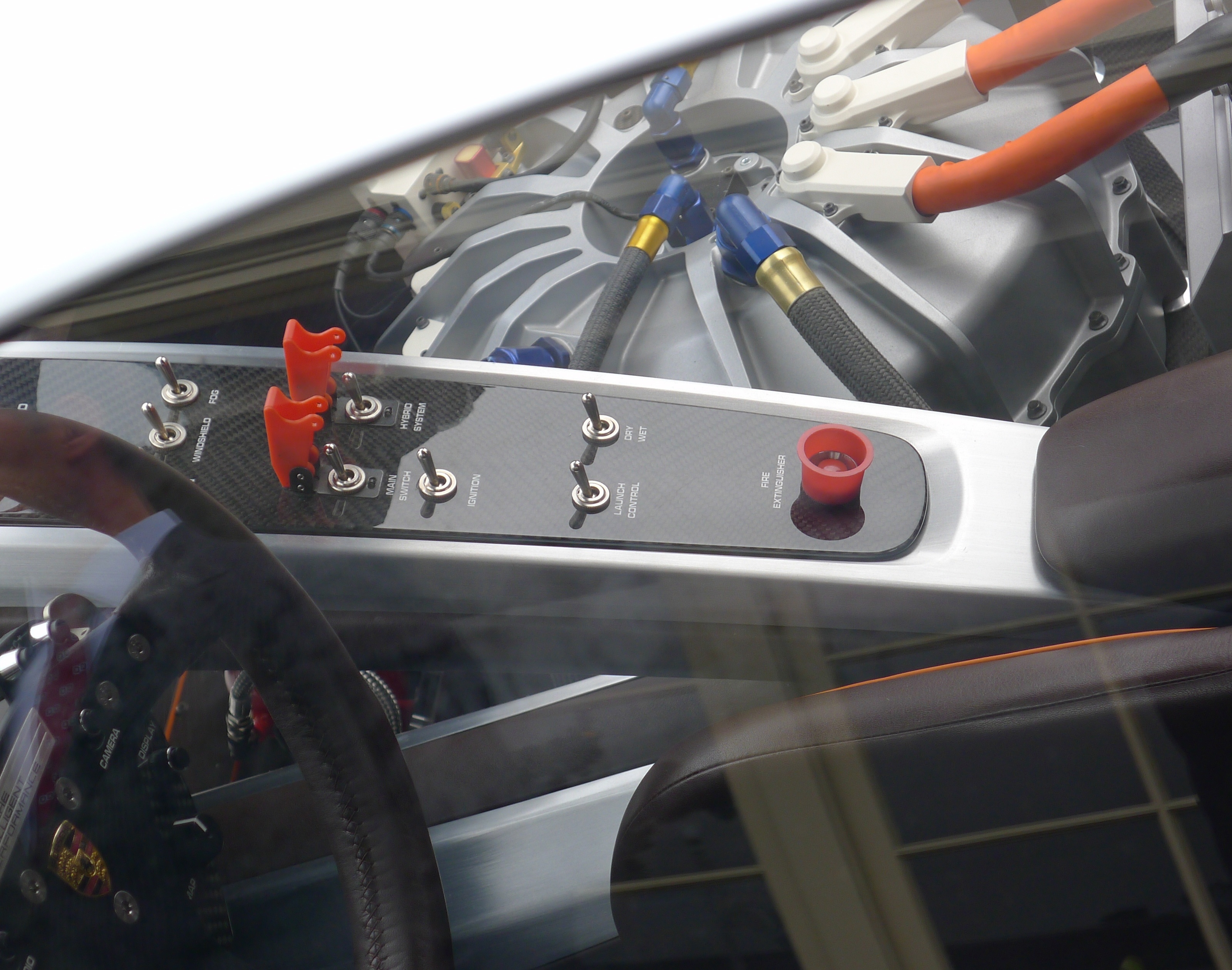
Launch Control (automotive)
Launch control is an electronic aid to assist drivers of both racing and street cars to accelerate from a standing start. Motorcycles have been variously fitted with mechanical and electronic devices for both street and race. Popular automobiles with launch control include the BMW M series, certain marques of the Volkswagen Group with Direct-Shift Gearbox (most notably the Bugatti Veyron), Porsche 911 (sport+ mode), Panamera Turbo, Alfa Romeo with TCT gearbox and certain General Motors products. Mitsubishi also incorporated launch control into their Twin Clutch SST gearbox, on its "S-Sport" mode, but the mode is only available in the Evolution X MR and MR Touring (USDM). The Jaguar F-Type includes launch control. The Nissan GT-R has electronics to control launch but the company does not use the term "launch control" since some owners have equated the term with turning off the stability control to launch the car, which may void the warranty of the drivetrain. One version of Nis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Gun
A radar speed gun (also radar gun and speed trap gun) is a device used to measure the speed of moving objects. It is used in law-enforcement to measure the speed of moving vehicles and is often used in professional spectator sport, for things such as the measurement of bowling speeds in cricket, speed of pitched baseballs, and speed of tennis serves. A radar speed gun is a Doppler radar unit that may be hand-held, vehicle-mounted or static. It measures the speed of the objects at which it is pointed by detecting a change in frequency of the returned radar signal caused by the Doppler effect, whereby the frequency of the returned signal is increased in proportion to the object's speed of approach if the object is approaching, and lowered if the object is receding. Such devices are frequently used for speed limit enforcement, although more modern LIDAR speed gun instruments, which use pulsed laser light instead of radar, began to replace radar guns during the first decade of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre Per Second
The metre per second is the unit of both speed (a scalar quantity) and velocity (a vector quantity, which has direction and magnitude) in the International System of Units (SI), equal to the speed of a body covering a distance of one metre in a time of one second. The SI unit symbols are m/s, m·s−1, m s−1, or . Sometimes it is abbreviated as "mps". Conversions is equivalent to: : = 3.6 km/h (exactly) : ≈ 3.2808 feet per second (approximately) : ≈ 2.2369 miles per hour (approximately) : ≈ 1.9438 knots (approximately) 1 foot per second = (exactly) 1 mile per hour = (exactly) 1 km/h = (exactly) Relation to other measures The benz, named in honour of Karl Benz, has been proposed as a name for one metre per second. Although it has seen some support as a practical unit, primarily from German sources, it was rejected as the SI unit of velocity and has not seen widespread use or acceptance. Unicode character The "metre per second" symbol is encoded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)