|
žŁž│┘å ž¦┘äž┤ž¦┘üž╣┘Ŗ
Hassan or Hasan ( ar, žŁž│┘å ) is an Arabic masculine given name in the Muslim world. As a surname, Hassan may be Arabic, Irish, Scottish, or Jewish (Sephardic and Mizrahic) (see Hassan (surname)). Etymology and spelling The name Hassan in Arabic means 'handsome' or 'good', or 'benefactor'. There are two different Arabic names that are both romanized with the spelling "Hassan". However, they are pronounced differently, and in Arabic script spelled differently. * The more common name ' (as in the name of the Islamic prophet Muhammad's grandson Hasan ibn Ali), coming from the Arabic language triconsonantal root ßĖż-S-N, has two short vowels and a single . Its meaning is 'the good' or 'the handsome'. Its usual form in Classical Arabic is ž¦┘䞣ž│┘å ''al-ßĖżasan'', incorporating the definite article ''al-'', which may be omitted in modern Arabic names. * The name ', which comes from the same Arabic root, has a long vowel and a doubled . Its meaning is 'doer of good' or 'bene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasan Ibn Ali
Hasan ibn Ali ( ar, ž¦┘䞣ž│┘å ž©┘å ž╣┘ä┘Ŗ, translit=Al-ßĖżasan ibn ╩┐Al─½; ) was a prominent early Islamic figure. He was the eldest son of Ali and Fatima and a grandson of the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. He briefly ruled as Caliphate, caliph from January 661 until August 661. He is considered as the second Imamate in Shia doctrine, Imam in Shia Islam, succeeding Ali and preceding his brother Husayn ibn Ali, Husayn. As a grandson of the prophet, he is part of the and the , also is said to have participated in the event of Mubahala. During the Ali as Caliph, caliphate of Ali (), Hasan accompanied him in the military campaigns of the First Fitna, First Muslim Civil War. After Assassination of Ali, Ali's assassination in 661, Hasan was acknowledged caliph in Kufa. His sovereignty was not recognized by Syria's governor Mu'awiya I (), who led an army into Kufa while pressing Hasan for abdication in letters. In response, Hasan sent a vanguard und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hassan II Of Morocco
Hassan II ( ar, ž¦┘䞣ž│┘å ž¦┘äž½ž¦┘å┘Ŗ, translit=al-ßĖżasan aß╣»-ß╣»h─ün─½;), with the prefix "Mulay" before his enthronement 9 July 1929 ŌĆō 23 July 1999) was the King of Morocco from 1961 until his death in 1999. He was a member of the 'Alawi dynasty. He was the eldest son of Sultan Mohammed V, and his second wife, Lalla Abla bint Tahar. He was the first commander-in-chief of the Royal Armed Forces and was named crown prince in 1957. He was enthroned as king in 1961 following his father's death. Hassan's reign was marked by the start of the Western Sahara conflict and the Sand War. He was also the target of two failed coup d'├®tats that were opposed to the absolute monarchy in Morocco: one in 1971 and the other in 1972. Hassan's conservative rule reportedly strengthened the 'Alawi dynasty's rule over Morocco and Western Sahara. He was accused of authoritarian practices and civil rights abuses, particularly during the Years of Lead. A truth commission was set up after his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swahili Language
Swahili, also known by its local name , is the native language of the Swahili people, who are found primarily in Tanzania, Kenya and Mozambique (along the East African coast and adjacent litoral islands). It is a Bantu language, though Swahili has borrowed a number of words from foreign languages, particularly Arabic, but also words from Portuguese, English and German. Around forty percent of Swahili vocabulary consists of Arabic loanwords, including the name of the language ( , a plural adjectival form of an Arabic word meaning 'of the coast'). The loanwords date from the era of contact between Arab slave traders and the Bantu inhabitants of the east coast of Africa, which was also the time period when Swahili emerged as a lingua franca in the region. The number of Swahili speakers, be they native or second-language speakers, is estimated to be approximately 200 million. Due to concerted efforts by the government of Tanzania, Swahili is one of three official languages (th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
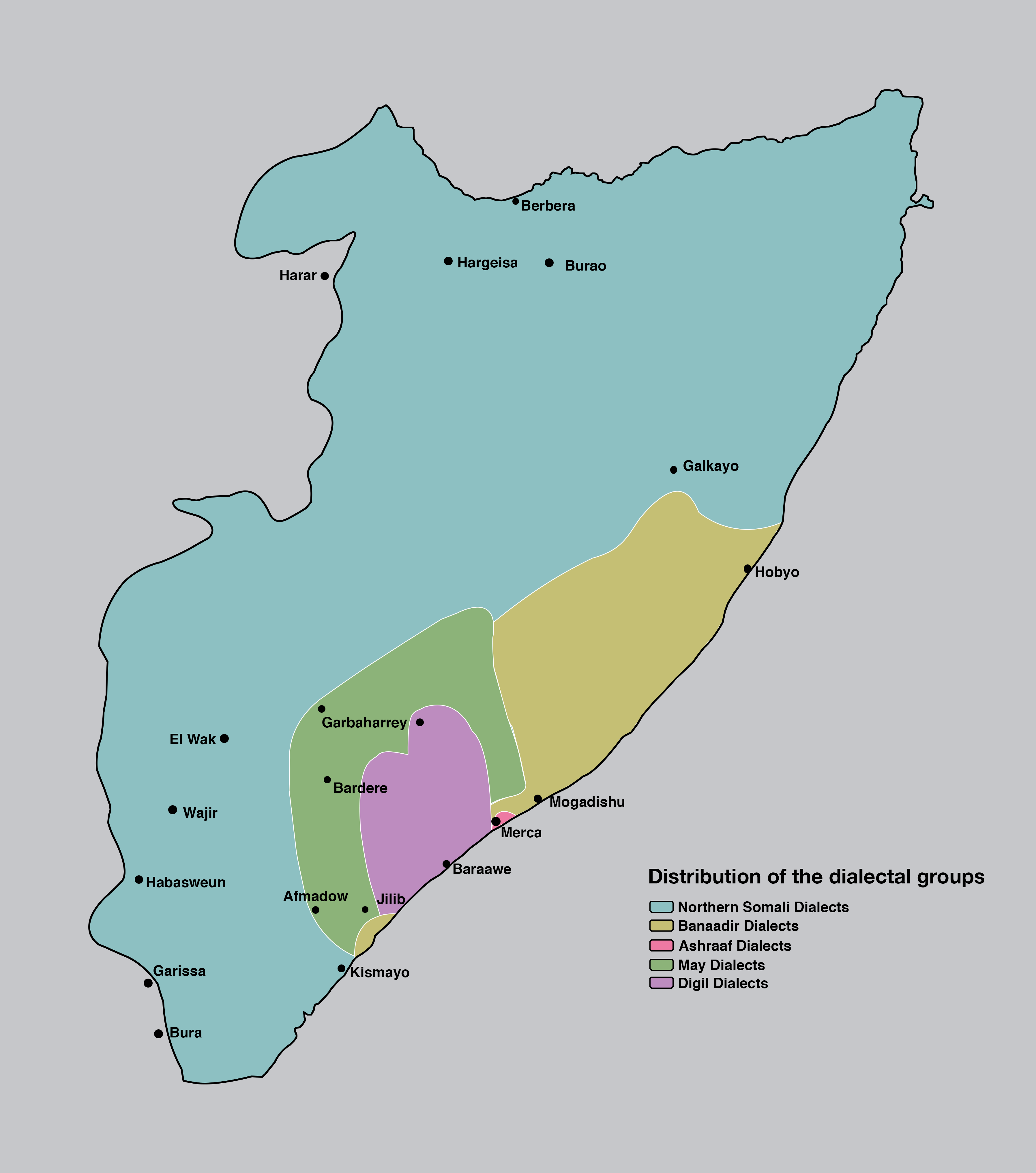
Somali Language
Somali (Latin script: ; Wadaad writing, Wadaad: ; Osmanya: ÉÆ¢ÉÆŹ ÉÆłÉÆØÉÆæÉÆøÉÆÉÉÆś ) is an Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic languages, Cushitic branch. It is spoken as a mother tongue by Somalis in Greater Somalia and the Somali diaspora. Somali is an official language in Somalia and Ethiopia, and a national language in Djibouti as well as in northeastern Kenya. The Somali language is written officially with the Somali Latin alphabet, Latin alphabet although the Arabic alphabet and several Somali scripts like Osmanya script, Osmanya, Kaddare script, Kaddare and the Gadabuursi Somali Script, Borama script are informally used.Lewis, I.M. (1958)The Gadabuursi Somali Script ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London, Vol. 21, pp. 134ŌĆō156. Classification Somali is classified within the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family, specifically, Lowland East Cushitic languages, Lowland East Cushitic in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkmen Language
Turkmen (, , , or , , , ), sometimes referred to as "Turkmen Turkic" or "Turkmen Turkish", is a Turkic language spoken by the Turkmens of Central Asia, mainly of Turkmenistan, Iran, and Afghanistan. It has an estimated 5 million native speakers in Turkmenistan, a further 719,000 speakers in northeastern Iran, 1.5 million people in northwestern Afghanistan and 155,000 in Pakistan. Turkmen has official status in Turkmenistan, but it does not have official status in Iran, Afghanistan, or Pakistan, where big communities of ethnic Turkmens live. Turkmen is also spoken to lesser varying degrees in Turkmen communities of Uzbekistan and Tajikistan and by diaspora communities, primarily in Turkey and Russia. Turkmen is a member of the Oghuz branch of the Turkic languages. The standardized form of Turkmen (spoken in Turkmenistan) is based on the Teke dialect, while Iranian Turkmen use mostly the Yomud dialect, and Afghan Turkmen use Ersary variety. Turkmen is closely related to Azerb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uyghur Khaganate
The Uyghur Khaganate (also Uyghur Empire or Uighur Khaganate, self defined as Toquz-Oghuz country; otk, É▒āÉ░åÉ░┤É░Ģ:É░åÉ░ŹÉ░Ģ:É░ēÉ░åÉ░æÉ░Ż, Toquz O╬│uz budun, Tang-era names, with modern Hanyu Pinyin: or ) was a Turkic empire that existed for about a century between the mid 8th and 9th centuries. They were a tribal confederation under the Orkhon Uyghur () nobility, referred to by the Chinese as the ''Jiu Xing'' ("Nine Clans"), a calque of the name ''Toquz Oghuz'' or ''Toquz Tughluq''. History Rise In 657, the Western Turkic Khaganate was defeated by the Tang dynasty, after which the Uyghurs defected to the Tang. Prior to this the Uyghurs had already shown an inclination towards alliances with the Tang when they fought with them against the Tibetan Empire and Turks in 627. In 742, the Uyghurs, Karluks, and Basmyls rebelled against the Second Turkic Khaganate. In 744, the Basmyls captured the Turk capital of ├¢t├╝ken and killed the reigning ├¢zmi┼¤ Khagan. Later t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Language
Turkish ( , ), also referred to as Turkish of Turkey (''T├╝rkiye T├╝rk├¦esi''), is the most widely spoken of the Turkic languages, with around 80 to 90 million speakers. It is the national language of Turkey and Northern Cyprus. Significant smaller groups of Turkish speakers also exist in Iraq, Syria, Germany, Austria, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Greece, the Caucasus, and other parts of Europe and Central Asia. Cyprus has requested the European Union to add Turkish as an official language, even though Turkey is not a member state. Turkish is the 13th most spoken language in the world. To the west, the influence of Ottoman TurkishŌĆöthe variety of the Turkish language that was used as the administrative and literary language of the Ottoman EmpireŌĆöspread as the Ottoman Empire expanded. In 1928, as one of Atat├╝rk's Reforms in the early years of the Republic of Turkey, the Ottoman Turkish alphabet was replaced with a Latin alphabet. The distinctive characteristics of the Turk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaysian Language
Malaysian Malay ( ms, Bahasa Melayu Malaysia), also known as Standard Malay (Malay: ''Bahasa Melayu Standard''), ( English translation: Malaysian language), or simply Malay, is a standardized form of the Malay language used in Malaysia (as opposed to the variety used in Indonesia, which is referred to as the "Indonesian" language). Malaysian Malay is standardized from the Johore-Riau dialect of Malay. It is spoken by much of the Malaysian population, although most learn a vernacular form of Malay or another native language first. Malay is a compulsory subject in primary and secondary schools. Status In Malaysia Article 152 of the Federation designates "Malay" as the official language, but the term "Malaysian" or ''bahasa Malaysia'' is used on official contexts from time to time. The choice of name can be politically contentious; in 1999 the Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka rejected the publication of some short stories as the preface to the publication used the term ''bahasa Mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesian Language
Indonesian ( ) is the official language, official and national language of Indonesia. It is a standard language, standardized variety (linguistics), variety of Malay language, Malay, an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language that has been used as a lingua franca in the multilingual Indonesian archipelago for centuries. Indonesia is the fourth most list of countries by population, populous nation in the world, with over 270 million inhabitantsŌĆöof which the majority speak Indonesian, which makes it one of the most List of languages by total number of speakers, widely spoken languages in the world.James Neil Sneddon. ''The Indonesian Language: Its History and Role in Modern Society''. UNSW Press, 2004. Most Indonesians, aside from speaking the national language, are fluent in at least one of the more than 700 indigenous languages of Indonesia, local languages; examples include Javanese language, Javanese and Sundanese language, Sundanese, which are commonly used at home a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdish Languages
Kurdish (, ) is a language or a group of languages spoken by Kurds in the geo-cultural region of Kurdistan and the Kurdish diaspora. Kurdish constitutes a dialect continuum, belonging to Western Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. The main three dialects or languages of Kurdish are Northern Kurdish (), Central Kurdish (), and Southern Kurdish (). A separate group of non-Kurdish Northwestern Iranian languages, the ZazaŌĆōGorani languages, are also spoken by several million ethnic Kurds.Kaya, Mehmet. The Zaza Kurds of Turkey: A Middle Eastern Minority in a Globalised Society. The majority of the Kurds speak Kurmanji, and most Kurdish texts are written in Kurmanji and Sorani. Kurmanji is written in the Hawar alphabet, a derivation of the Latin script, and Sorani is written in the Sorani alphabet, a derivation of Arabic script. The classification of Laki as a dialect of Southern Kurdish or as a fourth language under Kurdish is a matter of debate, but the diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakh Language
The Kazakh or simply Qazaq (Latin: or , Cyrillic: or , Arabic Script: or , , ) is a Turkic language of the Kipchak branch spoken in Central Asia by Kazakhs. It is closely related to Nogai, Kyrgyz and Karakalpak. It is the official language of Kazakhstan and a significant minority language in the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture in Xinjiang, north-western China and in the Bayan-Ûlgii Province of western Mongolia. The language is also spoken by many ethnic Kazakhs throughout the former Soviet Union (some 472,000 in Russia according to the 2010 Russian Census), Germany, and Turkey. Like other Turkic languages, Kazakh is an agglutinative language and employs vowel harmony. '' Ethnologue'' recognizes three mutually intelligible dialect groups, Northeastern Kazakh, the most widely spoken variety which also serves as the basis for the standard language, Southern Kazakh and Western Kazakh. The language share a degree of mutual intelligiblity with closely related Karakalpak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |