|
Cyrillic Script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin and Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of tsar Simeon I the Great, probably by disciples of the two Byzantine brothers Saint Cyril and Saint Methodius, who had previously created the Glagoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarusian Language
Belarusian ( be, беларуская мова, biełaruskaja mova, link=no, ) is an East Slavic language. It is the native language of many Belarusians and one of the two official state languages in Belarus. Additionally, it is spoken in some parts of Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, Poland, and Ukraine by Belarusian minorities in those countries. Before Belarus gained independence in 1991, the language was only known in English as ''Byelorussian'' or ''Belorussian'', the compound term retaining the English-language name for the Russian language in its second part, or alternatively as ''White Russian''. Following independence, it became known as ''Belarusan'' and since 1995 as ''Belarusian'' in English. As one of the East Slavic languages, Belarusian shares many grammatical and lexical features with other members of the group. To some extent, Russian, Rusyn, Ukrainian, and Belarusian retain a degree of mutual intelligibility. Its predecessor stage is known in Western aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. Besides Russia itself, Russian is an official language in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely as a lingua franca throughout Ukraine, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. It was the ''de facto'' language of the former Soviet Union, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 and continues to be used in public life with varying proficiency in all of the post-Soviet states. Russian has over 258 million total speakers worldwide. It is the most spoken Slavic language, and the most spoken native language in Europe, as well as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Language
Ukrainian ( uk, украї́нська мо́ва, translit=ukrainska mova, label=native name, ) is an East Slavic language of the Indo-European language family. It is the native language of about 40 million people and the official state language of Ukraine in Eastern Europe. Written Ukrainian uses the Ukrainian alphabet, a variant of the Cyrillic script. The standard Ukrainian language is regulated by the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine (NANU; particularly by its Institute for the Ukrainian Language), the Ukrainian language-information fund, and Potebnia Institute of Linguistics. Comparisons are often drawn to Russian, a prominent Slavic language, but there is more mutual intelligibility with Belarusian,Alexander M. Schenker. 1993. "Proto-Slavonic," ''The Slavonic Languages''. (Routledge). pp. 60–121. p. 60: " hedistinction between dialect and language being blurred, there can be no unanimity on this issue in all instances..."C.F. Voegelin and F.M. Voegelin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalmyk Language
Kalmyk Oirat ( xal-RU, Хальмг Өөрдин келн, links=no, ''Haľmg Öördin keln'', ), commonly known as the Kalmyk language ( xal-RU, Хальмг келн, links=no, ''Haľmg keln'', ), is a variety of the Oirat language, natively spoken by the Kalmyk people of Kalmykia, a federal subject of Russia. In Russia, it is the standard form of the Oirat language (based on the Torgut dialect), which belongs to the Mongolic language family. The Kalmyk people of the Northwest Caspian Sea of Russia claim descent from the Oirats from Eurasia, who have also historically settled in Mongolia and Northwest China. According to UNESCO, the language is "Definitely endangered". сән /sən/. Nevertheless, in inflected forms of such words, short vowels tend to become elongated: сән /sæn/ "good" > сәәг /sæːgə/ "good-", күн /kyn/ "man"> күүнә /kyːnæ/ "man-". Despite that, long vowels still may be pronounced in non-initial syllables. This happens if a word con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invasion, it was the eighth-most populous country in Europe, with a population of around 41 million people. It is also bordered by Belarus to the north; by Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary to the west; and by Romania and Moldova to the southwest; with a coastline along the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov to the south and southeast. Kyiv is the nation's capital and largest city. Ukraine's state language is Ukrainian; Russian is also widely spoken, especially in the east and south. During the Middle Ages, Ukraine was the site of early Slavic expansion and the area later became a key centre of East Slavic culture under the state of Kievan Rus', which emerged in the 9th century. The state eventually disintegrated into rival regional powers and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic Numerals
Cyrillic numerals are a numeral system derived from the Cyrillic script, developed in the First Bulgarian Empire in the late 10th century. It was used in the First Bulgarian Empire and by South and East Slavic peoples. The system was used in Russia as late as the early 18th century, when Peter the Great replaced it with arabic numerals as part of his civil script reform initiative. Cyrillic numbers played a role in Peter the Great's currency reform plans, too, with silver wire kopecks issued after 1696 and mechanically minted coins issued between 1700 and 1722 inscribed with the date using Cyrillic numerals. By 1725, Russian Imperial coins had transitioned to arabic numerals. The Cyrillic numerals may still be found in books written in the Church Slavonic language. General description The system is a quasi-decimal alphabetic numeral system, equivalent to the Ionian numeral system but written with the corresponding graphemes of the Cyrillic script. The order is based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short U
Short U (Ў ў; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. The only Slavic language using this letter in its orthography is Belarusian, though it is used as a phonetic symbol in some Russian and Ukrainian dictionaries. Among the non-Slavic languages using Cyrillic alphabets, ў is used in Dungan, Karakalpak, Karachay-Balkar, Mansi, Sakhalin Nivkh, Ossetian and Siberian Yupik. It is also used in Uzbek – this letter corresponds to Oʻ in the Uzbek Latin alphabet. Short U The letter originates from the letter izhitsa with a breve (Іереѵ̆ская власть, пучина Егеѵ̆ская, etc.) used in certain Ukrainian books at the end of the 16th and the beginning of the 17th centuries. Later, this character was probably in use in the Romanian Cyrillic script, from where it was borrowed in 1836 by the compilers of Ukrainian poetry book ''Rusalka Dnistrovaja'' (Русалка днѣстровая). The book's foreword reads “we have accepted Serbia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
We (Cyrillic)
We (Ԝ ԝ; italics: '''') is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In all of its forms it looks exactly like the Latin letter W (W w ''''). We is used in the Cyrillic orthography of the Kurdish language, in (some versions of the orthography of) the Yaghnobi language and in the Tundra Yukaghir language. Usage The pronunciations shown in the table are the primary ones for each language; for details consult the articles on the languages. Lowercase We is similar to some forms of Cyrillic Omega in appearance. Computing codes See also *Cyrillic characters in Unicode As of Unicode version 15.0 Cyrillic script is encoded across several blocks: * CyrillicU+0400–U+04FF 256 characters * Cyrillic SupplementU+0500–U+052F 48 characters * Cyrillic Extended-AU+2DE0–U+2DFF 32 characters * Cyrillic Extended-BU+A ... * Ѡ, a similar-looking letter in archaic Cyrillic texts for /o/ *W w : Latin letter W *Ў ў : Cyrillic letter Ў, another letter romanized as "W" Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Be (Cyrillic)
Be (Б italics: ''Б '') is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It commonly represents the voiced bilabial plosive , like the English pronunciation of in "ball". It should not be confused with the Cyrillic letter Ve (В в), which is shaped like Latin capital letter B but represents the voiced labiodental fricative . The Cyrillic letter Б (Be) is romanized using the Latin letter . History The Cyrillic letters Be and Ve (В в) were both derived from the Greek letter Beta (Β β). In the Early Cyrillic alphabet the name of the letter Be was (''buky/''), meaning "letter". In the Cyrillic numeral system, the letter Be had no numeric value because the letter Ve inherited the Greek letter Beta's numeric value. Form The Russian small letter (be) is similar (but not identical) in shape to the digit 6. Its lowercase form also somewhat resembles a lowercase letter B ("b"), the letter to which it corresponds in the Latin alphabet. After all, the lowerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izhitsa
Izhitsa or Izhica (Ѵ, ѵ; italics: ; OCS: Ѷжица, Russian: Ижица, Ukrainian: Іжиця) is a letter of the early Cyrillic alphabet and several later alphabets, usually the last in the row. It originates from the Greek letter upsilon (Y, υ) and was used in words and names derived from or via the Greek language, such as кѵрилъ (''kürilǔ'', "Cyril", from Greek Κύριλλος) or флаѵии (''flavii'', "Flavius", from Greek Φλάυιος). It represented the sounds or as normal letters и and в, respectively. The Glagolitic alphabet has a corresponding letter with the name ''izhitsa'' as well (Ⱛ, ⱛ). Also, izhitsa in its standard form or, most often, in a tailed variant (similar to Latin "y") was part of a digraph оѵ/оу representing the sound . The digraph is known as Cyrillic " uk", and today's Cyrillic letter u originates from its simplified form. The letter's traditional name, ''izhitsa'' (ижица), is explained as a diminutive eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
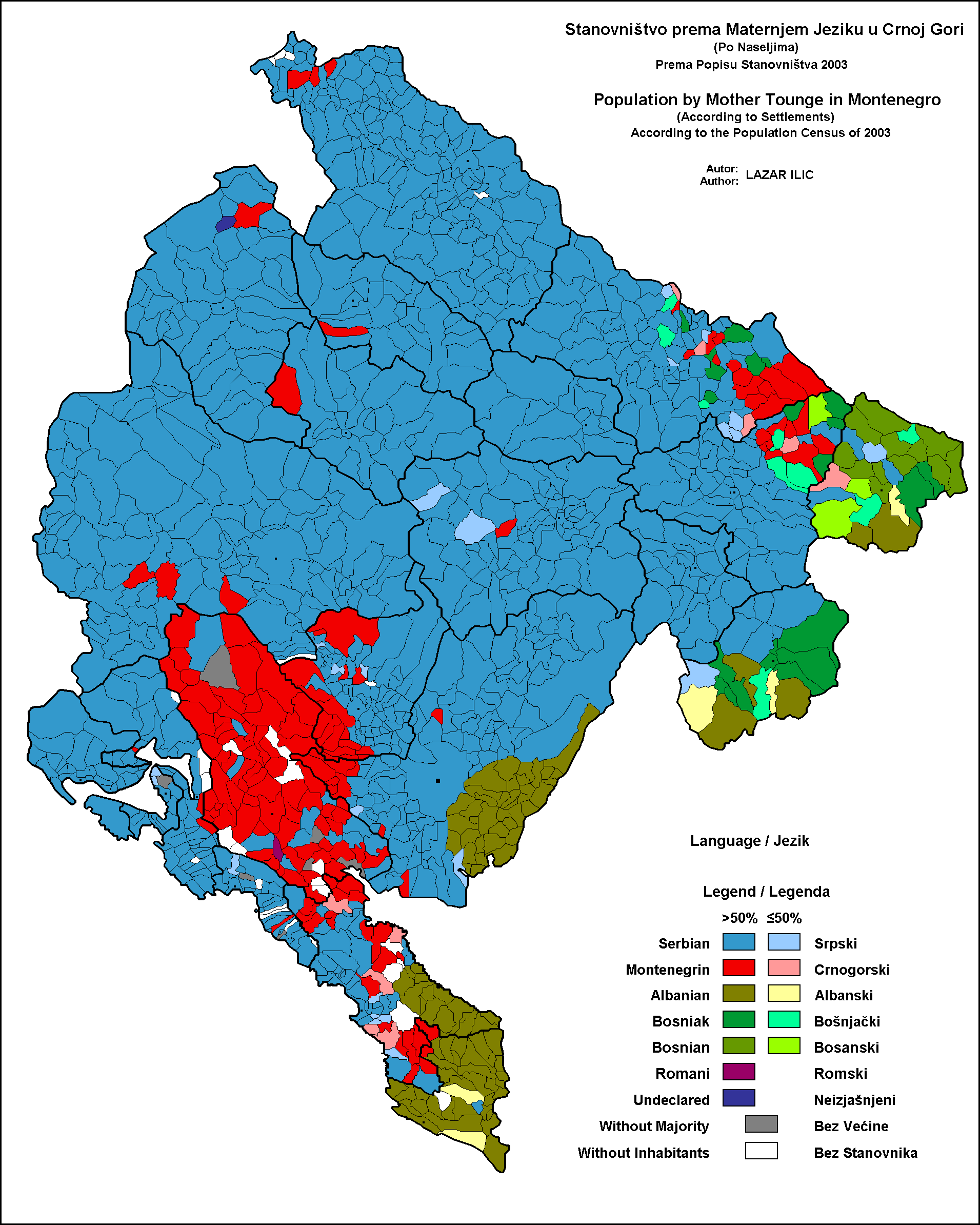
Montenegrin Language
Montenegrin ( ; cnr, label=none, / ) is a normative variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Montenegrins and is the official language of Montenegro. Montenegrin is based on the most widespread dialect of Serbo-Croatian, Shtokavian, more specifically on Eastern Herzegovinian, which is also the basis of Standard Croatian, Serbian, and Bosnian. Montenegro's language has historically and traditionally been called either Serbian or Montenegrin. The idea of a standardized Montenegrin standard language separate from Serbian appeared in the 1990s during the breakup of Yugoslavia, through proponents of Montenegrin independence from the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro. Montenegrin became the official language of Montenegro with the ratification of a new constitution on 22 October 2007. Language standardization In January 2008, the government of Montenegro formed the Board (Council) for Standardization of the Montenegrin Language, which aims to standardize the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |