|
α-ketobutyric Acid
α-Ketobutyric acid is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2C(O)CO2H. It is a colorless solid that melts just above room temperature. Its conjugate base α-ketobutyrate is the predominant form found in nature (near neutral pH). It results from the lysis of cystathionine. It is also one of the degradation products of threonine, produced by the catabolism of the amino acid by threonine dehydratase. It is also produced by the degradation of homocysteine and the metabolism of methionine. α-Ketobutyrate is transported into the mitochondrial matrix, where it is converted to propionyl-CoA by branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex. Further mitochondrial reactions produce succinyl-CoA. This is first through the enzyme mitochondria propionyl-CoA carboxylase with biotin as a cofactor to produce (''S'')-methylmalonyl-CoA. This is subsequently converted to (''R'')-methylmalonyl-CoA by mitochondrial methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase. Finally, mitochondrial methylmalonyl-CoA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylmalonyl-CoA Epimerase
Methylmalonyl-CoA is the thioester consisting of coenzyme A linked to methylmalonic acid. It is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of succinyl-CoA, which plays an essential role in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (aka the Citric Acid Cycle, or Krebs Cycle). Biosynthesis and metabolism Methylmalonyl-CoA results from the metabolism of fatty acid with an odd number of carbons, of amino acids valine, isoleucine, methionine, threonine or of cholesterol side-chains, forming Propionyl-CoA. The latter is also formed from propionic acid, which bacteria produce in the intestine. Propionyl-CoA and bicarbonate are converted to Methylmalonyl-CoA by the enzyme propionyl-CoA Carboxylase. It then is converted into succinyl-CoA by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MUT). This reaction is a reversible isomerization. In this way, the compound enters the Citric Acid Cycle. The following diagram demonstrates the aforementioned reaction: Propionyl CoA + Bicarbonate ‚Üí Methylmalonyl CoA ‚Üí Succin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Oxobutanoic Acid
Acetoacetic acid (IUPAC name: 3-oxobutanoic acid, also known as acetonecarboxylic acid or diacetic acid) is the organic compound with the formula CHCOCHCOOH. It is the simplest beta-keto acid, and like other members of this class, it is unstable. The methyl and ethyl esters, which are quite stable, are produced on a large scale industrially as precursors to dyes. Acetoacetic acid is a weak acid. Biochemistry Under typical physiological conditions, acetoacetic acid exists as its conjugate base, acetoacetate: : Unbound acetoacetate is primarily produced by liver mitochondria from its thioester with coenzyme A (CoA): : The acetoacetyl-CoA itself is formed by three routes: *3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA releases acetyl CoA and acetoacetate: *: *Acetoacetyl-CoA can come from beta oxidation of butyryl-CoA: *: *Condensation of pair of acetyl CoA molecules as catalyzed by thiolase. *: In mammals, acetoacetate produced in the liver (along with the other two "ketone bodies") is release ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxobutanoic Acid
{{Chemistry index ...
Ketobutyric acid, ketobutanoic acid, oxobutyric acid, or oxobutanoic acid may refer to the following chemical compounds: * α-Ketobutyric acid (2-oxobutyric acid) * β-Ketobutyric acid (acetoacetic acid or 3-oxobutyric acid) In addition, oxobutyric acid, or oxobutanoic acid may refer to: * 4-Oxobutanoic acid (succinic semialdehyde, 4-oxobutyric acid) See also * Dicarbonyl In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl () groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Hydroxybutyric Acid
2-Hydroxybutyric acid, is a hydroxybutyric acid with the hydroxyl group on the carbon adjacent to the carboxyl. It is a chiral compound having two enantiomers, D-2-hydroxybutyric acid and L-2-hydroxybutyric acid. Its conjugate base is known as ''alpha''-hydroxybutyrate and α-hydroxybutyrate. (R)-2-Hydroxybutanic Acid Structural Formula V1.svg, -2-hydroxybutyric acid, alt=Molecular diagram of 2-hydroxybutyric acid, with the central alcohol carbon labeled "(R)" (S)-2-Hydroxybutanic Acid Structural Formula V1.svg, -2-hydroxybutyric acid, alt=Molecular diagram of 2-hydroxybutyric acid, with the central alcohol carbon labeled "(S)" 2-Hydroxybutyrate, the conjugate base of 2-hydroxybutyric acid, is produced in mammalian tissues (principally hepatic) that catabolize L-threonine or synthesize glutathione. Oxidative stress or detoxification demands can dramatically increase the rate of hepatic glutathione synthesis. Under such metabolic stress conditions, supplies of L-cysteine for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
α-Aminobutyric Acid
α-Aminobutyric acid (AABA), also known as homoalanine in biochemistry, is a non-proteinogenic alpha amino acid with chemical formula C4H9NO2. The straight two carbon side chain is one carbon longer than alanine, hence the prefix homo-. The conjugate base of α-aminobutyric acid is the carboxylate α-aminobutyrate. Homoalanine is biosynthesized by transaminating oxobutyrate, a metabolite in isoleucine biosynthesis. It is used by nonribosomal peptide synthases. One example of a nonribosomal peptide containing homoalanine is ophthalmic acid, which was first isolated from calf lens. α-Aminobutyric acid is one of the three isomers of aminobutyric acid. The two other are the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and β-aminobutyric acid (BABA) which is known for inducing plant disease resistance Plant disease resistance protects plants from pathogens in two ways: by pre-formed structures and chemicals, and by infection-induced responses of the immune system. Relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butyric Acid
Butyric acid (; from , meaning "butter"), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula . It is an oily, colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. Isobutyric acid (2-methylpropanoic acid) is an isomer. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. The acid does not occur widely in nature, but its esters are widespread. It is a common industrial chemical and an important component in the mammalian gut. History Butyric acid was first observed in an impure form in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. However, Chevreul did not publish his early research on butyric acid; instead, he deposited his findings in manuscript form with the secretary of the Academy of Sciences in Paris, France. Henri Braconnot, another French chemist, was also researching the composition of butter and was publishing his findings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sotolon
Sotolon (also known as sotolone) is a butenolide lactone and an extremely potent aroma compound, with the typical smell of fenugreek or curry at high concentrations and maple syrup, caramel, or burnt sugar at lower concentrations. Sotolon is the major aroma and flavor component of fenugreek seed and lovage, and is one of several aromatic and flavor components of artificial maple syrup. It is also present in molasses, aged rum, aged sake and white wine, flor sherry, roast tobacco, and dried fruiting bodies of the mushroom '' Lactarius helvus''. Sotolon can pass through the body relatively unchanged, and consumption of foods high in sotolon, such as fenugreek, can impart a maple syrup aroma to one's sweat and urine. In some individuals with the genetic disorder maple syrup urine disease, sotolon is spontaneously produced in their bodies and excreted in their urine, leading to the disease's characteristic smell. This molecule is thought to be responsible for the mysterious maple s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vin Jaune
is a special and characteristic type of white wine made in the Jura (wine), Jura region in eastern France. It is similar to dry fino Sherry and gets its character from being matured in a barrel under a film of yeast (wine), yeast, known as the ''voile'', on the wine's surface. ''Vin jaune'' shares many similarities with Sherry, including some aromas (wine), aromas, but unlike Sherry, it is not a fortified wine. The wine is made from the Savagnin grape, with some of the most premium examples coming from the marl based vineyards in the Ch√¢teau-Chalon AOC. In other French wine regions, there has been experimentation in producing similar style wines from Chardonnay and other local List of grape varieties, grape varieties using cultured yeast such as the ''vin de voile'' wine produced in the Gaillac.J. Robinson (ed), ''"The Oxford Companion to Wine"'', Third Edition, p. 750, Oxford University Press 2006, Production Vin jaune is made from late harvest Savagnin grapes, a white vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-CoA Redox, oxidation. The energy released is available in the form of Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. The Hans Krebs (biochemist), Krebs cycle is used by organisms that generate energy via Cellular respiration, respiration, either anaerobic respiration, anaerobically or aerobic respiration, aerobically (organisms that Fermentation, ferment use different pathways). In addition, the cycle provides precursor (chemistry), precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NADH, which are used in other reactions. Its central importance to many Metabolic pathway, biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest metabolism components. Even though it is branded as a "cycle", it is not necessa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosylcobalamin
Adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), also known as coenzyme B12, cobamamide, and dibencozide, is one of the biologically active forms of vitamin B12. Adenosylcobalamin participates as a cofactor in radical-mediated 1,2-carbon skeleton rearrangements. These processes require the formation of the deoxyadenosyl radical through homolytic dissociation of the carbon-cobalt bond. This bond is exceptionally weak, with a bond dissociation energy of 31 kcal/mol, which is further lowered in the chemical environment of an enzyme active site. An enzyme that uses adenosylcobalamin as a coenzyme is methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MCM). Further experimentation has also determined adenosylcobalamin's role in regulating expression of some bacterial genes. By binding to CarH, AdoCbl can modulate carotenoid genes, which confer warm colors onto various plants. Carotenoid transcription is activated by sunlight, due to the response from AdoCbl. There are other photoreceptors across different bacterial communities, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
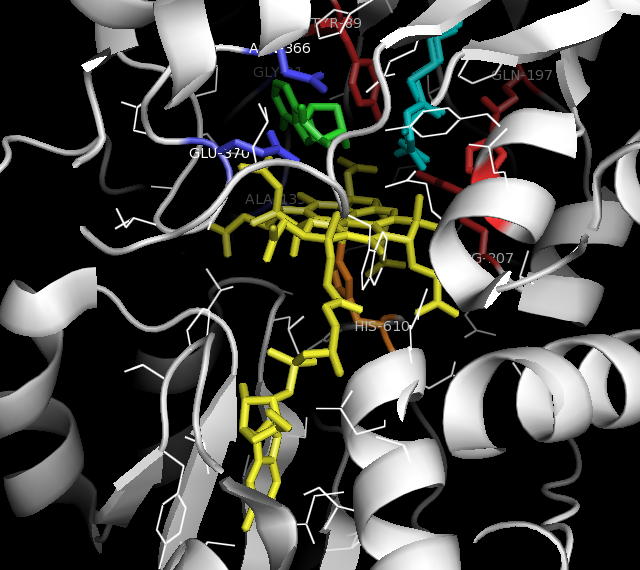
Methylmalonyl-CoA Mutase
Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (, MCM), mitochondrial, also known as methylmalonyl-CoA isomerase, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MUT'' gene. This vitamin B12-dependent enzyme catalyzes the isomerization of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA in humans. Mutations in ''MUT'' gene may lead to various types of methylmalonic aciduria. MCM was first identified in rat liver and sheep kidney in 1955. In its latent form, it is 750 amino acids in length. Upon entry to the mitochondria, the 32 amino acid mitochondrial leader sequence at the N-terminus of the protein is cleaved, forming the fully processed monomer. The monomers then associate into homodimers, and bind AdoCbl (one for each monomer active site) to form the final, active holoenzyme form. Structure Gene The ''MUT'' gene lies on the chromosome location of 6p12.3 and consists of 13 exons, spanning over 35kb. Protein The mature enzyme is a homodimer with the N-terminal CoA binding domain and the C- terminal cobala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |