|
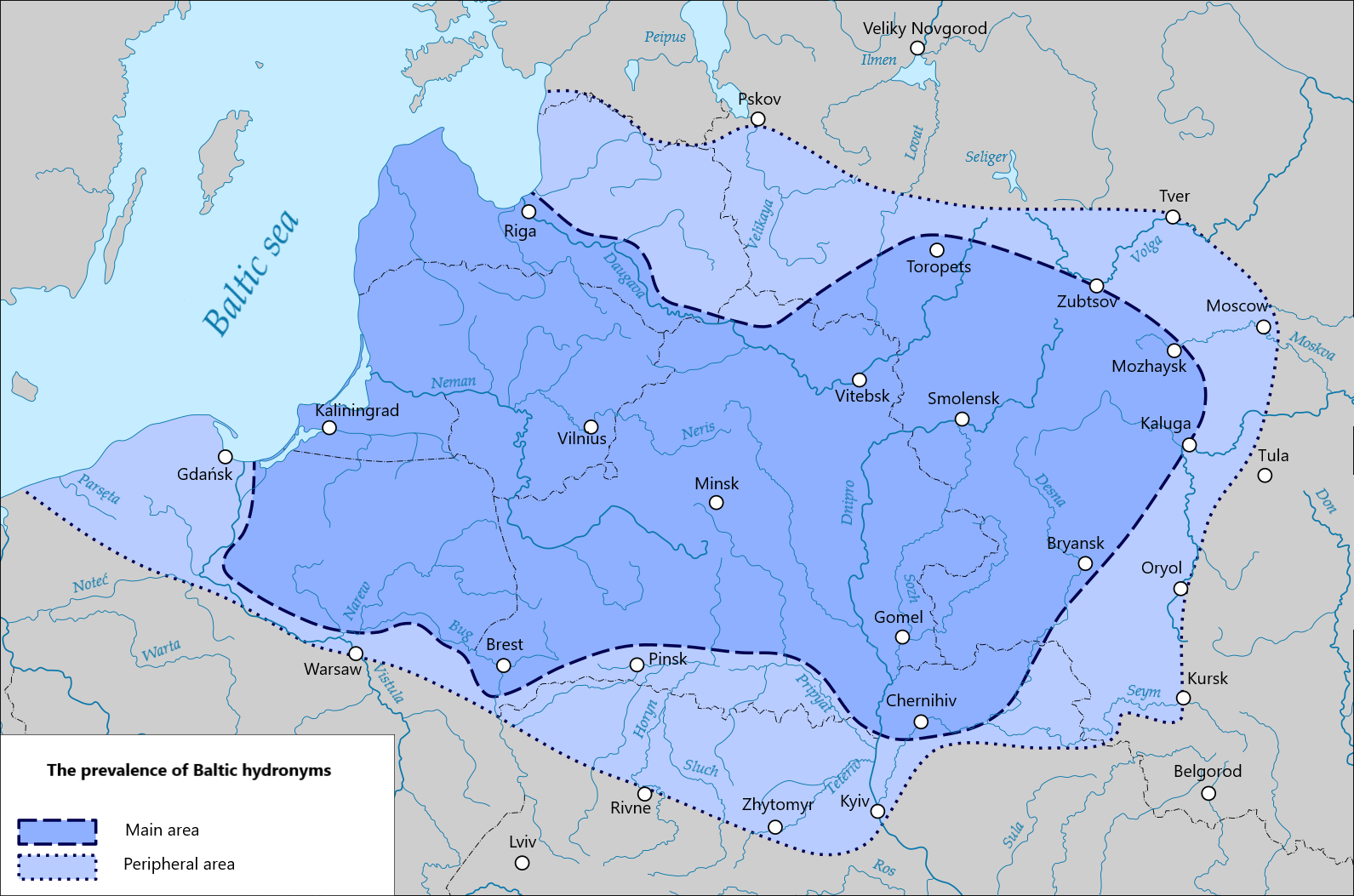
Lithuanian Language
Lithuanian (, ) is an East Baltic languages, East Baltic language belonging to the Baltic languages, Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the language of Lithuanians and the official language of Lithuania as well as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are approximately 2.8 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 1 million speakers elsewhere. Around half a million inhabitants of Lithuania of non-Lithuanian background speak Lithuanian daily as a second language. Lithuanian is closely related to neighbouring Latvian language, Latvian, though the two languages are not mutually intelligible. It is written in a Latin script. In some respects, some linguists consider it to be the most conservative (language), conservative of the existing Indo-European languages, retaining features of the Proto-Indo-European language that had disappeared through development from other descendant languages. History Among Indo-European languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chipewyan Language
Chipewyan or Dënesųłinë́ (ethnonym: ), often simply called Dëne, is the language spoken by the Chipewyan people of northwestern Canada. It is categorized as part of the Northern Athabaskan language family. It has nearly 12,000 speakers in Canada, mostly in Saskatchewan, Alberta, Manitoba and the Northwest Territories.Statistics Canada: 2006 Census Sum of 'Chipewyan' and 'Dene'. It has official status only in the Northwest Territories, alongside eight other [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogonek
The tail or ( ; Polish: , "little tail", diminutive of ) is a diacritic hook placed under the lower right corner of a vowel in the Latin alphabet used in several European languages, and directly under a vowel in several Native American languages. It is also placed on the lower right corner of consonants in some Latin transcriptions of various indigenous languages of the Caucasus mountains. An ogonek can also be attached to the bottom of a vowel in Old Norse or Icelandic language, Old Icelandic to show length or vowel affection (linguistics), affection. For example, in Old Norse, ''ǫ'' represents the Old Norwegian vowel , which in Old Icelandic merges with ''ø'' ‹ö› and in modern Scandinavian languages is represented by the letter ''å''. Use * Avestan language, Avestan romanization (letters ''ą'', ''ą̇'', ''m̨'') * Cahto language, Cahto (''ą'', ''ę'') * Cayuga language, Cayuga (''ę'', ''ǫ'') * Chickasaw language, Chickasaw (''ą'', ''į'', ''ǫ'') * Chipewyan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winnebago Language
The Ho-Chunk language (), also known as Winnebago, is the language of the Ho-Chunk people of the Ho-Chunk Nation of Wisconsin and Winnebago Tribe of Nebraska. The language is part of the Siouan language family and is closely related to other Chiwere Siouan dialects, including those of the Iowa, Missouria, and Otoe. "Winnebago", a name now used for the Ho-Chunk who were forcibly removed to Nebraska, is an exonym, an Anglicization of the Sauk and Fox word ''Oinepegi''. The anglicized form of the endonym is "Ho-Chunk". Phonology Phonemic inventory Ho-Chunk's vowel sounds are distinguished by nasality and length. That is to say, the use of a nasal vowel or a long vowel affects a word's meaning. This is evident in examples such as compared to , and compared to . All of Ho-Chunk's vowels show a length distinction, but only have nasal counterparts. Ho-Chunk's consonants are listed in the following table: Typical of Mississippi Valley Siouan languages, Ho-Chunk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Orthography
Lithuanian orthography employs a Latin-script alphabet of 32 letters, two of which denote sounds not native to the Lithuanian language. Additionally, it uses five digraphs. Alphabet Today, the Lithuanian alphabet consists of 32 letters. It features an unusual collation order in that "Y" occurs between I nosinė (Į) and J. While absent from the alphabet, letters Q, W and X have their place in collation order: Q is located between P and R, and W with X are preceded by letter V. Those letters may be used in spelling of foreign names. The distinctive Lithuanian letter '' Ė'' was used for the first time in Daniel Klein's '' Grammatica Litvanica'', and has been firmly established in the Lithuanian language since then. However, linguist August Schleicher used ''Ë'' (with two points above it) instead of ''Ė'' for expressing the same. In the ''Grammatica Litvanica'' Klein also established the letter '' W'' for marking the sound ''V'', the use of which was later abolished in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tutchone Language
Tutchone is an Athabaskan language spoken by the Northern and Southern Tutchone First Nations in central and southern regions of Yukon Territory, Canada. Tutchone belongs to the Northern Athabaskan linguistic subfamily and has two primary varieties, Southern and Northern. Although they are sometimes considered separate languages, Northern and Southern Tutchone speakers are generally able to understand each other in conversation, albeit with moderate difficulty. Southern Tutchone is spoken in the Yukon communities of Aishihik, Burwash Landing, Champagne, Haines Junction, Kloo Lake, Klukshu, Lake Laberge, and Whitehorse. Northern Tutchone is spoken in the Yukon communities of Mayo, Pelly Crossing, Stewart Crossing, Carmacks, and Beaver Creek. Phonology Northern Tutchone The consonants and vowels of Northern Tutchone and their orthography are as follows: Consonants Vowels Vowels are differentiated for nasalization and high, mid, and low tone. * Nasalized: į ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra Otomi
Sierra Otomi Highland Otomi (''Otomi de la Sierra'') is a dialect cluster of the Otomi language spoken in Mexico by ca. 70,000 people in the highlands of Eastern Hidalgo, Western Veracruz and Northern Puebla. The speakers themselves call the language ''Yųhų'' (Eastern Highland) or ''Ñųhų'' (Texcatepec and Tenango). Lastra 2001 classifies it as an Eastern Otomi language together with Ixtenco Otomi, Tilapa Otomi, and Acazulco Otomi. The three varieties of Sierra Otomi—Eastern Highland, Texcatepec, and Tenango—are above 70% lexically similar; the Eastern Highland dialects are above 80%, and will be considered here. Distribution Municipalities with significant Sierra Otomi populations include the following (Dow 2005:236). Many of these municipalities also have Tepehua, Totonac, and Nahuatl speakers. ; Hidalgo * Acaxochitlan * Huehuetla * San Bartolo Tutotepec * Tenango de Doria *Tulancingo ;Puebla * Francisco Z. Mena * Pahuatlán * Pantepec * Tlacuilotepec * Tlaxco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assiniboine Language
The Assiniboine language (; also known as Assiniboin, Hohe, or Nakota, Nakoda, Nakon or Nakona, or Stoney) is a Nakotan Siouan languages, Siouan language of the Great Plains, Northern Plains. The name ''Assiniboine'' comes from the term , from Ojibwe language, Ojibwe, meaning 'Stone Siouans'. The reason they were called this was that Assiniboine people used heated stone to boil their food. In Canada, Assiniboine people are known as Nakoda (Stoney), Stoney Indians, while they called themselves Nakota, ''Nakota'' or ''Nakoda'', meaning 'allies'''.'' Classification The Dakotan group of the Siouan family has five main divisions: Dakota people, Dakota (Santee-Sisseton), Dakota (Yankton-Yanktonai), Lakota people, Lakota (Teton), Nakoda (Assiniboine) and Nakoda (Stoney), Nakoda (Stoney).Miller, D., Smith, D., McGeshick, J. R., Shanley, J., & Shields, C. (2008). ''The History of the Assiniboine and Sioux Tribes of the Fort Peck Indian Reservation, Montana'', 1800-2000. Montana: Montana H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sekani Language
The Sekani language or Tse’khene is a Northern Athabaskan language spoken by 135 of the Sekani people of north-central British Columbia, Canada Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun .... Most of them are only semispeakers, and it is considered critically endangered. Phonology Consonants Sekani has 33 consonants: Vowels Tone Sekani has two tones: low and high. High tone is the more common tone. Syllables phonologically marked for tone are low. For example, means , while means . Nasalization Nasalization of vowels is phonemic. The root means , while the root means . Nasal vowels also contrast with vowels followed by . Orthography The orthography of the Kwadcha Tsek'ene dictionary uses the following letters. In addition, represents , represents , repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasalization
In phonetics, nasalization (or nasalisation in British English) is the production of a sound while the velum is lowered, so that some air escapes through the nose during the production of the sound by the mouth. An archetypal nasal sound is . In the International Phonetic Alphabet, nasalization is indicated by printing a tilde diacritic above the symbol for the sound to be nasalized: is the nasalized equivalent of , and is the nasalized equivalent of . A subscript diacritic , called an or , is sometimes seen, especially when the vowel bears tone marks that would interfere with the superscript tilde. For example, are more legible in most fonts than . Nasal vowels Many languages have nasal vowels to different degrees, but only a minority of world languages around the world have nasal vowels as contrasting phonemes. That is the case, among others, of French, Portuguese, Hindustani, Nepali, Breton, Gheg Albanian, Hmong, Hokkien, Yoruba, and Cherokee. Those nasal vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Close Back Rounded Vowel
The close back rounded vowel, or high back rounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is u. In most languages, this rounded vowel is pronounced with protruded lips ('endolabial'). However, in a few cases the lips are compressed ('exolabial'). alternates with labio-velar approximant in certain languages, such as French, and in the diphthong A diphthong ( ), also known as a gliding vowel or a vowel glide, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of ...s of some languages, with the non-syllabic diacritic and are used in different transcription systems to represent the same sound. Close back protruded vowel The close back protruded vowel is the most common variant of the close back rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vowel Length
In linguistics, vowel length is the perceived or actual length (phonetics), duration of a vowel sound when pronounced. Vowels perceived as shorter are often called short vowels and those perceived as longer called long vowels. On one hand, many languages do not distinguish vowel length phoneme, phonemically, meaning that vowel length alone does not change the meanings of words. However, the amount of time a vowel is uttered can change based on factors such as the phonetic characteristics of the sounds around it: the phonetic environment. An example is that vowels tend to be pronounced longer before a voiced consonant and shorter before a voiceless consonant in the standard accents of General American English, American and Received Pronunciation, British English. On the other hand, vowel length is indeed an important phonemic factor in certain languages, meaning vowel length can change word-meanings, for example in Arabic phonology#Vowels, Arabic, Czech phonology, Czech, Dravidia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |