|
é atiya
é atiya, also ''Satiya'', or ''Shatiya'' was the ruler-'mayor' of EniéÀasi, during the Amarna letters period of 1350ã1335 BC. In the entire correspondence of 382–letters, his name is only referenced in his own letter to the Ancient Egyptian pharaoh, EA 187, ( EA for 'el Amarna'). é atiya's city/city-state of EniéÀasi is only referenced in one other letter, authored by another mayor of EniéÀasi, Abdi-RiéÀa. é atiya's letter no. 187 é atiya's single letter to pharaoh, is a moderately short letter, entitled: ''"A daughter sent to the Pharaoh"''. As 5 lines of the body of the letter are missing, (a lacuna), the main subject is lost, except for the final sentence concerning é atiya's daughter. The letter, title: ''"A daughter sent to the Pharaoh"'' :Sa to the kin, my lord, y god, my Sun: Messge of ''é atiya'', the ruler of [ EniéÀasi ], your [ser]vant, the Prostration formula, dirt und[er the f]eet of the king, my lord. I [fa]ll [a]t the feet of the king, ylord, my god, my S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EniéÀasi
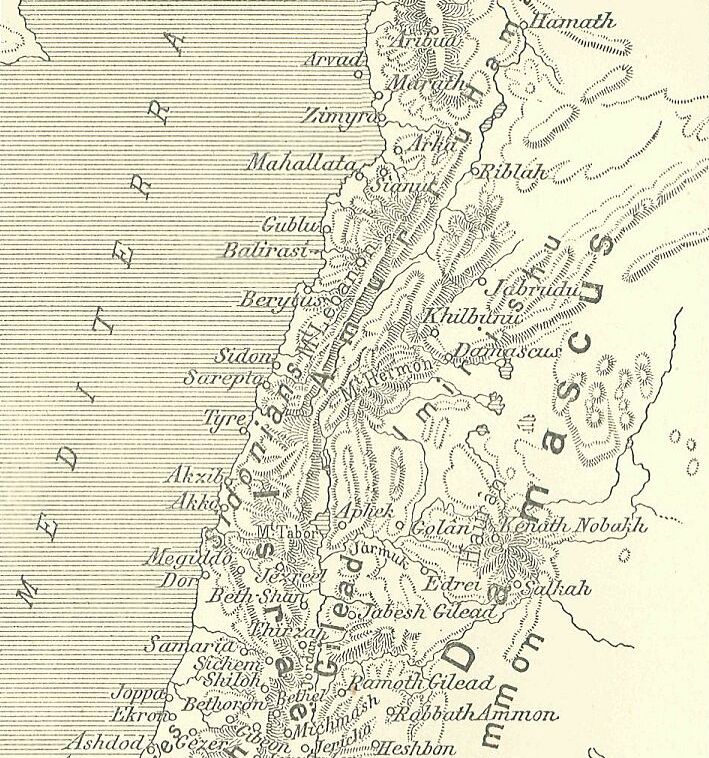
EniéÀasi, was a city, or city-state located in the Beqaa Valley-(called '' Amqu'', or ''Amka'') of Lebanon, during the 1350-1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. Of the 382–Amarna letters, EniéÀasi is only referenced in two letters. EniéÀasi was located near ''HaéÀabu'', (Tell HaéÀbe), and ''Hasi'', (Tell Hizzin?), southwest of Baalbek. Two 'mayors', or rulers of EniéÀasi were é atiya and Abdi-RiéÀa, who each authored a letter to the Egyptian pharaoh, EA 187- (title: ''A daughter sent to the Pharaoh''), and EA 363- (title: ''A joint report on Amqu–(4)''). ( EA is for 'el Amarna'.) See also *Abdi-RiéÀa, mayor * é atiya, mayor *Amarna letters *Amarna lettersãlocalities and their rulers This is a list of Amarna letters –Text corpus, categorized by: Amarna lettersãlocalities and their rulers. It includes countries, regions, and the cities or city-states. The regions are included in Canaan and the Levant. EA: '' 'el Amarna ... References * Moran, William L. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdi-RiéÀa
Abdi-RiéÀa was a ruler-'mayor' of EniéÀasi, during the period of the Amarna letters correspondence (1350ã1335 BC). Another mayor of EniéÀasi, é atiya, is found in the Amarna letters corpus. The name "Abdi-RiéÀa" means ''"servant-RiéÀa"''. Abdi-RiéÀa is only referenced in his own letter EA 363, a letter to pharaoh, ( EA for 'el Amarna'). Letter no. 363 is a unique letter, being part of a letter–series, (by the same scribe): :EA 174-(1), ''"Report on Amqu (1)"'' :EA 175-(2), ''"Report on Amqu (2)"'' :EA 176-(3), ''"Report on Amqu (3)"'' :EA 363-(4), ''"Report on Amqu (4)"'' the Amqu being the ''"Beqaa Valley area"'' of Lebanon. As letter EA 363 was discovered later, (in a separate in-situ deposit), than the original letters of the Amarna letters correspondence, it is undamaged. Abdi-RiéÀa letter EA 363, title: "A joint report on Amqu (4)" :Say to the king-(i.e. Pharaoh), my lord, my god, my Sun: Message of ''Abdi-RiéÀa'', your servant, the ruler of E(ni)éÀasi. I fall in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Lettersãlocalities And Their Rulers
This is a list of Amarna letters –Text corpus, categorized by: Amarna lettersãlocalities and their rulers. It includes countries, regions, and the cities or city-states. The regions are included in Canaan and the Levant. EA: '' 'el Amarna' ''–(Akhenaten's capitol of Akhetaten). The Amarna letters text corpus contains 382 numbered letters; there are "sub-Text corpora" in the letters, most notably the 68–letter ''corpus'' of Rib-Hadda of Gubla–(Byblos). Localities / Rulers Sub-corpus lists No. 201ã206: ''"Ready for marching orders (1ã6)"'' List of letters: EA 201ã206.Actually authored by the same scribe. Also scribed EA 195, See: Prostration formula. Leaders only in reference Leaders that are only referred to in the letter corpus. See also * Foreign relations of Egypt during the Amarna period References * Moran, William L. ''The Amarna Letters The Amarna letters (; sometimes referred to as the Amarna correspondence or Amarna tablets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letters Writers
Amarna (; ar, ÄÏìÄ¿ì ÄÏÄÝìÄˋ, al-ò¢amárnah) is an extensive Egyptian archaeological site containing the remains of what was the capital city of the late Eighteenth Dynasty. The city was established in 1346 BC, built at the direction of the Pharaoh Akhenaten, and abandoned shortly after his death in 1332 BC. The name that the ancient Egyptians used for the city is transliterated in English as Akhetaten or Akhetaton, meaning " the horizon of the Aten".David (1998), p. 125 The site is on the east bank of the Nile River, in what today is the Egyptian province of Minya. It is about south of the city of al-Minya, south of the Egyptian capital, Cairo, and north of Luxor (site of the previous capital, Thebes). The city of Deir Mawas lies directly to its west. On the east side of Amarna there are several modern villages, the chief of which are l-Till in the north and el-Hagg Qandil in the south. Activity in the region flourished from the Amarna Period until the later Roman era. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William L
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ÿÃÃÃôäÃÃÃôÃ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ÃÂÃÃÃà åà ÃÃà Ã, ''VilhjûÀlmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palátium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which housed the Roman Empire, Imperial residences. Most European languages have a version of the term (''palais'', ''palazzo'', ''palacio'', etc.), and many use it for a wider range of buildings than English. In many parts of Europe, the equivalent term is also applied to large private houses in cities, especially of the aristocracy; often the term for a large country house is different. Many historic palaces are now put to other uses such as parliaments, museums, hotels, or office buildings. The word is also sometimes used to describe a lavishly ornate building used for public entertainment or exhibitions such as a movie palace. A palace is distinguished from a castle while the latter clearly is fortified or has the style of a fortification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostration Formula
In the 1350 BC correspondence of 382–letters, called the Amarna letters, the prostration formula is usually the opening subservient remarks to the addressee, the Egyptian pharaoh. The formula is based on prostration, namely reverence and submissiveness. Often the letters are from vassal rulers or vassal city-states, especially in Canaan but also in other localities. The formula is often repetitive, or multi-part, with parts seeming to repeat and can go forward in a typical standard format. However, the prostration formula may also be duplicated in a similar format at the end of a letter, or a foreshortened part of the formula may be entered, for effect, in the middle of a letter. Some example letters with the ''Prostration formula'' The letters EA 242 and 246 are from Biridiya of Magidda-(Megiddo), (EA for 'el Amarna'). Biridiya letter 242, no. 1 of 7: title: ''"Request granted"'' :Say to the king-(i.e. pharaoh), my lord and my Sun: Message-(' um– ma') of Biridiya, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacuna (manuscripts)
A lacuna ( lacunae or lacunas) is a gap in a manuscript, inscription, text, painting, or musical work. A manuscript, text, or section suffering from gaps is said to be "lacunose" or "lacunulose". Weathering, decay, and other damage to old manuscripts or inscriptions are often responsible for lacunae - words, sentences, or whole passages that are missing or illegible. Palimpsests are particularly vulnerable. To reconstruct the original text, the context must be considered. In papyrology and textual criticism, this may lead to competing reconstructions and interpretations. Published texts that contain lacunae often mark the section where text is missing with a bracketed ellipsis. For example, "This sentence contains 20 words, and ..nouns," or, "Finally, the army arrived at ..and made camp." Notable examples See also * Unfinished work Unfinished may refer to: *Unfinished creative work, a work which a creator either chose not to finish or was prevented from finishing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr õËõÈ''; cop, , Púrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parò¢é'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire in 30 BC. However, regardless of gender, "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom. The term "pharaoh" was not used contemporaneously for a ruler until a possible reference to Merneptah, c. 1210 BC during the Nineteenth Dynasty, nor consistently used until the decline and instability that began with the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty. In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as three titles: the Horus, the Sedge and Bee ( ''nswt-bjtj''), and the Two Ladies or Nebty ( ''nbtj'') name. The Golden Horus and the nomen and prenomen titles were added later. In Egyptian society, religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as Rome, Athens, Sparta, Carthage, and the Italian city-states during the Middle Ages and Renaissance, such as Florence, Venice, Genoa and Milan. With the rise of nation states worldwide, only a few modern sovereign city-states exist, with some disagreement as to which qualify; Monaco, Singapore and Vatican City are most commonly accepted as such. Singapore is the clearest example, with full self-governance, its own currency, a robust military and a population of 5.5 million. Several non-sovereign cities enjoy a high degree of autonomy and are sometimes considered city-states. Hong Kong, Macau, and members of the United Arab Emiratesãmost notably Dubai and Abu Dhabiãare often cited as such. Historical background Ancient and medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letters
The Amarna letters (; sometimes referred to as the Amarna correspondence or Amarna tablets, and cited with the abbreviation EA, for "El Amarna") are an archive, written on clay tablets, primarily consisting of diplomatic correspondence between the Ancient Egypt, Egyptian administration and its representatives in Canaan and Amurru kingdom, Amurru, or neighboring kingdom leaders, during the New Kingdom, spanning a period of no more than thirty years between c. 1360ã1332 BC (see Amarna letters#Chronology, here for dates).Moran, p.xxxiv The letters were found in Upper Egypt at el-Amarna, the modern name for the ancient Egyptian capital of ''Akhetaten'', founded by pharaoh Akhenaten (1350sã1330s BC) during the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. The Amarna letters are unusual in Egyptological research, because they are written not in the language of ancient Egypt, but in cuneiform, the writing system of ancient Mesopotamia. Most are in a variety of Akkadian language, Akkadian sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna
Amarna (; ar, ÄÏìÄ¿ì ÄÏÄÝìÄˋ, al-ò¢amárnah) is an extensive Egyptian archaeological site containing the remains of what was the capital city of the late Eighteenth Dynasty. The city was established in 1346 BC, built at the direction of the Pharaoh Akhenaten, and abandoned shortly after his death in 1332 BC. The name that the ancient Egyptians used for the city is transliterated in English as Akhetaten or Akhetaton, meaning " the horizon of the Aten".David (1998), p. 125 The site is on the east bank of the Nile River, in what today is the Egyptian province of Minya. It is about south of the city of al-Minya, south of the Egyptian capital, Cairo, and north of Luxor (site of the previous capital, Thebes). The city of Deir Mawas lies directly to its west. On the east side of Amarna there are several modern villages, the chief of which are l-Till in the north and el-Hagg Qandil in the south. Activity in the region flourished from the Amarna Period until the later Roman era ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |