|
(Norbornadiene)molybdenum Tetracarbonyl
(Norbornadiene)molybdenum tetracarbonyl is the organomolybdenum compound with the formula (C7H9)Mo(CO)4. Structurally, the compound consists of the norbornadiene bonded to a Mo(CO)4 fragment. The compound is a yellow, volatile solid. It is prepared by thermal or photochemical substitution of molybdenum hexacarbonyl. The compound was originally examined as a potential antiknock agent An antiknock agent is a gasoline additive used to reduce engine knocking and increase the fuel's octane rating by raising the temperature and pressure at which auto-ignition occurs. The mixture known as gasoline or petrol, when used in high compr .... (Norbornadiene)molybdenum tetracarbonyl is a precursor to other derivatives of the type L2Mo(CO)4. This conversion exploits the lability of the diene ligand: :(C7H9)Mo(CO)4 + 2 L → C7H9 + L2Mo(CO)4 References {{DEFAULTSORT:Norbornadiene)molybdenum tetracarbonyl Molybdenum(0) compounds Carbonyl complexes Octahedral compounds Diene co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organomolybdenum Compound
Organomolybdenum chemistry is the chemistry of chemical compounds with Mo-C bonds. The heavier group 6 elements molybdenum and tungsten form organometallic compounds similar to those in organochromium chemistry but higher oxidation states tend to be more common. Mo(0) and more reduced states Molybdenum hexacarbonyl is the precursor to many substituted derivatives. It reacts with organolithium reagents to give anionic acyls which can be O-alkylated to give Fischer carbenes. 144px, Structure of (mesitylene)molybdenum tricarbonyl. Mo(CO)6 reacts with arenes to give piano-stool complexes such as (mesitylene)molybdenum tricarbonyl. Cycloheptatrienemolybdenum tricarbonyl, which is related to (arene)Mo(CO)3, reacts with trityl salts to give the cycloheptatrienyl complex: :(C7H8)Mo(CO)3 + (C6H5)3C+ → C7H7)Mo(CO)3sup>+ + (C6H5)3CH file:CHTMo(CO)3.png, 144px, Structure of Cycloheptatrienemolybdenum tricarbonyl. Reduction of Mo(CO)6 gives [Mo(CO)5]2− which is formally M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norbornadiene
Norbornadiene is an organic compound In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ... and a bicyclic hydrocarbon. Norbornadiene is of interest as a metal-binding ligand, whose complexes are useful for homogeneous catalysis. It has been intensively studied owing to its high reactivity and distinctive structural property of being a diene that cannot isomerization, isomerize (isomers would be anti-Bredt alkenes). Norbornadiene is also a useful Diels–Alder_reaction#The_dienophile, dienophile in Diels-Alder reactions. Synthesis Norbornadiene can be formed by a Diels-Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and acetylene : Reactions Quadricyclane, a valence isomer, can be obtained from norbornadiene by a photochemical reaction when assisted by a photochemical sensitizer, sensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
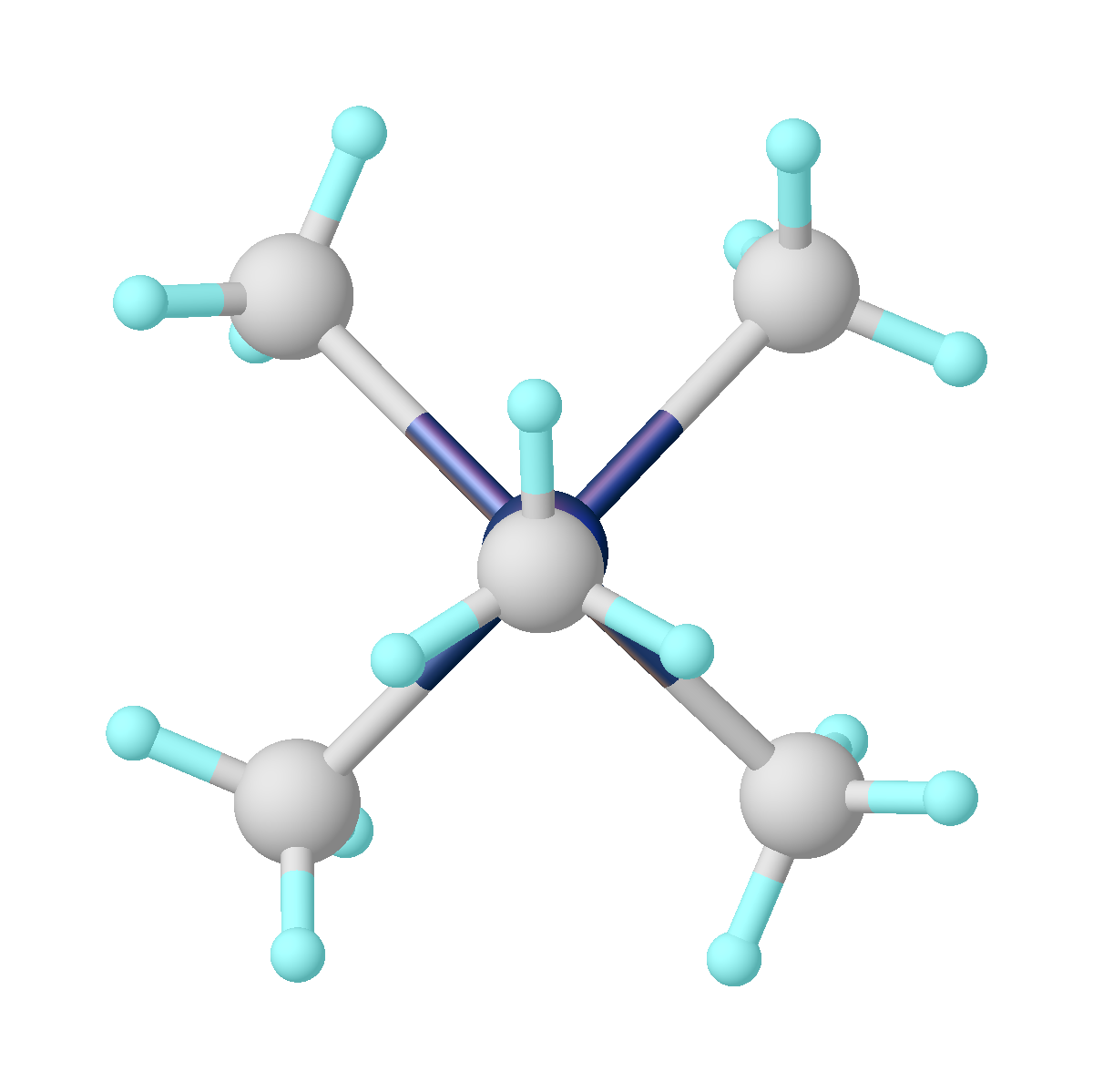
Molybdenum Hexacarbonyl
Molybdenum hexacarbonyl (also called molybdenum carbonyl) is the chemical compound with the formula Mo(CO)6. This colorless solid, like its chromium and tungsten analogues, is noteworthy as a volatile, air-stable derivative of a metal in its zero oxidation state. Structure and properties Mo(CO)6 adopts an octahedral geometry consisting of six rod-like CO ligands radiating from the central Mo atom. A recurring minor debate in some chemical circles concerns the definition of an "organometallic" compound. Usually, organometallic indicates the presence of a metal directly bonded via a M–C bond to an organic fragment, which must in turn have a C–H bond. Mo(CO)6 is prepared by the reduction of molybdenum chlorides or oxides under a pressure of carbon monoxide, although it would be unusual to prepare this inexpensive compound in the laboratory. The compound is somewhat air-stable and sparingly soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. Occurrence Mo(CO)6 has been detected in landfil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiknock Agent
An antiknock agent is a gasoline additive used to reduce engine knocking and increase the fuel's octane rating by raising the temperature and pressure at which auto-ignition occurs. The mixture known as gasoline or petrol, when used in high compression internal combustion engines, has a tendency to knock (also called "pinging" or "pinking") and/or to ignite early before the correctly timed spark occurs (''pre-ignition'', refer to engine knocking). Notable early antiknock agents, especially Tetraethyllead, added to gasoline included large amounts of toxic lead. The chemical was responsible for global negative impacts on health, and the phase out of leaded gasoline from the 1970s onward was reported by the UN to be responsible for $2.4 trillion in annual benefits, 1.2 million fewer premature deaths, higher overall intelligence and 58 million fewer crimes," the United Nations Environmental Programme said. Some other chemicals used as gasoline additives are thought to be less toxic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdenum(0) Compounds
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, but the element was discovered (in the sense of differentiating it as a new entity from the mineral salts of other metals) in 1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The metal was first isolated in 1781 by Peter Jacob Hjelm. Molybdenum does not occur naturally as a free metal on Earth; it is found only in various oxidation states in minerals. The free element, a silvery metal with a grey cast, has the sixth-highest melting point of any element. It readily forms hard, stable carbides in alloys, and for this reason most of the world production of the element (about 80%) is used in steel alloys, including high-strength alloys and superalloys. Most molybdenum compounds have low solubility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonyl Complexes
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a carbonyl group is often referred to as a carbonyl compound. The term carbonyl can also refer to carbon monoxide as a ligand in an inorganic or organometallic complex (a metal carbonyl, e.g. nickel carbonyl). The remainder of this article concerns itself with the organic chemistry definition of carbonyl, where carbon and oxygen share a double bond. Carbonyl compounds In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group characterizes the following types of compounds: Other organic carbonyls are urea and the carbamates, the derivatives of acyl chlorides chloroformates and phosgene, carbonate esters, thioesters, lactones, lactams, hydroxamates, and isocyanates. Examples of inorganic carbonyl compounds are carbon dioxide and carbonyl sulfide. A sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedral Compounds
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. A regular octahedron is the dual polyhedron of a cube. It is a rectified tetrahedron. It is a square bipyramid in any of three orthogonal orientations. It is also a triangular antiprism in any of four orientations. An octahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a cross polytope. A regular octahedron is a 3-ball in the Manhattan () metric. Regular octahedron Dimensions If the edge length of a regular octahedron is ''a'', the radius of a circumscribed sphere (one that touches the octahedron at all vertices) is :r_u = \frac a \approx 0.707 \cdot a and the radius of an inscribed sphere (tangent to each of the octahedron's faces) is :r_i = \frac a \approx 0.408\cdot a while the midradius, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diene Complexes
In organic chemistry a diene ( ) (diolefin ( ) or alkadiene) is a covalent compound that contains two double bonds, usually among carbon atoms. They thus contain two alk''ene'' units, with the standard prefix ''di'' of systematic nomenclature. As a subunit of more complex molecules, dienes occur in naturally occurring and synthetic chemicals and are used in organic synthesis. Conjugated dienes are widely used as monomers in the polymer industry. Polyunsaturated fats are of interest to nutrition. Classes Dienes can be divided into three classes, depending on the relative location of the double bonds: #Cumulated dienes have the double bonds sharing a common atom. The result is more specifically called an allene. #Conjugated dienes have conjugated double bonds separated by one single bond. Conjugated dienes are more stable than other dienes because of resonance. #Unconjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by two or more single bonds. They are usually less stable tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |