|
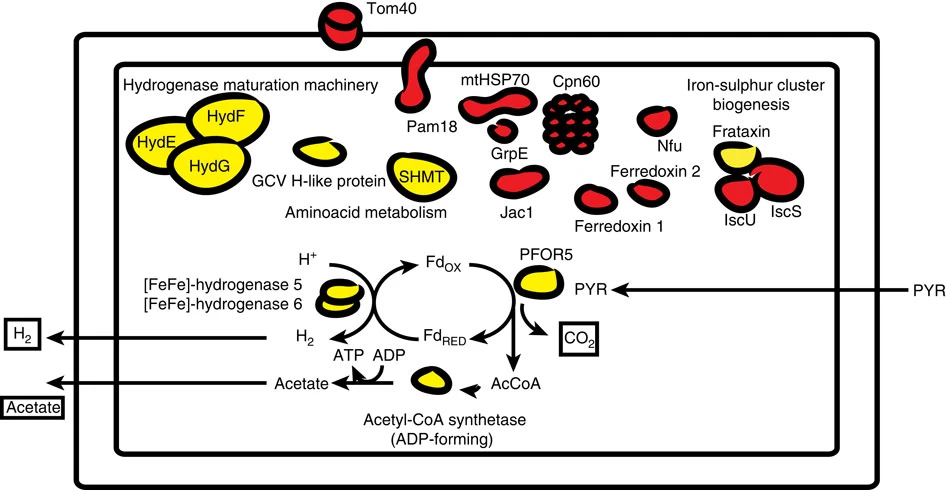
Hydrogenosome
A hydrogenosome is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in some anaerobic ciliates, flagellates, and fungi. Hydrogenosomes are highly variable organelles that have presumably evolved from protomitochondria to produce molecular hydrogen and ATP in anaerobic conditions. Hydrogenosomes were discovered in 1973 by D. G. Lindmark and M. Müller. Because hydrogenosomes hold evolutionary lineage significance for organisms living in anaerobic or oxygen-stressed environments, many research institutions have since documented their findings on how the organelle differs in various sources. History Hydrogenosomes were isolated, purified, biochemically characterized and named in the early 1970s by Lindmark and Müller at Rockefeller University. In addition to this seminal study on hydrogenosomes, they also demonstrated for the first time the presence of pyruvate:ferredoxin oxido-reductase and hydrogenase in eukaryotes. Further studies were subsequently conducted on the biochemical cytolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalteriomonas Lanterna
''Psalteriomonas lanterna'' is a species of amoebae in the group of Heterolobosea. The cells of the flagellate stage show four nuclei, four ventral grooves and four mastigont systems, each with four flagellum, flagella. It lacks a Golgi apparatus and reproduction occurs in both stages of its life cycle. References Further reading * * * * External links * Percolozoa Species described in 1990 {{Excavata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metopus Palaeformis
''Metopus'' is a genus of anaerobic organisms An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygena ... from the family of Metopidae. References Further reading * * * * * * * Intramacronucleata Ciliate genera {{Ciliate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blastocystis
''Blastocystis'' is a genus of single-celled heterokont parasites belonging to a group of organisms that are known as the Stramenopiles (also called Heterokonts) that includes algae, diatoms, and water molds. Blastocystis consists of several species, living in the gastrointestinal tracts of species as diverse as humans, farm animals, birds, rodents, reptiles, amphibians, fish, and cockroaches. ''Blastocystis'' exhibits low host specificity, and many different species of ''Blastocystis'' can infect humans, and by current convention, any of these species would be identified as ''Blastocystis hominis''. ''Blastocystis'' is one of the most common human parasites in the world and has a global distribution. It is the most common parasitic infection in the United States, where it infected approximately 23% of the total population during year 2000. In less developed areas, infection rates as high as 100% have been observed. High rates of infection are found in individuals in developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial Genome
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondrion, mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. This sequencing revealed that the human mtDNA includes 16,569 base pairs and encodes 13 proteins. Since animal mtDNA evolves faster than nuclear genetic markers, it represents a mainstay of phylogenetics and evolutionary biology. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and biogeography. Origin Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are thought to be of separate evolutionary origin, with the mtDNA being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neocallimastix
''Neocallimastix'' is a genus of obligately anaerobic rumen fungi A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ... in the family Neocallimastigaceae. A specialised group of chytrids grow in the rumen of herbivorous animals, where they degrade cellulose and thus play a primary role in the complex microbial ecology of the rumen. References External links * Neocallimastigomycota Fungus genera {{Fungus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimastix Pyriformis
''Trimastix'' is a genus of excavates, the sole occupant of the order Trimastigida. ''Trimastix'' are bacterivorous, free living and anaerobic. When first observed in 1881 by William Kent, the morphology of Trimastix was not well describedKent, W. S. (1881). A manual of the infusoria: including a description of all known flagellate, ciliate, and tentaculiferous protozoa, British and foreign, and an account of the organization and affinities of the sponges (Vol. 1). David Bogue, London, England. but over time the oral structure and flagellar organization have become clearer.Brugerolle, G., & Patterson, D. (1997). Ultrastructure of Trimastix convexa Hollande, an amitochondriate anaerobic flagellate with a previously undescribed organization. European Journal of Protistology, 33(2), 121-130. There are few known species, and the genus's role in the ecosystem is largely unknown. However, it is known that they generally live in marine environments within the tissues of decaying organism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histomonas Meleagridis
''Histomonas meleagridis'' is a species of parasitic protozoan that infects a wide range of birds including chickens, turkeys, peafowl, quail and pheasants, causing infectious enterohepatitis, or histomoniasis (blackhead diseases). ''H. meleagridis'' can infect many birds, but it is most deadly in turkeys. It inhabits the lumen of cecum and parenchyma of liver, where it causes extensive necrosis. It is transmitted by another cecal parasite, the nematode ''Heterakis gallinarum''. Description ''H. meleagridis'' is a microscopic, pleomorphism (microbiology), pleomorphic protozoan, and can exist in Polymorphism (biology), two forms, amoeboid and flagellation, flagellated. Within the tissue, it is present as an amoeboid protozoan, while in the lumen or free in the contents of cecum, it lives as an elongated flagellation, flagellated form. The amoeboid form is typically 8-15 micrometre, μm in diameter, whereas the flagellation, flagellated form can reach up to 30 μm in diameter.Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |