|
Blackwater (waste)
Blackwater in a sanitation context denotes wastewater from toilets, which likely contains pathogens which may spread by the fecal–oral route. Blackwater can contain feces, urine, water and toilet paper from flush toilets. Blackwater is distinguished from greywater, which comes from sinks, baths, washing machines, and other kitchen appliances apart from toilets. Greywater results from washing food, clothing, dishes, as well as from showering or bathing. Blackwater and greywater are kept separate in "ecological buildings", such as autonomous buildings. Recreational vehicles often have separate holding tanks for greywater from showers and sinks, and blackwater from the toilet. Definition According to one source: Water coming from domestic equipment other than toilets (e.g., bathtubs, showers, sinks, washing machines) is called greywater. In some sanitation systems, it is preferred to keep the greywater separate from blackwater to reduce the amount of water that gets heavily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems aim to protect human health by providing a clean environment that will stop the transmission of disease, especially through the fecal–oral route.SuSanA (2008)Towards more sustainable sanitation solutions Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) For example, diarrhea, a main cause of malnutrition and stunted growth in children, can be reduced through adequate sanitation. There are many other diseases which are easily transmitted in communities that have low levels of sanitation, such as ascariasis (a type of intestinal worm infection or helminthiasis), cholera, hepatitis, polio, schistosomiasis, and trachoma, to name just a few. A range of sanitation technologies and approaches exists. Some examples are community-led total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composting
Compost is a mixture of ingredients used as plant fertilizer and to improve soil's physical, chemical and biological properties. It is commonly prepared by decomposing plant, food waste, recycling organic materials and manure. The resulting mixture is rich in plant nutrients and beneficial organisms, such as bacteria, protozoa, nematodes and fungi. Compost improves soil fertility in gardens, landscaping, horticulture, urban agriculture, and organic farming, reducing dependency on commercial chemical fertilizers. The benefits of compost include providing nutrients to crops as fertilizer, acting as a soil conditioner, increasing the humus or humic acid contents of the soil, and introducing beneficial microbes that help to suppress pathogens in the soil and reduce soil-borne diseases. At the simplest level, composting requires gathering a mix of 'greens' (green waste) and 'browns' (brown waste). Greens are materials rich in nitrogen such as leaves, grass, and food scraps. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems aim to protect human health by providing a clean environment that will stop the transmission of disease, especially through the fecal–oral route.SuSanA (2008)Towards more sustainable sanitation solutions Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) For example, diarrhea, a main cause of malnutrition and stunted growth in children, can be reduced through adequate sanitation. There are many other diseases which are easily transmitted in communities that have low levels of sanitation, such as ascariasis (a type of intestinal worm infection or helminthiasis), cholera, hepatitis, polio, schistosomiasis, and trachoma, to name just a few. A range of sanitation technologies and approaches exists. Some examples are community-led total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Soil
Night soil is a historically used euphemism for human excreta collected from cesspools, privies, pail closets, pit latrines, privy middens, septic tanks, etc. This material was removed from the immediate area, usually at night, by workers employed in this trade. Sometimes it could be transported out of towns and sold on as a fertilizer. Another definition is "untreated excreta transported without water (e.g. via containers or buckets)". The term "night soil" is largely an outdated term, used in historical contexts. The modern term is "fecal sludge"; fecal sludge management is an ongoing challenge, particularly in developing countries. Night soil was produced as a result of a sanitation system in areas without sewer systems or septic tanks. In this system of waste management, the human feces are collected without dilution with water. Collection and disposal Feces were excreted into a container such as a chamber pot, and sometimes collected in the container with urine and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Sanitation
Ecological sanitation, commonly abbreviated as ecosan (also spelled eco-san or EcoSan), is an approach to sanitation provision which aims to safely reuse excreta in agriculture. It is an approach, rather than a technology or a device which is characterized by a desire to "close the loop", mainly for the nutrients and organic matter between sanitation and agriculture in a safe manner. One of the aims is to minimise the use of non-renewable resources. When properly designed and operated, ecosan systems provide a hygienically safe system to convert human excreta into nutrients to be returned to the soil, and water to be returned to the land. Ecosan is also called resource-oriented sanitation. Definition The definition of ecosan has varied in the past. In 2012, a widely accepted definition of ecosan was formulated by Swedish experts: "Ecological sanitation systems are systems which allow for the safe recycling of nutrients to crop production in such a way that the use of non-re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constructed Wetland
A constructed wetland is an artificial wetland to treat sewage, greywater, stormwater runoff or industrial wastewater. It may also be designed for land reclamation after mining, or as a mitigation step for natural areas lost to land development. Constructed wetlands are engineered systems that use the natural functions of vegetation, soil, and organisms to provide secondary treatment to wastewater. The design of the constructed wetland has to be adjusted according to the type of wastewater to be treated. Constructed wetlands have been used in both centralized and decentralized wastewater systems. Primary treatment is recommended when there is a large amount of suspended solids or soluble organic matter (measured as biochemical oxygen demand and chemical oxygen demand). Similar to natural wetlands, constructed wetlands also act as a biofilter and/or can remove a range of pollutants (such as organic matter, nutrients, pathogens, heavy metals) from the water. Constructed wetland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Container-based Sanitation
Container-based sanitation (abbreviated as CBS) refers to a sanitation system where toilets collect human excreta in sealable, removable containers (also called cartridges) that are transported to treatment facilities. This type of sanitation involves a commercial service which provides certain types of portable toilets, and delivers empty containers when picking up full ones. The service transports and safely disposes of or reuses collected excreta. The cost of collection of excreta is usually borne by the users. With suitable development, support and functioning partnerships, CBS can be used to provide low-income urban populations with safe collection, transport and treatment of excrement at a lower cost than installing and maintaining sewers. In most cases, CBS is based on the use of urine-diverting dry toilets. A key benefit of container-based sanitation systems is its relative low-cost. In addition, the process assures there is no human contact with excreta. Feces can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae Fuel
Algae fuel, algal biofuel, or algal oil is an alternative to liquid fossil fuels that uses algae as its source of energy-rich oils. Also, algae fuels are an alternative to commonly known biofuel sources, such as corn and sugarcane. When made from seaweed (macroalgae) it can be known as seaweed fuel or seaweed oil. It is also carbon negative unless the dead plant matter is burned, as the energy (stored as hydrogen gas) is produced by solar photosynthesis and comes from the sun. The emissions from burning the hydrogen make up only water and air. Several companies and government agencies are funding efforts to reduce capital and operating costs and make algae fuel production commercially viable. Like fossil fuel, algae fuel releases when burnt, but unlike fossil fuel, algae fuel and other biofuels only release recently removed from the atmosphere via photosynthesis as the algae or plant grew. The energy crisis and the world food crisis have ignited interest in algaculture (farmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthship
An Earthship is a style of architecture developed in the late 20th century to early 21st century by architect Michael Reynolds. Earthships are designed to behave as passive solar earth shelters made of both natural and upcycled materials such as earth-packed tires. Earthships may feature a variety of amenities and aesthetics, and are designed to withstand the extreme temperatures of a desert, managing to stay close to 70 °F (21 °C) regardless of outside weather conditions. Earthship communities were originally built in the desert of northern New Mexico, near the Rio Grande, and the style has spread to small pockets of communities around the globe, in some cases in spite of legal opposition to its construction and adoption. Reynolds developed the Earthship design after moving to New Mexico and completing his degree in architecture, intending them to be " off-the-grid-ready" homes, with minimal reliance on public utilities and fossil fuels. They are constructed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermifilter
A vermifilter (also vermi-digester or lumbrifilter) is an aerobic treatment system, consisting of a Bioreactor, biological reactor containing media that filters Organic matter, organic material from wastewater. The media also provides a habitat for Aerobic organism, aerobic bacteria and Vermicompost#Suitable worm species, composting earthworms that purify the wastewater by removing pathogens and Biochemical oxygen demand, oxygen demand. The "trickling action" of the wastewater through the media Dissolved Oxygen, dissolves oxygen into the wastewater, ensuring the treatment environment is aerobic for rapid decomposition of organic substances. Vermifilters are most commonly used for sewage treatment and for agro-industrial wastewater treatment. Vermifilters can be used for Secondary treatment#Primary treatment, primary, Secondary treatment, secondary and Secondary treatment#Tertiary treatment, tertiary treatment of sewage, including Blackwater (waste), blackwater and greywater in Ons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
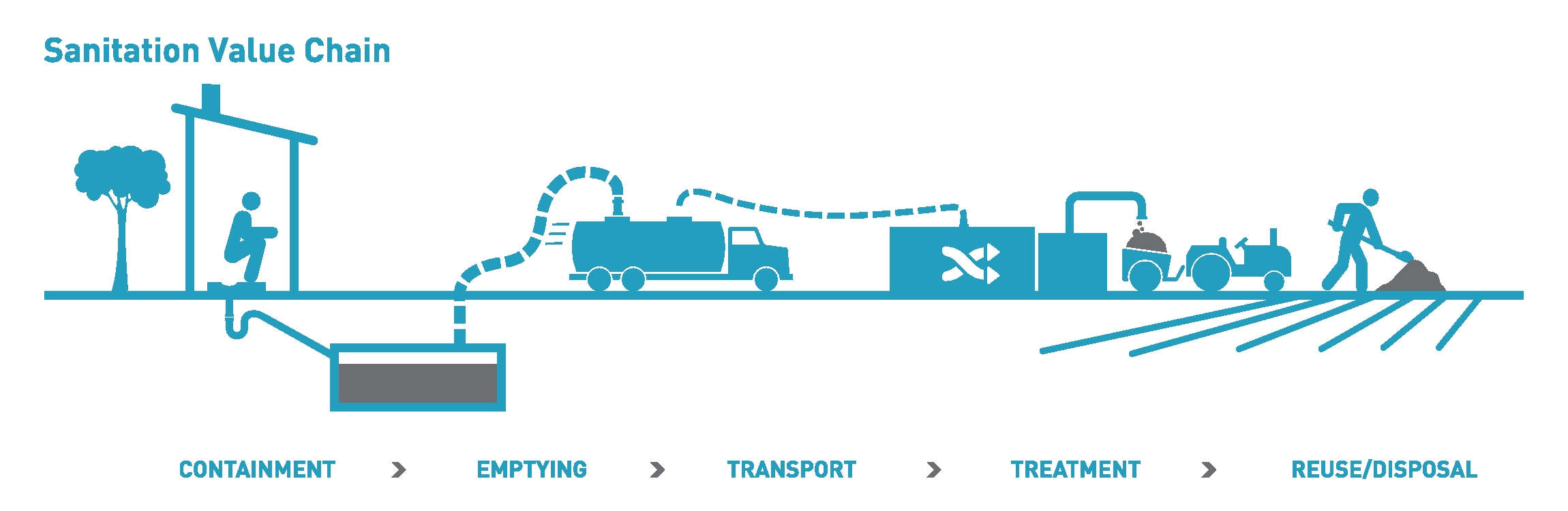
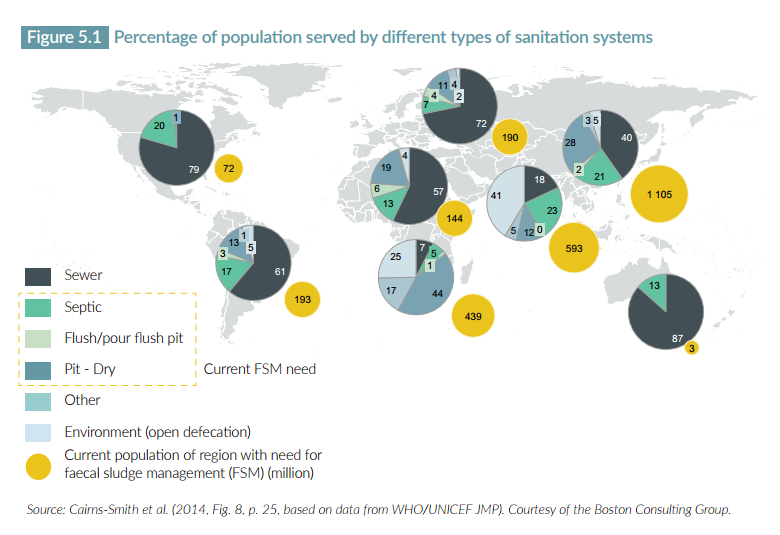



.jpg)

