|
Ascaris
''Ascaris'' is a genus of parasitic nematode worms known as the "small intestinal roundworms", which is a type of parasitic worm. One species, '' Ascaris lumbricoides'', affects humans and causes the disease ascariasis. Another species, ''Ascaris suum'', typically infects pigs. '' Parascaris equorum'', the equine roundworm, is also commonly called an "ascarid". Their eggs are deposited in feces and soil. Plants with the eggs on them infect any organism that consumes them. ''A. lumbricoides'' is the largest intestinal roundworm and is the most common helminth infection of humans worldwide. Infestation can cause morbidity by compromising nutritional status, affecting cognitive processes, inducing tissue reactions such as granuloma to larval stages, and by causing intestinal obstruction, which can be fatal. Morphology * Adult: cylindrical shape, creamy white or pinkish in color * Male: average 15–30 cm (6–12 inches); more slender than the female * Female: average 20†... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascaris Lumbricoides Life Cycle
''Ascaris'' is a genus of parasitic nematode worms known as the "small intestinal roundworms", which is a type of parasitic worm. One species, ''Ascaris lumbricoides'', affects humans and causes the disease ascariasis. Another species, ''Ascaris suum'', typically infects pigs. ''Parascaris equorum'', the equine roundworm, is also commonly called an "ascarid". Their eggs are deposited in feces and soil. Plants with the eggs on them infect any organism that consumes them. ''A. lumbricoides'' is the largest intestinal roundworm and is the most common helminth infection of humans worldwide. Infestation can cause morbidity by compromising nutritional status, affecting cognitive processes, inducing tissue reactions such as granuloma to larval stages, and by causing intestinal obstruction, which can be fatal. Morphology * Adult: cylindrical shape, creamy white or pinkish in color * Male: average 15–30 cm (6–12 inches); more slender than the female * Female: average 20–35 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
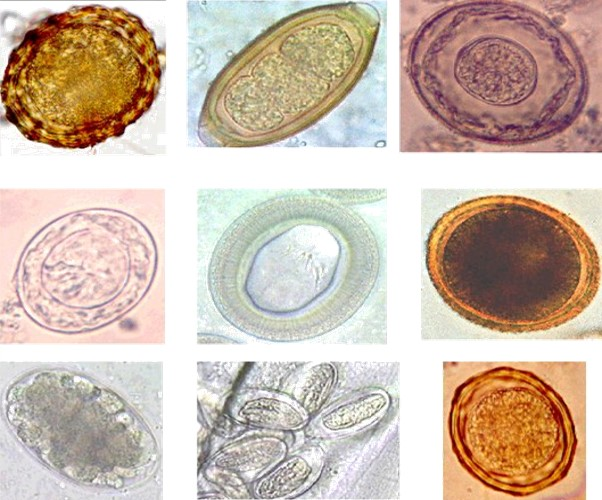
Ascaris Lumbricoides
''Ascaris lumbricoides'' is a large parasitic worm that causes ascariasis in humans. A roundworm of genus '' Ascaris'', it is the most common parasitic worm in humans. An estimated one-sixth of the human population is at some point infected by a roundworm such as ''A. lumbricoides''; people living in tropical and subtropical countries are at greater risk of infection. It has been proposed that ''Ascaris lumbricoides'' and ''Ascaris suum'' (pig roundworm) are the same species. Lifecycle ''Ascaris lumbricoides'', a roundworm, infects humans via the fecal-oral route. Eggs released by adult females are shed in feces. Unfertilized eggs are often observed in fecal samples but never become infective. Fertilized eggs embryonate and become infectious after 18 days to several weeks in soil, depending on the environmental conditions (optimum: moist, warm, shaded soil).Parasites - Ascariasis. (14 February 2018). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ascariasis/biology.html Infe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascariasis
Ascariasis is a disease caused by the parasitic roundworm ''Ascaris lumbricoides''. Infections have no symptoms in more than 85% of cases, especially if the number of worms is small. Symptoms increase with the number of worms present and may include shortness of breath and fever in the beginning of the disease. These may be followed by symptoms of abdominal swelling, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Children are most commonly affected, and in this age group the infection may also cause poor weight gain, malnutrition, and learning problems. Infection occurs by ingestion of food or drink contaminated with ''Ascaris'' eggs from feces. The eggs hatch in the intestines, the larvae burrow through the gut wall, and migrate to the lungs via the blood. There they break into the alveoli and pass up the trachea, where they are coughed up and may be swallowed. The larvae then pass through the stomach for a second time into the intestine, where they become adult worms. It is a type of soil-tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascaris Suum
''Ascaris suum'', also known as the large roundworm of pig, is a parasitic nematode that causes ascariasis in pigs. While roundworms in pigs and humans are today considered as two species (''A. suum'' and '' A. lumbricoides'') with different hosts, cross-infection between humans and pigs is possible; some researchers have thus argued they are the same species. Ascariasis is associated with contact to pigs and pig manure in Denmark. ''A. suum'' is distributed worldwide and grows up to in length. ''Ascaris'' infections are treated with ascaricides. ''A. suum'' is in the family Ascarididae, and is one of the oldest associations to mankind. Life cycle Pigs get infected with ''A. suum'' by ingesting infectious parasite eggs that are present in the environment. The larvae of Ascaris complete two moults within the egg; therefore, the larvae emerging from the egg is not a second-stage larva (L2) as was previously presumed, but rather a third stage larva (L3) covered by a loosened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helminth
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in their mammalian hosts for many years due to their ability to manipulate the host's immune response by secreting immunomodul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode Genera
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over time. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity published in the mega journ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepsin
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pepsin is an aspartic protease, using a catalytic aspartate in its active site. It is one of three principal endopeptidases (enzymes cutting proteins in the middle) in the human digestive system, the other two being chymotrypsin and trypsin. There are also exopeptidases which remove individual amino acids at both ends of proteins (carboxypeptidases produced by the pancreas and aminopeptidases secreted by the small intestine). During the process of digestion, these enzymes, each of which is specialized in severing links between particular types of amino acids, collaborate to break down dietary proteins into their components, i.e., peptides and amino acids, which can be readily absorbed by the sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Edition Of Systema Naturae
The 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' is a book written by Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus and published in two volumes in 1758 and 1759, which marks the starting point of zoological nomenclature. In it, Linnaeus introduced binomial nomenclature for animals, something he had already done for plants in his 1753 publication of '' Species Plantarum''. Starting point Before 1758, most biological catalogues had used polynomial names for the taxa included, including earlier editions of ''Systema Naturae''. The first work to consistently apply binomial nomenclature across the animal kingdom was the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. The International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature therefore chose 1 January 1758 as the "starting point" for zoological nomenclature, and asserted that the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' was to be treated as if published on that date. Names published before that date are unavailable, even if they would otherwise satisfy the rules. The only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Parasites (human)
Endoparasites Protozoan organisms Helminths (worms) Helminth organisms (also called helminths or intestinal worms) include: Tapeworms Flukes Roundworms Other organisms Ectoparasites References {{Portal bar, Biology, Medicine * Parasites Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ... * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the host's body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant- parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over time. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity published in the mega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascaridida
The order Ascaridida includes several families of parasitic roundworms with three "lips" on the anterior end. They were formerly placed in the subclass Rhabditia by some, but morphological and DNA sequence data rather unequivocally assign them to the Spiruria. The Oxyurida and Rhigonematida are occasionally placed in the Ascaridida as superfamily Oxyuroidea, but while they seem indeed to be Spiruria, they are not as close to ''Ascaris'' as such a treatment would place them.Tree of Life Web Project (ToL) (2002)Nematoda Version of 2002-JAN-01. Retrieved 2008-NOV-02. These "worms" contain a number of important parasites of humans and domestic animals. Important families include: * The Anisakidae are also called the "marine mammal ascarids". The larvae of these worms cause anisakiasis when ingested by humans in raw or insufficiently cooked fish, but do not reproduce in humans. * The Ascarididae include the giant intestinal roundworms (''Ascaris'' spp.). * The Cosmocercidae includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)