|
Songkran (Thailand)
Songkran ( th, เทศกาลสงกรานต์, ) is the Thai New Year's national holiday. Songkran is on 13 April every year, but the holiday period extends from 14 to 15 April. In 2018 the Thai cabinet extended the festival nationwide to five days, 12–16 April, to enable citizens to travel home for the holiday. In 2019, the holiday was observed 12–16 April as 13 April fell on a Saturday. The word "Songkran" comes from the Sanskrit word ', literally "astrological passage", meaning transformation or change. It coincides with the rising of Aries on the astrological chart and with the New Year of many calendars of South and Southeast Asia, in keeping with the Hindu Calendar and Buddhist calendar. The New Year takes place at virtually the same time as the new year celebrations of many countries in South Asia like Bangladesh, Cambodia, China (Dai People of Yunnan Province), India (Baisakhi in Punjab, Bengal Gajan Utsav, Bengal Charak Utsav, Bengali New Year (Poy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaysian Siamese
The Malaysian Siamese or Thai Malaysians are an ethnicity or community who principally resides in Peninsular Malaysia which is a relatively homogeneous cultural region to Southern Burma and Southern Thailand but was separated by the Anglo-Siamese Treaty of 1909 between the United Kingdom and the Kingdom of Siam. The treaty established the modern Malaysia-Thailand Border which starts from Golok River in Kelantan and ends at Padang Besar in Perlis. Demographics In 2000, the national statistics cited 50,211 individuals of Siamese ethnicity in Malaysia. Among these, 38,353 (or 76.4% of them) hold Malaysian citizenship. Culture The Malaysian Siamese community share cultural similarities with the natives who inhabit the Malay Peninsula. Community activities, ethnolinguistic identity and languages spoken by Malaysian Siamese are similar to their brethren in the fourteen provinces of Southern Thailand as well as the southernmost Burmese. The Malaysian Siamese lead a way of li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surya Siddhanta
The ''Surya Siddhanta'' (; ) is a Sanskrit treatise in Indian astronomy dated to 505 CE,Menso Folkerts, Craig G. Fraser, Jeremy John Gray, John L. Berggren, Wilbur R. Knorr (2017)Mathematics Encyclopaedia Britannica, Quote: "(...) its Hindu inventors as discoverers of things more ingenious than those of the Greeks. Earlier, in the late 4th or early 5th century, the anonymous Hindu author of an astronomical handbook, the ''Surya Siddhanta'', had tabulated the sine function (...)" in fourteen chapters.Plofkerpp. 71–72 The ''Surya Siddhanta'' describes rules to calculate the motions of various planets and the moon relative to various constellations, diameters of various planets, and calculates the orbits of various astronomical bodies. The text is known from a palm-leaf manuscript, and several newer manuscripts. It was composed or revised c. 800 CE from an earlier text also called the ''Surya Siddhanta''. The ''Surya Siddhanta'' text is composed of verses made up of two lines, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian Day
The Julian day is the continuous count of days since the beginning of the Julian period, and is used primarily by astronomers, and in software for easily calculating elapsed days between two events (e.g. food production date and sell by date). The Julian period is a chronological interval of 7980 years; year 1 of the Julian Period was . The Julian calendar year is year of the current Julian Period. The next Julian Period begins in the year . Historians used the period to identify Julian calendar years within which an event occurred when no such year was given in the historical record, or when the year given by previous historians was incorrect. The Julian day number (JDN) is the integer assigned to a whole solar day in the Julian day count starting from noon Universal Time, with Julian day number 0 assigned to the day starting at noon on Monday, January 1, 4713 BC, proleptic Julian calendar (November 24, 4714 BC, in the proleptic Gregorian calendar), a date at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proleptic Gregorian Calendar
The proleptic Gregorian calendar is produced by extending the Gregorian calendar backward to the dates preceding its official introduction in 1582. In nations that adopted the Gregorian calendar after its official and first introduction, dates occurring in the interim period of 15 October 1582 (the first date of use of Gregorian calendrical dates, being dated 5 October 1582 in the preceding Julian calendar) to the date on which the pertinent nation adopted the Gregorian calendar and abandoned the Julian calendar are sometimes 'Gregorianized' also. For example, the birthday of U.S. President George Washington was originally dated 11 February 1731 (Old Style) because Great Britain, of which he was born a subject, used (until September 1752) the Julian calendar and dated the beginning of English years as 25 March. After Great Britain switched to the Gregorian calendar, Washington's birthday was dated 22 February 1732 proleptically, according to the Gregorian calendar applied backward. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thai Solar Calendar
The Thai solar calendar ( th, ปฏิทินสุริยคติ, , "solar calendar") was adopted by King Chulalongkorn (Rama V) in 1888 CE as the Siamese version of the Gregorian calendar, replacing the Thai lunar calendar as the legal calendar in Thailand (though the latter is still also used, especially for traditional and religious events). Years are now counted in the Buddhist Era (B.E.): , () which is 543 years ahead of the Gregorian calendar. Years The Siamese generally used two calendars, a ''sacred'' and a ''popular'' ( ''vulgar'' in the classical sense). The vulgar or minor era (, ''chula sakarat'') was thought to have been instituted when the worship of Gautama was first introduced, and corresponds to the traditional Burmese calendar (abbreviated ME or BE, the latter not to be confused with the abbreviation for the Buddhist Era, which is the sacred era.) Rattanakosin Era King Chulalongkorn decreed a change in vulgar reckoning to the '' Rattanakosin Era'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chulasakarat
Chula Sakarat or Chulasakarat ( pi, Culāsakaraj; my, ကောဇာသက္ကရာဇ်, ; km, ចុល្លសករាជ "''Chulasakarach''"; th, จุลศักราช, , , abbrv. จ.ศ. ''Choso'') is a lunisolar calendar derived from the Burmese calendar, whose variants were in use by most mainland Southeast Asian kingdoms down to the late 19th century. The calendar is largely based on an older version of the Hindu calendar though unlike the Indian systems, it employs a version of the Metonic cycle. The calendar therefore has to reconcile the sidereal years of the Hindu calendar with Metonic cycle's tropical years by adding intercalary months and intercalary days on irregular intervals. Although the name ''Culāsakaraj'' is a generic term meaning "Lesser Era" in Pali, the term ''Chula Sakarat'' is often associated with the various versions of the calendar used in regions that make up modern-day Thailand. The calendar is used in Myanmar and the Sipsong Pann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calendar Era
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one '' epoch'' of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, it is the year as per the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era (the Coptic Orthodox and Ethiopian Orthodox churches have their own Christian eras). In antiquity, regnal years were counted from the accession of a monarch. This makes the chronology of the ancient Near East very difficult to reconstruct, based on disparate and scattered king lists, such as the Sumerian King List and the Babylonian Canon of Kings. In East Asia, reckoning by era names chosen by ruling monarchs ceased in the 20th century except for Japan, where they are still used. Ancient dating systems Assyrian eponyms For over a thousand years, ancient Assyria used a system of eponyms to identify each year. Each year at the Akitu festival (celebrating the Mesopotamian new year), one of a small group of high officials (including the king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the original Anno Domini (AD) and Before Christ (BC) notations used for the same calendar era. The two notation systems are numerically equivalent: " CE" and "AD " each describe the current year; "400 BCE" and "400 BC" are the same year. The expression traces back to 1615, when it first appeared in a book by Johannes Kepler as the la, annus aerae nostrae vulgaris (), and to 1635 in English as " Vulgar Era". The term "Common Era" can be found in English as early as 1708, and became more widely used in the mid-19th century by Jewish religious scholars. Since the later 20th century, BCE and CE have become popular in academic and scientific publications because BCE and CE are religiously neutral terms. They are used by others who wish to be sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
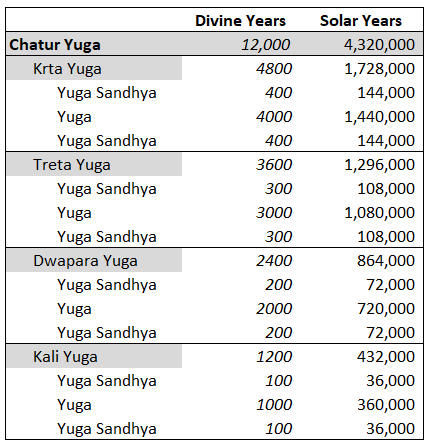
Kali Yuga
''Kali Yuga'', in Hinduism, is the fourth and worst of the four ''yugas'' (world ages) in a '' Yuga Cycle'', preceded by '' Dvapara Yuga'' and followed by the next cycle's '' Krita (Satya) Yuga''. It is believed to be the present age, which is full of conflict and sin. The "Kali" of ''Kali Yuga'' means "strife", "discord", "quarrel", or "contention" and ''Kali Yuga'' is associated with the demon Kali (not to be confused with the goddess Kālī). According to Puranic sources, Krishna's death marked the end of '' Dvapara Yuga'' and the start of ''Kali Yuga'', which is dated to 17/18 February 3102 BCE. Lasting for 432,000 years (1,200 divine years), ''Kali Yuga'' began years ago and has years left as of CE. ''Kali Yuga'' will end in the year 428,899 CE. Etymology ''Yuga'' ( sa, युग), in this context, means "an age of the world", where its archaic spelling is ''yug'', with other forms of ''yugam'', , and ''yuge'', derived from ''yuj'' ( sa, युज् ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karma
Karma (; sa, कर्म}, ; pi, kamma, italic=yes) in Sanskrit means an action, work, or deed, and its effect or consequences. In Indian religions, the term more specifically refers to a principle of cause and effect, often descriptively called the principle of karma, wherein intent and actions of an individual (cause) influence the future of that individual (effect): Good intent and good deeds contribute to good karma and happier rebirths, while bad intent and bad deeds contribute to bad karma and bad rebirths. As per some scripture, there is no link of rebirths with karma. The concept of karma is closely associated with the idea of rebirth in many schools of Indian religions (particularly Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism), as well as Taoism.Eva Wong, Taoism, Shambhala Publications, , pp. 193 In these schools, karma in the present affects one's future in the current life, as well as the nature and quality of future lives—one's '' saṃsāra''. This concept ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuga
A ''yuga'', in Hinduism, is generally used to indicate an age of time. In the ''Rigveda'', a ''yuga'' refers to generations, a long period, a very brief period, or a yoke (joining of two things). In the ''Mahabharata'', the words ''yuga'' and ''kalpa'' (a day of Brahma) are used interchangeably to describe the cycle of creation and destruction. The names "''Yuga''" and "Age" commonly denote a (pronounced ''Chatur Yuga''), a cycle of four world ages, for example, in the ''Surya Siddhanta'' and ''Bhagavad Gita'' (part of the ''Mahabharata''), unless expressly limited by the name of one of its minor ages: '' Krita (Satya) Yuga'', ''Treta Yuga'', ''Dvapara Yuga'', or ''Kali Yuga''. Etymology ''Yuga'' ( sa, युग) means "a yoke" (joining of two things), "generations", or "a period of time" such as an age, where its archaic spelling is ''yug'', with other forms of ''yugam'', , and ''yuge'', derived from ''yuj'' ( sa, युज्, , to join or yoke), believed derived from ' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuga Cycle
A ''Yuga'' Cycle ( ''chatur yuga'', ''maha yuga'', etc.) is a cyclic age (epoch) in Hindu cosmology. Each cycle lasts for 4,320,000 years (12,000 divine years) and repeats four ''yugas'' (world ages): '' Krita (Satya) Yuga'', ''Treta Yuga'', ''Dvapara Yuga'', and ''Kali Yuga''. As a ''Yuga'' Cycle progresses through the four ''yugas'', each '' yuga's'' length and humanity's general moral and physical state within each ''yuga'' decrease by one-fourth. ''Kali Yuga'', which lasts for 432,000 years, is believed to have started in 3102 BCE. Near the end of ''Kali Yuga'', when virtues are at their worst, a cataclysm and a re-establishment of ''dharma'' occur to usher in the next cycle's ''Satya Yuga'', prophesied to occur by Kalki. There are 71 ''Yuga'' Cycles in a ''manvantara'' (age of Manu) and 1,000 ''Yuga'' Cycles in a '' kalpa'' (day of Brahma). Lexicology A ''Yuga'' Cycle has several names. Age or ''Yuga'' ( sa, युग, , an age of the gods): : "Age" and "''Yuga''", some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)